一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-基础功能-ComponentScan支持多包扫描(六)
实现功能
1.我们看到@ComponentScan注解一个开始定义就是需要支持,扫描多个包,将多个包的类名获取到。现在就实现这个功能。

实现思路
根据传入的字符串数组,获得多个包下的类全限制名。
实现步骤
--基于之前的代码--
1.在PackageUtils.增加一个扫描多个包的方法
1 /** 2 * 支持同时扫描多个包的路径下的类全限制名以及其子包的所有类的全限制名 包名直接使用逗号分割 3 * 4 * @param packageNames:传入多个包名 5 * @param isRecursion:是否扫描包的子包 6 * @return 返回所以扫描到类全限制名 7 */ 8 public static Set<String> getClassNames(String[] packageNames, boolean isRecursion) { 9 //1.创建一个Set集合将每个包下的类放在一起。 10 Set<String> classNamesSet=new HashSet<String>(); 11 // 数值的长度 12 int length = packageNames.length; 13 for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) { 14 Set<String> classNameSet = PackageUtils.getClassName(packageNames[i], isRecursion); 15 //每次都将包放在总的Set集合中 16 classNamesSet.addAll(classNameSet); 17 } 18 return classNamesSet; 19 }
2.修改AbstractApplicationContext的构造函数,标红处
1 public AbstractApplicationContext(Class<?> classType) { 2 //判断配置类是否有Configuration注解 3 Configuration annotation = classType.getAnnotation(Configuration.class); 4 if(annotation!=null){ 5 //获得组件扫描注解 6 ComponentScan componentScan = classType.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class); 7 //获得包名 8 this.basePackage = componentScan.basePackages(); 9 //根据包名获得类全限制名 10 //Set<String> classNames = PackageUtils.getClassName(this.basePackage[0], true); 11 //将扫描一个包,修改为多个包 12 Set<String> classNames = PackageUtils.getClassNames(this.basePackage, true); 13 //通过类名创建对象 14 Iterator<String> iteratorClassName = classNames.iterator(); 15 while(iteratorClassName.hasNext()){ 16 String className = iteratorClassName.next(); 17 try { 18 //通过类全名创建对象 19 Object instance = Class.forName(className).newInstance(); 20 //将对象加到容器中,对象名就类全名 21 this.getContext().addObject(instance.getClass().getSimpleName(),instance); 22 } catch (InstantiationException e) { 23 e.printStackTrace(); 24 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { 25 e.printStackTrace(); 26 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 27 e.printStackTrace(); 28 } 29 } 30 } 31 }
测试代码
1.Config类-,扫描ioc.core.test.config包和ioc.core.test.service包
package ioc.core.test.config; import ioc.core.annotation.ComponentScan; import ioc.core.annotation.Configuration; //使用定义@Configuration定义该类是一个配置类 @Configuration //使用ComponentScan设置扫描包的路径 @ComponentScan(basePackages={"ioc.core.test.config","ioc.core.test.service"}) public class Config { }
2.测试类,输出容器中的对象
package ioc.core.test; import org.junit.Test; import ioc.core.impl.AnntationApplicationContext; import ioc.core.test.config.Config; public class AnntationApplicationContextTest { @Test public void login(){ try { AnntationApplicationContext context=new AnntationApplicationContext(Config.class); System.out.println(context.getContext().getObjects()); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
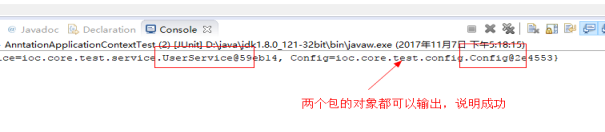
3.测试结果,将两个包的类的对象都放在了容器里面。成功。