一起写框架-Ioc内核容器的实现-基础功能-ComponentScan(四)
功能说明
该步骤实现的功能包括:
1. 启动程序时,将@ComponentScan加载的类,创建对象并放在容器里面。
2. 通过ApplicatoinContext的getBean()方法获得容器里面的对象。 (放在下一篇文实现)
实现步骤
1.定义一个扫描注解@ComponentScan
1 package ioc.core.annotation; 2 3 import java.lang.annotation.Documented; 4 import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; 5 import java.lang.annotation.Retention; 6 import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; 7 import java.lang.annotation.Target; 8 //表示用于运行时的注解 9 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 10 //表示只能在类或者接口的上面使用 11 @Target(value=ElementType.TYPE) 12 @Documented 13 public @interface ComponentScan { 14 15 /** 16 * 声明一个注解属性用于接收扫描的包路径 17 * @return 18 */ 19 String[] basePackages() default {} ; 20 21 }
2.定义一个@Configuration标识配置类
package ioc.core.annotation; import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; /** * 标识配置类注解的定义 * @author ranger * */ //表示用于运行时的注解 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //表示只能在类或者接口的上面使用 @Target(value=ElementType.TYPE) @Documented public @interface Configuration { }
2.定义容器 Context接口
1 package ioc.core; 2 import java.util.Map; 3 4 /** 5 * Ioc框架的容器接口 6 * @author ranger 7 * 8 */ 9 public interface Context { 10 11 /** 12 * 用于获得容器中的所有对象 13 * @return 14 */ 15 Map<String,Object> getObjects(); 16 17 /** 18 * 用于增加容器中的对象 19 * @param key 20 * @param value 21 */ 22 void addObject(String key, Object value); 23 24 }
3.定义容器操作接口ApplicationContext
1 package ioc.core; 2 /** 3 * Ioc框架的容器操作接口 4 * @author ranger 5 * 6 */ 7 public interface ApplicationContext { 8 9 10 /** 11 * 通过容器里面的对象名,返回容器中的对象 12 * @param objectName 13 * @return 14 */ 15 Object getBean(String objectName); 16 }
4.实现容器
1 package ioc.core.impl; 2 3 import java.util.HashMap; 4 import java.util.Map; 5 6 import ioc.core.Context; 7 8 /** 9 * 实现框架容器,用于存储扫描注解创建的所有对象。 10 * @author ranger 11 * 12 */ 13 public class ContextImpl implements Context { 14 15 //使用Map来存储对象,为什么使用Map对象呢?因为预留对象名可以设置的需要。 16 Map<String,Object> objects=new HashMap<String,Object>(); 17 18 @Override 19 public Map<String,Object> getObjects() { 20 21 return this.objects; 22 } 23 24 @Override 25 public void addObject(String key,Object value) { 26 objects.put(key, value); 27 } 28 }
5.实现扫描包。获得包以及该包子包的所有类的类全名。
--使用到一个工具类从包中读取包和其子包类名--
1 package ioc.core.utils; 2 3 import java.io.File; 4 import java.io.IOException; 5 import java.net.JarURLConnection; 6 import java.net.URL; 7 import java.net.URLClassLoader; 8 import java.util.Enumeration; 9 import java.util.HashSet; 10 import java.util.Set; 11 import java.util.jar.JarEntry; 12 import java.util.jar.JarFile; 13 14 /** 15 * 本类用于读取包下面的类名 16 * 来自博客 17 * http://blog.csdn.net/aust_glj/article/details/53385651 18 * 19 */ 20 public class PackageUtils { 21 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 22 String packageName = "ioc.core.annotation"; 23 Set<String> classNames = getClassName(packageName, true); 24 if (classNames != null) { 25 for (String className : classNames) { 26 System.out.println(className); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 31 /** 32 * 获取某包下所有类 33 * @param packageName 包名 34 * @param isRecursion 是否遍历子包 35 * @return 类的完整名称 36 */ 37 public static Set<String> getClassName(String packageName, boolean isRecursion) { 38 Set<String> classNames = null; 39 ClassLoader loader = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); 40 String packagePath = packageName.replace(".", "/"); 41 42 URL url = loader.getResource(packagePath); 43 if (url != null) { 44 String protocol = url.getProtocol(); 45 if (protocol.equals("file")) { 46 classNames = getClassNameFromDir(url.getPath(), packageName, isRecursion); 47 } else if (protocol.equals("jar")) { 48 JarFile jarFile = null; 49 try{ 50 jarFile = ((JarURLConnection) url.openConnection()).getJarFile(); 51 } catch(Exception e){ 52 e.printStackTrace(); 53 } 54 55 if(jarFile != null){ 56 getClassNameFromJar(jarFile.entries(), packageName, isRecursion); 57 } 58 } 59 } else { 60 /*从所有的jar包中查找包名*/ 61 classNames = getClassNameFromJars(((URLClassLoader)loader).getURLs(), packageName, isRecursion); 62 } 63 64 return classNames; 65 } 66 67 /** 68 * 从项目文件获取某包下所有类 69 * @param filePath 文件路径 70 * @param className 类名集合 71 * @param isRecursion 是否遍历子包 72 * @return 类的完整名称 73 */ 74 private static Set<String> getClassNameFromDir(String filePath, String packageName, boolean isRecursion) { 75 Set<String> className = new HashSet<String>(); 76 File file = new File(filePath); 77 File[] files = file.listFiles(); 78 for (File childFile : files) { 79 if (childFile.isDirectory()) { 80 if (isRecursion) { 81 className.addAll(getClassNameFromDir(childFile.getPath(), packageName+"."+childFile.getName(), isRecursion)); 82 } 83 } else { 84 String fileName = childFile.getName(); 85 if (fileName.endsWith(".class") && !fileName.contains("$")) { 86 className.add(packageName+ "." + fileName.replace(".class", "")); 87 } 88 } 89 } 90 91 return className; 92 } 93 94 95 /** 96 * @param jarEntries 97 * @param packageName 98 * @param isRecursion 99 * @return 100 */ 101 private static Set<String> getClassNameFromJar(Enumeration<JarEntry> jarEntries, String packageName, boolean isRecursion){ 102 Set<String> classNames = new HashSet<String>(); 103 104 while (jarEntries.hasMoreElements()) { 105 JarEntry jarEntry = jarEntries.nextElement(); 106 if(!jarEntry.isDirectory()){ 107 /* 108 * 这里是为了方便,先把"/" 转成 "." 再判断 ".class" 的做法可能会有bug 109 * (FIXME: 先把"/" 转成 "." 再判断 ".class" 的做法可能会有bug) 110 */ 111 String entryName = jarEntry.getName().replace("/", "."); 112 if (entryName.endsWith(".class") && !entryName.contains("$") && entryName.startsWith(packageName)) { 113 entryName = entryName.replace(".class", ""); 114 if(isRecursion){ 115 classNames.add(entryName); 116 } else if(!entryName.replace(packageName+".", "").contains(".")){ 117 classNames.add(entryName); 118 } 119 } 120 } 121 } 122 123 return classNames; 124 } 125 126 /** 127 * 从所有jar中搜索该包,并获取该包下所有类 128 * @param urls URL集合 129 * @param packageName 包路径 130 * @param isRecursion 是否遍历子包 131 * @return 类的完整名称 132 */ 133 private static Set<String> getClassNameFromJars(URL[] urls, String packageName, boolean isRecursion) { 134 Set<String> classNames = new HashSet<String>(); 135 136 for (int i = 0; i < urls.length; i++) { 137 String classPath = urls[i].getPath(); 138 139 //不必搜索classes文件夹 140 if (classPath.endsWith("classes/")) {continue;} 141 142 JarFile jarFile = null; 143 try { 144 jarFile = new JarFile(classPath.substring(classPath.indexOf("/"))); 145 } catch (IOException e) { 146 e.printStackTrace(); 147 } 148 149 if (jarFile != null) { 150 classNames.addAll(getClassNameFromJar(jarFile.entries(), packageName, isRecursion)); 151 } 152 } 153 154 return classNames; 155 } 156 }
--容器操作类的公用代码写在AbstractApplicationContext抽象类的构造函数里面,方便以后扩展其他的加载情况--
1 package ioc.core.impl; 2 3 import java.util.Iterator; 4 import java.util.Set; 5 6 import ioc.core.ApplicationContext; 7 import ioc.core.Context; 8 import ioc.core.annotation.ComponentScan; 9 import ioc.core.annotation.Configuration; 10 import ioc.core.utils.PackageUtils; 11 12 public abstract class AbstractApplicationContext implements ApplicationContext{ 13 //声明一个线程变量,存储容器对象,表示同一条线程,一个ApplicationContext只操作一个容器对象。 14 private ThreadLocal<Context> contexts=new ThreadLocal<Context>(); 15 16 17 protected String[] basePackage=null; 18 /** 19 * 将容器操作加载创建对象的代码写抽象类里面,这样可以方便以后扩展多种实现。 20 * @param classType 21 */ 22 public AbstractApplicationContext(Class<?> classType) { 23 //判断配置类是否有Configuration注解 24 Configuration annotation = classType.getAnnotation(Configuration.class); 25 if(annotation!=null){ 26 //获得组件扫描注解 27 ComponentScan componentScan = classType.getDeclaredAnnotation(ComponentScan.class); 28 //获得包名 29 this.basePackage = componentScan.basePackages(); 30 //根据包名获得类全限制名 31 Set<String> classNames = PackageUtils.getClassName(this.basePackage[0], true); 32 //通过类名创建对象 33 Iterator<String> iteratorClassName = classNames.iterator(); 34 while(iteratorClassName.hasNext()){ 35 String className = iteratorClassName.next(); 36 try { 37 //通过类全名创建对象 38 Object instance = Class.forName(className).newInstance(); 39 //将对象加到容器中,对象名就类全名 40 this.getContext().addObject(instance.getClass().getSimpleName(),instance); 41 } catch (InstantiationException e) { 42 e.printStackTrace(); 43 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { 44 e.printStackTrace(); 45 } catch (ClassNotFoundException e) { 46 e.printStackTrace(); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 } 51 52 public String[] getBasePackage() { 53 return basePackage; 54 } 55 56 57 public Context getContext(){ 58 if(contexts.get()==null){ 59 //调用容器 60 Context context=new ContextImpl(); 61 contexts.set(context); 62 } 63 return contexts.get(); 64 } 65 66 67 68 }
----实现AnnotationApplicationContext注解操作类,继承bstractApplicationContext---
注意:这里还没有实现getBean方法。先实现启动程序时,包下面的所有类有没有加入到容器里了--
1 package ioc.core.impl; 2 3 public class AnntationApplicationContext extends AbstractApplicationContext { 4 5 public AnntationApplicationContext(Class<?> classType) { 6 super(classType); 7 } 8 9 @Override 10 public Object getBean(String objectName) { 11 12 return null; 13 } 14 }
测试代码
测试是否可以获得指定扫描包下的类的对象
1.创建一个测试源码包存放测试代码

2. Config类,是一个配置类。里面定义扫描包的路径
1 package ioc.core.test.config; 2 3 import ioc.core.annotation.ComponentScan; 4 import ioc.core.annotation.Configuration; 5 6 //使用定义@Configuration定义该类是一个配置类 7 @Configuration 8 //使用ComponentScan设置扫描包的路径 9 @ComponentScan(basePackages="ioc.core.test") 10 public class Config { 11 12 }
3. 编写一个普通的UserService类测试
package ioc.core.test.service; /** * 一个普通的类,用于测试是否可以创建对象 * @author ranger * */ public class UserService { public void login(){ System.out.println("-登录-"); } }
4. 创建一个AnntationApplicationContextTest测试类
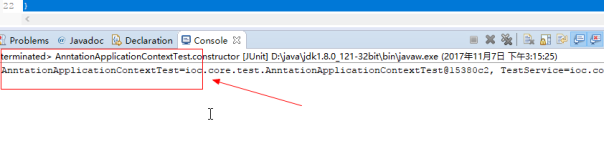
package ioc.core.test; import org.junit.Test; import ioc.core.impl.AnntationApplicationContext; import ioc.core.test.config.Config; public class AnntationApplicationContextTest { @Test public void constructor(){ try { AnntationApplicationContext context=new AnntationApplicationContext(Config.class); //如果可以打印出容器里面的对象,说明成功 System.out.println(context.getContext().getObjects()); } catch (Exception e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } }
5.测试结果,获得UserService的对象。成功!