JavaEE基础02-spring4(AOP+web应用)
AOP的功能先从一个例子开始。
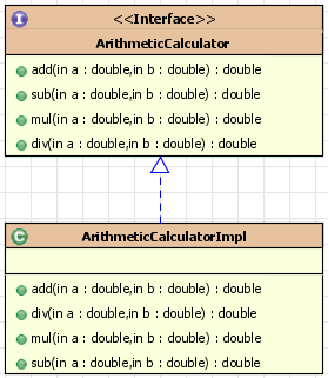

加减乘除的一个功能,需要在每个方法开始和结束时打印东西。(就是需求一)
方法一(非常不推荐):

package com.guigu.spring2; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/18. */ public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator{ @Override public int add(int a, int b) { System.out.println("日志开始了:"+a+"加"+b); int add=a+b ; System.out.println(add); return add; } @Override public int sub(int a, int b) { System.out.println("日志开始了:"+a+"减"+b); int sub=a-b; System.out.println(sub); return sub ; } }
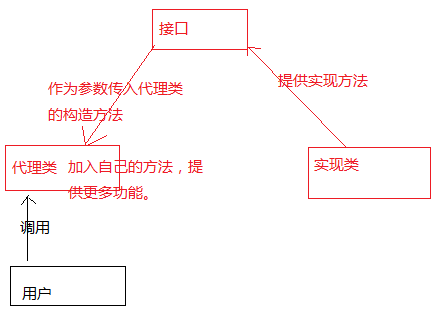
方法二:使用静态代理(不推荐)(但是需要复习一下代理的思想)
下图中被代理类是接口的实现类,代理类也需要实现接口,这样才能提供方法。

package com.guigu.spring2; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/18. */ public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator{ @Override public int add(int a, int b) { int add=a+b ; System.out.println(add); return add; } @Override public int sub(int a, int b) { int sub=a-b; System.out.println(sub); return sub ; } }

package com.guigu.spring2; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/18. */ public class StaticProxy implements ArithmeticCalculator{ private ArithmeticCalculator ar; public StaticProxy(ArithmeticCalculator ar) { this.ar=ar; } @Override public int add(int a, int b) { String s="加"; noQueue(a,b,s); int add = ar.add(a, b); return add; } @Override public int sub(int a, int b) { String s="减"; noQueue(a,b,s); int sub = ar.sub(a, b); return sub; } // 代理类本身自带功能; public void noQueue(int a,int b,String s) { System.out.println("日志开始了:"+a+s+b); } }

package com.guigu.spring2; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/18. */ public class main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArithmeticCalculator a2 = new StaticProxy(new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl()); a2.add(2,1); a2.sub(2,1); } } //日志开始了:2加1 //3 //日志开始了:2减1 //1
方法三:使用动态代理(详细内容去java基础反射复习)(可以用,但是和aop比起来麻烦得多)

package com.guigu.spring2; import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler; import java.lang.reflect.Method; import java.lang.reflect.Proxy; import java.util.Arrays; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/18. */ public class LoggingProxy { //要代理的对象 private ArithmeticCalculator target; public LoggingProxy(ArithmeticCalculator target) { this.target = target; } public ArithmeticCalculator getLoggingProxy(){ //代理对象由哪一个类加载器进行加载 ClassLoader loader=target.getClass().getClassLoader(); //代理对象的类型,即其中有哪些方法 Class<?>[] interfaces=new Class[]{ArithmeticCalculator.class}; //当调用代理对象其中的方法时,会执行的代码 InvocationHandler h=new InvocationHandler() { /** * proxy: 正在返回的那个代理对象,一般情况下,invoke方法里不使用(调用里面的方法会导致死循环) * method: 正在被调用的方法 * args: 传入的参数 */ @Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { String methodName=method.getName(); System.out.println("日志:"+methodName+"begins with"+ Arrays.asList(args)); //执行方法 Object result = method.invoke(target, args); System.out.println("日志:"+methodName+"ends with"+ result); return result; } }; ArithmeticCalculator proxy = (ArithmeticCalculator) Proxy.newProxyInstance(loader, interfaces, h); return proxy; } }

public class main { public static void main(String[] args) { ArithmeticCalculator a1 = new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl(); ArithmeticCalculator a2 = new LoggingProxy(a1).getLoggingProxy(); a2.add(2,1); a2.sub(2,1); } } //日志:addbegins with[2, 1] //3 //日志:addends with3 //日志:subbegins with[2, 1] //1 //日志:subends with1
上面是自己写的,下面是ppt里的。对比着看吧,反正效果一样的,log先忽视掉。
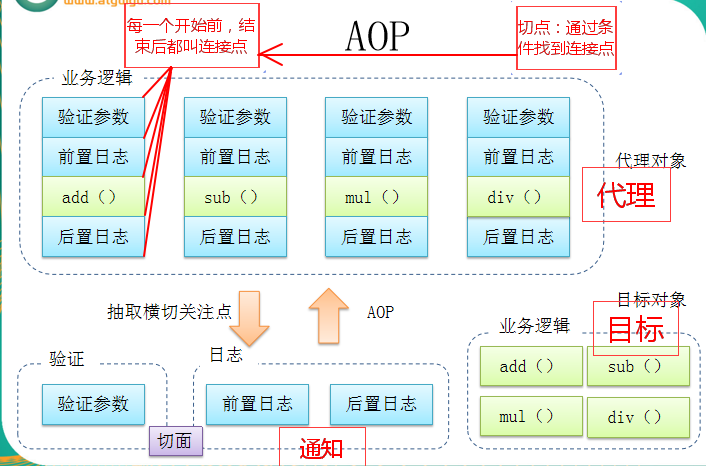

了解了上面的内容,springAop正式开始。(重点)
1,加入jar包
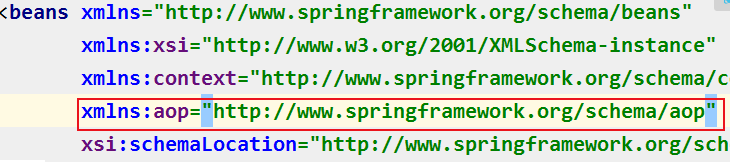
2,在配置文件中加入aop的命名空间
3,基于注解的方式
①在配置文件中加入
<!--使Aspect注解起作用,自动匹配的类生成代理对象-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
②把横切关注点的代码抽象到切面的类中。
切面首先是一个ioc中的bean,即加入@component 注解
切面还需要加入@Aspect 注解
③在类中声明各种通知

声明一个方法
在方法前加上@......注解,在注解后加上具体的类(具体看下面代码)
④可以在通知方法中声明一个类型为joinpoint的参数。然后就能访问链接细节。如方法名称和参数值
------------------------------具体代码-------------------------------

package com.guigu.spring2aop; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/18. */ @Component public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator { @Override public int add(int a, int b) { int add=a+b ; System.out.println(add); return add; } @Override public int sub(int a, int b) { int sub=a-b; System.out.println(sub); return sub ; } }

package com.guigu.spring2aop; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/18. */ //把类声明为切面 1,放入ioc容器 2,声明为切面 @Aspect @Component public class LoggingAspect { //声明该方法是一个前置 @Before("execution(public int com.guigu.spring2aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int,int))") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); List<Object> args= Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()); System.out.println("日志开始了 "+name+" 参数 "+args); } @After("execution(* com.guigu.spring2aop.*.*(int,int))") public void afterMethod(){ System.out.println("日志结束了"); } }

package com.guigu.spring2aop; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/18. */ public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext c = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ArithmeticCalculator ari=(ArithmeticCalculator)c.getBean("arithmeticCalculatorImpl"); ari.add(3,1); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.guigu.spring2aop"> </context:component-scan> <!--使Aspect注解起作用,自动匹配的类生成代理对象--> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> </beans>
-----------------------五种通知---------------------------
环绕通知不常用看看就行。
以动态代理里的方法为例,看懂各个通知所在的位置。
@Override public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable { String methodName=method.getName(); System.out.println("日志:"+methodName+"begins with"+ Arrays.asList(args)); Object result = null; try { //前置通知的位置 //执行方法 result = method.invoke(target, args); //返回通知的位置 } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); //异常通知的位置 } //后置通知的位置,因为可能会出异常,所以不能访问到方法的返回值。 System.out.println("日志:"+methodName+"ends with"+ result); return result; }
回到aspect介绍五种通知。

@Aspect @Component public class LoggingAspect { @Before("execution(* com.guigu.spring2aop.*.*(..))") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); List<Object> args= Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()); System.out.println("日志开始了 "+name+" 参数 "+args); } //后置通知:在目标方法执行后(无论是否发生异常),都会执行 //不能访问目标方法执行的结果。结果在返回通知里。 @After("execution(* com.guigu.spring2aop.*.*(..))") public void afterMethod(){ System.out.println("日志结束了"); } //返回通知:方法正常结束受执行的代码。可以访问到方法的返回值。 @AfterReturning(value = "execution(* com.guigu.spring2aop.*.*(..))",returning = "result") public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint,Object result){ String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("The method "+ name + " ends with "+result); } //异常通知:方法出现异常时会执行的代码。可以访问到异常对象,可以指定特定异常出现时再执行。 @AfterThrowing(value = "execution(* com.guigu.spring2aop.*.*(..))",throwing = "ex") public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint,Exception ex){ String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("The method "+ name + " occurs exception: with "+ex); } /**(不常用,看看就行) * 环绕通知,需要携带ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数。 * 类似于动态代理的全过程:ProceedingJoinPoint类型的参数可以决定是否执行目标方法。 * 且环绕通知必须有返回值,返回值即为目标方法的返回值。 */ // @Around("execution(* com.guigu.spring2aop.*.*(..))") // public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjd){ // Object result =null; // String name = pjd.getSignature().getName(); // //执行目标方法 // try { // System.out.println("前置通知 "+name+" begins with "+Arrays.asList(pjd.getArgs())); // result = pjd.proceed(); // System.out.println("返回通知 "+name+" result "+result); // } catch (Throwable throwable) { // throwable.printStackTrace(); // System.out.println("异常通知 "+name+" occurs exception: "+ throwable); // } // System.out.println("后置通知 "+name+" ends with "+Arrays.asList(pjd.getArgs())); // return result; // } }
--------------1优先级,2重用切点表达式------------
//1.优先级。用@order注解来表明优先级,数字越低,优先级越高,不声明就是任意优先级(最低) @Order(2) @Aspect @Component public class ValidationAspect { @Before("LoggingAspect.declareJoinPointExpression()") public void validationMethod(){ System.out.println("--->验证"); } } //---------上面验证类,下面日志类--------- @Aspect @Component public class LoggingAspect { //2.定义一个方法,用于声明切入点表达式。一般该方法中不添加其他代码。 //在本类中调用看下面,在其他类中调用的例子看验证类(ValidationAspect) @Pointcut("execution(* com.guigu.spring2aop.*.*(..))") public void declareJoinPointExpression(){} @Before("declareJoinPointExpression()") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String name = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); List<Object> args= Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs()); System.out.println("日志开始了 "+name+" 参数 "+args); }
-----------------以上是基于注解,下面是基于xml文件------------------(看一看)
实现过程就是,把类的注解删了,然后加入xml文件。

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <bean id="arithmeticCalculator" class="com.guigu.spring2aop.ArithmeticCalculatorImpl"> </bean> <!--配置切面的bean--> <bean id="loggingAspect" class="com.guigu.spring2aop.LoggingAspect"> </bean> <bean id="validationAspect" class="com.guigu.spring2aop.ValidationAspect"> </bean> <!--配置aop--> <aop:config> <!--配置切点表达式--> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(public int com.guigu.spring2aop.*.*(..))" id="pointcut"></aop:pointcut> <!--配置切面及通知--> <aop:aspect ref="loggingAspect" order="2"> <aop:before method="beforeMethod" pointcut-ref="pointcut"></aop:before> <aop:after method="afterMethod" pointcut-ref="pointcut"></aop:after> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="pointcut" returning="result"></aop:after-returning> <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="pointcut" throwing="ex"></aop:after-throwing> </aop:aspect> <aop:aspect ref="validationAspect"> <aop:before method="validationMethod" pointcut-ref="pointcut"></aop:before> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
经过配置,效果就一样了。
-----------------spring对jdbc的支持------------------(看一看就行)
一,JdbcTemplate插件



//看的顺序是从最下面的test往上看。 public class JdbcTest { private ApplicationContext c = null; JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; { c = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) c.getBean("jdbcTemplate"); } //获取单个列的值,或做统计查询 @Test public void testQueryForObject2() { String sql="select count(id) from admin"; long count=jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,long.class); System.out.println(count); } //查到实体类的集合 //调用query方法 @Test public void testQueryForList() { String sql = "select * from admin where id>?"; RowMapper<Admin> rowmapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Admin.class); List<Admin> admins = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, rowmapper, 1); System.out.println(admins); } /** * 查到实体类 * 不是调用queryForObject(String var1, Class<T> var2, object...args) * 而是调用queryForObject(String var1, RowMapper<> rowMapper, object...args) * 1.其中RowMapper 指定如何去映射结果集的行,常用的实现类为BeanPropertyRowMapper * 2.使用sql中的别名完成类名(表里的列名)和类的属性名(bean里的)的映射。 * 3.不支持级联属性,JdbcTemplate只是jdbc工具,而不是orm框架。 */ @Test public void testQueryForObject() { String sql = "select * from admin where id=?"; RowMapper<Admin> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Admin.class); Admin admin = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, 1); } //批量更新:批量地inset,update,delete //最后一个参数是object[] 的list类型:因为修改一条需要一个object的数组,那么多条就要多个object的数组。 @Test public void testBatchUpdate() { String sql = "insert into admin(username,password) values(?,?)"; List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>(); batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"AA", "123"}); batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"BB", "123"}); batchArgs.add(new Object[]{"CC", "123"}); jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs); } @Test public void testUpdate() { String sql = "update admin set username=? where id=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, "锤子", 1); } //连接数据库 @Test public void test() throws Exception { DataSource dataSource = (DataSource) c.getBean("dataSource"); Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection(); System.out.println(connection); } }

url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/girls
username=root
password=
driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:dd.properties"/>--> <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="location" value="classpath:dd.properties"></property> </bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="username" value="${username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${password}"></property> <property name="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}"></property> <property name="url" value="${url}"></property> </bean> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate"> <constructor-arg ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans>
在开发中怎么用?(使用了注解记得去xml文件里进行配置)
@Component public class AdminDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; //主要说明的是开发中实现增删改查,所以简化了连接池部分, // 不要这样搞连接。开发中写一个专门的连接类。 { ApplicationContext c = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); jdbcTemplate = (JdbcTemplate) c.getBean("jdbcTemplate"); } public Admin testQueryForObject(int id) { String sql = "select * from admin where id=?"; RowMapper<Admin> rowMapper = new BeanPropertyRowMapper<>(Admin.class); Admin admin = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, rowMapper, id); return admin; } }
二,NamedParameterJdbcTemplate具名参数(看一看)
其他步骤(xml文件连接数据库,得到NamedParameterJdbcTemplate类)的编写同上。
<bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate"> <constructor-arg ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg> </bean>
第一种方法:
好处是:若有多个参数,则不用再去对应位置,直接对应参数名,便于维护
缺点是:较为麻烦
@Test public void testNamedParameterJdbcTemplate(){ String sql =" insert into admin(username,password) values(:un,:pw)"; Map<String,Object> paramMap=new HashMap<>(); paramMap.put("un","小米"); paramMap.put("pw","123"); namedParameterJdbcTemplate.update(sql,paramMap); }
第二种方法:
@Test public void testNamedParameterJdbcTemplateUpdate(){ String sql="insert into admin(username,password) values(:username,:password)"; Admin admin = new Admin(); admin.setUsername("xiaomi"); admin.setPassword("123"); BeanPropertySqlParameterSource b = new BeanPropertySqlParameterSource(admin); n.update(sql, b); }
------------spring中的事务管理------------(重点看)
复习一下,四个关键属性(ACID):原子性(atomicity),一致性(consistency),隔离性(isolation),持久性(durability)。
以前学过jdbc的事物管理,重复代码很多,不易于维护。
现在aop来进行事物管理,将事务管理代码从业务方法中分离出来, 以声明的方式来实现事务管理.
以用户买书为例:用户买一本书,账户金额减掉书的价格,书的库存减少1。作为一个事务。
准备工作:数据库里3个表,用户账户表,书表,书的库存表。
第一步:分别写出,1)用户买的书的价格。2)用户账户金额减书的价格。3)书的库存减少1


package com.guigu.spring4.shiwu; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/21. */ public interface BookShopDao { //根据书号获取书的单价 public int findBookPriceByIsbn(int isbn); //更新库存,书号对应的库存减一 public void updateBookStock(int isbn); //更新用户的账户余额:使 username 的 balance-price public void updateUserAccount(String username ,int price); }

package com.guigu.spring4.shiwu; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/21. */ @Repository("bookShop") public class BookShopImpl implements BookShopDao { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Override public int findBookPriceByIsbn(int isbn) { String sql = "select price from book where isbn=?"; return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class, isbn); } @Override public void updateBookStock(int isbn) { //检查书的库存是否够,不够就抛出异常。 String sql2 = "select stock from book_stock where isbn=?"; int stock = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql2, Integer.class, isbn); if (stock <= 0) throw new RuntimeException("库存不足"); String sql = "update book_stock set stock = stock-1 where isbn=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, isbn); } @Override public void updateUserAccount(String username, int price) { //检查用户余额是否够,不够就抛出异常。 String sql2 = "select balance from account where username=?"; int stock = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql2, Integer.class, username); if (stock < price) throw new RuntimeException("余额不足"); String sql = "update account set balance = balance-? where username=?"; jdbcTemplate.update(sql, price, username); } }
第二步:使用注解的方法加上事务。

package com.guigu.spring4.shiwu; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/21. */ public interface BookShopService { public void purchase (String username,int isbn); }

package com.guigu.spring4.shiwu; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/21. */ @Service("bookShopService") public class BookShopServiceImpl implements BookShopService{ @Autowired private BookShopDao bookShopDao; //添加事务注解. @Transactional @Override public void purchase(String username, int isbn) { //获取书的单价 int bp = bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn(isbn); //更新书的库存 bookShopDao.updateBookStock(isbn); //更新用户余额 bookShopDao.updateUserAccount(username,bp); } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.alibaba.com/schema/stat http://www.alibaba.com/schema/stat.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd"> <!-- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:dd.properties"/>--> <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="location" value="classpath:dd.properties"></property> </bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="username" value="${username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${password}"></property> <property name="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}"></property> <property name="url" value="${url}"></property> </bean> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <context:component-scan base-package="com.guigu.spring4.shiwu"> </context:component-scan> <!--配置事务管理器--> <bean id="dataSourceTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!--启动事务注解--> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven> </beans>

package com.guigu.spring4.shiwu;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/21.
*/
public class STTest {
private ApplicationContext a=null;
private BookShopDao bookShopDao =null;
private BookShopService bookShopService=null;
{
a=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
bookShopDao =(BookShopDao)a.getBean("bookShop");
bookShopService=(BookShopService)a.getBean("bookShopService");
}
@Test
public void test04(){
bookShopService.purchase("小明",1002);
}
@Test
public void test01(){
System.out.println(bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn(1001));
}
@Test
public void test02(){
bookShopDao.updateBookStock(1001);
}
@Test
public void test03(){
bookShopDao.updateUserAccount("小明",100);
}
}
第三步:事务里的事务如何处理。

package com.guigu.spring4.shiwu; import java.util.List; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/21. */ public interface Cashier { //一个人买多本书 public void checkout(String username, List<Integer> isbns); }

package com.guigu.spring4.shiwu; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; import java.util.List; /** * Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/21. */ public class CashierImpl implements Cashier { @Autowired private BookShopService bookShopService; @Transactional @Override public void checkout(String username, List<Integer> isbns) { for (int isbn : isbns) { bookShopService.purchase(username,isbn); } } }

package com.guigu.spring4.shiwu;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
/**
* Created by Zhuxiang on 2020/5/21.
*/
@Service("bookShopService")
public class BookShopServiceImpl implements BookShopService{
@Autowired
private BookShopDao bookShopDao;
//添加事务注解,使用propagation指定事务的传播行为,即当前的事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,
//如何使用事务,一,默认值为required,即使用调用方法的事务。(看图理解)
//二,使用自己的事务REQUIRES_NEW,调用的事务方法的事务被挂起。(看图理解)
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
@Override
public void purchase(String username, int isbn) {
//获取书的单价
int bp = bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn(isbn);
//更新书的库存
bookShopDao.updateBookStock(isbn);
//更新用户余额
bookShopDao.updateUserAccount(username,bp);
}
}
默认情况图:CashierImpl里的事务是Tx1,BookShopServiceImpl里的事务是图中的purchase().

新建情况图:
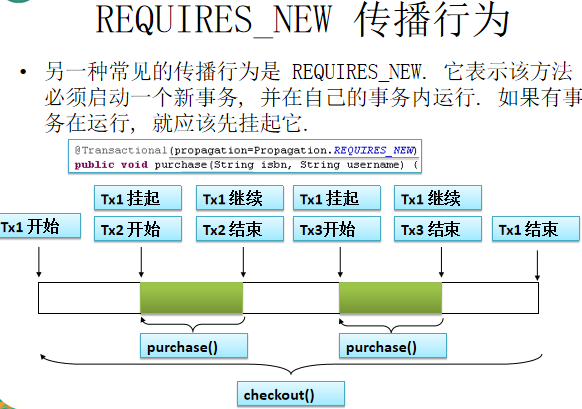
如何使用事务,事务的其他属性(和上面的一样重要)
//添加事务注解,使用propagation指定事务的传播行为,即当前的事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时, //如何使用事务,一,默认值为required,即使用调用方法的事务。(看图理解) //二,使用自己的事务REQUIRES_NEW,调用的事务方法的事务被挂起。(看图理解) //三,指定隔离级别,isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED(读已提交) //四,虽然默认异常后全回滚,但是也可以自己设置(通常情况不会去设置)。 // 比如设置在账户余额不回滚 : noRollbackFor=UserAccountException.class, // 结果就是继续执行下面的方法,把库存减1。 //五,使用readOnly=true指定事务为只读。只能查。 //六,使用timeout 指定强制回滚之前事务可以占用的时间。如timeout = 3就是 // 给事务3秒时间,如果在时间内没有完成就强制回滚。可以让程序睡4秒测试一下:Thread.sleep(4000)。 @Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED,noRollbackFor=UserAccountException.class)
为了测试4,我们多加一个异常类 UserAccountException ,如果余额不足就进入这个异常类,它继承了runtimeException类。

最后,不使用注解作配置,而使用xml文件配置,达到同样的效果。具体操作时记得把注解删了,还要加上引用类的set方法。

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.alibaba.com/schema/stat http://www.alibaba.com/schema/stat.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd"> <!-- <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:dd.properties"/>--> <bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="location" value="classpath:dd.properties"></property> </bean> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"> <property name="username" value="${username}"></property> <property name="password" value="${password}"></property> <property name="driverClassName" value="${driverClassName}"></property> <property name="url" value="${url}"></property> </bean> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!--配置bean--> <bean id="bookShopImpl" class="com.guigu.spring4.shiwu.BookShopImpl"> <property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property> </bean> <bean id="bookShopServiceImpl" class="com.guigu.spring4.shiwu.BookShopServiceImpl"> <property name="bookShopImpl" ref="bookShopImpl"></property> </bean> <bean id="cashierImpl" class="com.guigu.spring4.shiwu.CashierImpl"> <property name="bookShopServiceImpl" ref="bookShopServiceImpl"></property> </bean> <!--1.配置事务管理器--> <bean id="dataSourceTransactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/> </bean> <!--2.配置事务属性--> <tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="dataSourceTransactionManager"> <tx:attributes> <tx:method name="purchase" propagation="REQUIRED" timeout="5"/> <tx:method name="get*" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/> <tx:method name="*"/> </tx:attributes> </tx:advice> <!--3.配置事务切入点,以及把事务切入点和事务属性关联起来--> <aop:config> <aop:pointcut id="txPointCut" expression="execution(* com.guigu.spring4.shiwu.*.*(..))"/> <aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointCut"></aop:advisor> </aop:config> </beans>
------------------spring在web应用的使用------------------(重要)
一,第一种方式:核心步骤,自己用代码把web应用和spring关联起来。
1. Spring 如何在 WEB 应用中使用 ?
1). 需要额外加入的 jar 包:
spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-webmvc-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
2). Spring 的配置文件, 没有什么不同
3). 如何创建 IOC 容器 ?
①. 非 WEB 应用在 main 方法中直接创建
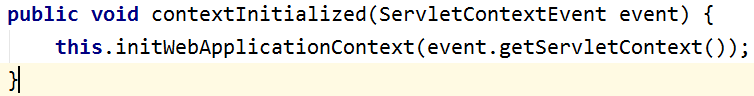
②. 应该在 WEB 应用被服务器加载时就创建 IOC 容器:
在 ServletContextListener#contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) 方法中创建 IOC 容器.
③. 在 WEB 应用的其他组件中如何来访问 IOC 容器呢 ?
在 ServletContextListener#contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) 方法中创建 IOC 容器后, 可以把其放在
ServletContext(即 application 域)的一个属性中.
④. 实际上, Spring 配置文件的名字和位置应该也是可配置的! 将其配置到当前 WEB 应用的初始化参数中较为合适.
二,第二种方式:核心步骤,调用spring里已经为开发者准备好的监听器与web应用关联。
4). 在 WEB 环境下使用 Spring
①. 需要额外加入的 jar 包:
spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-webmvc-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
②. Spring 的配置文件, 和非 WEB 环境没有什么不同
③. 需要在 web.xml 文件中加入如下配置:
<!-- 配置 Spring 配置文件的名称和位置 -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- 启动 IOC 容器的 ServletContextListener -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
---------------------------代码------------------------------
第一种的代码,主要看思想。
记得导服务器里的servlet包


public class Listener implements ServletContextListener, HttpSessionListener, HttpSessionAttributeListener { // Public constructor is required by servlet spec public Listener() { } // ------------------------------------------------------- // ServletContextListener implementation // ------------------------------------------------------- public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) { /* This method is called when the servlet context is initialized(when the Web application is deployed). You can initialize servlet context related data here. */ //获取spring配置文件的名称。 ServletContext servletContext = sce.getServletContext(); String initParameter = servletContext.getInitParameter("contextConfigLocation"); //创建ioc容器 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(initParameter); //把ioc容器放在servletContext的一个属性里。 servletContext.setAttribute("ac",ac); }
public class Person { String name; public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } @Override public String toString() { return "Person{" + "name='" + name + '\'' + '}'; } }
public class Servlet extends HttpServlet { protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { } protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { ServletContext servletContext =getServletContext(); ApplicationContext a=(ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("ac"); Person person =(Person) a.getBean("person"); System.out.println(person); } }
<bean id="person" class="com.guigu.spring6.web.Person"> <property name="name" value="zx"></property> </bean>
applicationContext.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee http://xmlns.jcp.org/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_4_0.xsd" version="4.0"> <!--加入监听器--> <listener> <listener-class>com.guigu.spring6.web.Listener</listener-class> </listener> <!--和spring配置文件建立联系--> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!--需要一个servlet做测试--> <servlet> <servlet-name>Servlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.guigu.spring6.web.Servlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>Servlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/servlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
index.jsp <a href="servlet">test</a>
第二种的代码,进行了简化(不用自己写监听器了)。

<!--加入spring包准备好的监听器--> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!--和spring配置文件建立联系--> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param>
spring的配置文件applicationcontext.xml 不变。
person类 不变。

public class Servlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
}
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
ServletContext servletContext =getServletContext();
// ApplicationContext a=(ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT");
//和上面写的效果一样,spring给了我们对应的工具类,叫WebApplicationContextUtils
ApplicationContext a=WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
Person person =(Person) a.getBean("person");
System.out.println(person);
}
}
index.jsp 不变
--------------------spring带的监听器ContextLoaderListener的源码理解------------------
在web里配的监听器ContextLoaderListener,进入初始化方法看一看。
进入源码里,找到这个方法:
servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context);

这个方法存储ioc容器的key为:
WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE
点进去看,具体叫什么?

所以在servlet里这样的行为得到ioc容器是可以的:
ApplicationContext a=(ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.class.getName() + ".ROOT");
但是我们的spring已经封装了这个功能,和上面写的效果一样,spring给了我们对应的工具类,叫WebApplicationContextUtils
ApplicationContext a=WebApplicationContextUtils.getWebApplicationContext(servletContext);
走入这个工具类的getWebApplicationContext方法的源码。

进入源码。上面这个方法return了下面这个方法。
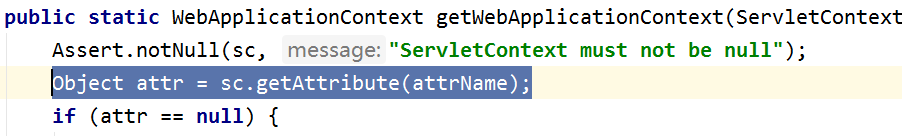
本质上还是通过那个一大串字符串作为key,来获得ioc容器。spring通过封装使代码简洁。




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号