一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-对象的调用-方法注入容器的对象(十一)
实现功能
就是在方法的上面加入@Autowired注解,容器中的对象会注入到对应类型的参数。
注意:暂时实现注入一个对象。所有方法的参数列表的参数只能有一个。
实现思路
其实实现的思路和给字段注入的逻辑是一样的。遍历类所有的方法有没有@Autowired,有的就给它赋予容器中对应的对象。
实现步骤
1. 在AbstractApplicationContext类增加两个方法区分属性注入(autowiredField)和方法注入(autowiredMethod)
1 /** 2 * 属性注入 3 * @param object 4 * @param context 5 * @throws IllegalArgumentException 6 * @throws IllegalAccessException 7 */ 8 private void autowiredField(Object object,Context context) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException { 9 // 5.获得对象的表结构 10 Class<? extends Object> classType = object.getClass(); 11 // 6.获得字段的结构 12 Field[] fields = classType.getDeclaredFields(); 13 for (int i = 0; i < fields.length; i++) { 14 // autowired获得注解 15 Autowired autowired = fields[i].getAnnotation(Autowired.class); 16 if (autowired != null) { 17 Class<?> fieldType = fields[i].getType(); 18 String fieldName = fields[i].getName(); 19 // 如果容器里面有对应的对象 20 Object fieldObject = context.getObject(fieldType, fieldName); 21 // 允许访问私有方法 22 if (fieldObject != null) { 23 // 属性是私有的也可以访问 24 fields[i].setAccessible(true); 25 // 将属性值赋予这个对象的属性 26 fields[i].set(object, fieldObject); 27 } 28 29 } 30 } 31 } 32 /** 33 * 注意set方法的规范 34 * 限定方法只能注入一个参数,并且注入对象的方法只能有一个参数 35 * @param object 36 * @param context 37 * @throws IllegalArgumentException 38 * @throws IllegalAccessException 39 * @throws InvocationTargetException 40 */ 41 private void autowiredMethod(Object object,Context context) throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException { 42 // 5.获得对象的表结构 43 Class<? extends Object> classType = object.getClass(); 44 // 6.获得类方法的结构 45 Method[] methods = classType.getDeclaredMethods(); 46 for (int i = 0; i < methods.length; i++) { 47 // autowired获得注解 48 Autowired autowired = methods[i].getAnnotation(Autowired.class); 49 if (autowired != null) { 50 //获得参数列表的类型 51 Class<?>[] parameterTypes = methods[i].getParameterTypes(); 52 53 String fieldName = methods[i].getName(); 54 55 // 如果容器里面有对应的对象,限定一个方法只能注入一个对象 56 Object methodObject = context.getObject(parameterTypes[0], fieldName); 57 // 允许访问私有方法 58 if (methodObject != null) { 59 // 属性是私有的也可以访问 60 methods[i].setAccessible(true); 61 // 将属性值赋予这个对象的属性 62 methods[i].invoke(object, methodObject); 63 } 64 65 } 66 } 67 }
2.修改autowired方法的逻辑。将原来只遍历属性的@Autowired注解,修改为同时遍历属性和方法上面的的对象注入注解@Autowired
/** * 给对象的属性注入关联的对象 * @throws IllegalArgumentException * @throws IllegalAccessException * @throws InvocationTargetException */ private void autowired() throws IllegalArgumentException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException { // 1.获得容器 Context context = contexts.get(); // 2.获得容器中的所有对象。 Map<String, Object> objects = context.getObjects(); // 3.获得容器中所有的对象值 Collection<Object> values = objects.values(); // 4.获得对象的迭代器 Iterator<Object> iterator = values.iterator(); while (iterator.hasNext()) { Object object = iterator.next(); //1.注入到属性 this.autowiredField(object, context); //2.注入到方法 this.autowiredMethod(object, context); } }
测试代码
测试目录结构
1.在UserServiceImpl类里面增加通过方法注入UserDAO的注解
1 package ioc.core.test.service.impl; 2 3 import ioc.core.annotation.Autowired; 4 import ioc.core.annotation.stereotype.Service; 5 import ioc.core.test.dao.UserDAO; 6 import ioc.core.test.service.UserService; 7 8 /** 9 * 一个普通的类,用于测试是否可以创建对象 10 * @author ranger 11 * 12 */ 13 @Service 14 public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { 15 16 @Autowired 17 private UserDAO userDAO; 18 19 @Override 20 public void login(){ 21 System.out.println("-登录Service-"); 22 userDAO.save(); 23 } 24 25 }
2.测试类调用UserController的对象
1 package ioc.core.test; 2 3 import org.junit.Test; 4 5 import ioc.core.impl.AnntationApplicationContext; 6 import ioc.core.test.config.Config; 7 import ioc.core.test.controller.UserController; 8 9 public class AnntationApplicationContextTest { 10 11 @Test 12 public void login(){ 13 try { 14 AnntationApplicationContext context=new AnntationApplicationContext(Config.class); 15 UserController userController = context.getBean("userController", UserController.class); 16 userController.login(); 17 System.out.println(context.getContext().getObjects()); 18 19 } catch (Exception e) { 20 e.printStackTrace(); 21 } 22 } 23 24 }
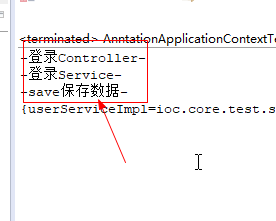
3.测试结果,同时可以调用UserController,UserServiceImpl,UserDAO对象。说明成功!