JavaScript中常见数据结构
数据结构
- 栈:一种遵从先进后出 (LIFO) 原则的有序集合;新添加的或待删除的元素都保存在栈的末尾,称作栈顶,另一端为栈底。在栈里,新元素都靠近栈顶,旧元素都接近栈底。
- 队列:与上相反,一种遵循先进先出 (FIFO / First In First Out) 原则的一组有序的项;队列在尾部添加新元素,并从头部移除元素。最新添加的元素必须排在队列的末尾。
- 链表:存储有序的元素集合,但不同于数组,链表中的元素在内存中并不是连续放置的;每个元素由一个存储元素本身的节点和一个指向下一个元素的引用(指针/链接)组成。
- 集合:由一组无序且唯一(即不能重复)的项组成;这个数据结构使用了与有限集合相同的数学概念,但应用在计算机科学的数据结构中。
- 字典:以 [键,值] 对为数据形态的数据结构,其中键名用来查询特定元素,类似于 Javascript 中的
Object。 - 散列:根据关键码值(Key value)直接进行访问的数据结构;它通过把关键码值映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度;这个映射函数叫做散列函数,存放记录的数组叫做散列表。
- 树:由 n(n>=1)个有限节点组成一个具有层次关系的集合;把它叫做“树”是因为它看起来像一棵倒挂的树,也就是说它是根朝上,而叶朝下的,基本呈一对多关系,树也可以看做是图的特殊形式。
- 图:图是网络结构的抽象模型;图是一组由边连接的节点(顶点);任何二元关系都可以用图来表示,常见的比如:道路图、关系图,呈多对多关系。
栈
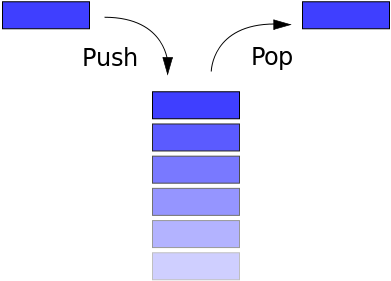
生活中常见的Stack的例子比如一摞书,你最后放上去的那本你之后会最先拿走;又比如浏览器的访问历史,当点击返回按钮,最后访问的网站最先从历史记录中弹出。
Stack一般具备以下方法:
- push:将一个元素推入栈顶
- pop:移除栈顶元素,并返回被移除的元素
- peek:返回栈顶元素
- isEmpty(): 栈中是否有元素
- clear(): 移除栈中所有元素
- size:返回栈中元素的个数
以对象形式实现栈
<script type="text/javascript">
function Stack() {
this.count = 0;
this.storage = {};
//将一个元素推入栈顶
this.push = function (value) {
this.storage[this.count] = value;
this.count++;
}
//移除栈顶元素,并返回被移除的元素
this.pop = function () {
if (this.count === 0) {
return undefined;
}
this.count--;
var result = this.storage[this.count];
delete this.storage[this.count];
return result;
}
//返回栈顶元素
this.peek = function () {
return this.storage[this.count - 1];
}
//栈中是否有元素
this.isEmpty = function () {
//使用es6语法判断对象中属性长度
//return Object.keys(this.storage).length==0;
return this.count==0;
}
//移除栈中所有元素
this.clear = function () {
this.count = 0
//return this.storage={};
}
//返回栈中元素的个数
this.size = function () {
return this.count;
}
}
var newStack = new Stack();
newStack.push("第一个元素");
newStack.push("第二个元素");
newStack.push("第三个元素");
console.log("打印栈中元素个数:" + newStack.size());
console.log("打印栈中栈顶元素:" + newStack.peek());
console.log("打印栈中移除元素:" + newStack.pop());
console.log("移除栈顶元素后再次打印栈中栈顶元素:" + newStack.peek());
console.log("判断栈中是否有元素:" + newStack.isEmpty());
console.log("移除栈中所有元素:" + newStack.clear());
console.log("移除后判断栈中是否有元素:" + newStack.isEmpty());
console.log("打印栈中移除元素:" + newStack.pop());
</script>
以数组形式实现栈
<script type="text/javascript">
function Stack() {
//保存栈内元素的数组
this.dataStore = [];
//top用来记录栈顶位置,初始化为0
this.top = 0;
this.push = function (element) {
this.dataStore[this.top++] = element; // 先在top位置加入元素,之后top加1
}
this.pop = function () {
// top先减1,然后返回top位置的元素
return this.dataStore[--this.top];
}
this.peek = function peek() {
return this.dataStore[this.top - 1];
}
this.isEmpty = function clear() {
return this.top ==0;
}
this.clear = function clear() {
this.top = 0;
}
this.length = function length() {
return this.top;
}
}
var newStack = new Stack();
newStack.push("第一个元素");
newStack.push("第二个元素");
newStack.push("第三个元素");
console.log("打印栈中元素个数:" + newStack.length());
console.log("打印栈中栈顶元素:" + newStack.peek());
console.log("打印栈中移除元素:" + newStack.pop());
console.log("移除栈顶元素后再次打印栈中栈顶元素:" + newStack.peek());
console.log("判断栈中是否有元素:" + newStack.isEmpty());
console.log("移除栈中所有元素:" + newStack.clear());
console.log("移除后判断栈中是否有元素:" + newStack.isEmpty());
</script>
Queue(队列)
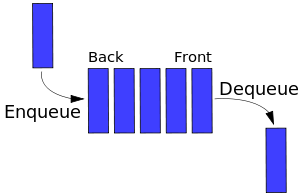
Queue和Stack有一些类似,不同的是Stack是先进后出,而Queue是先进先出。Queue在生活中的例子比如排队上公交,排在第一个的总是最先上车;又比如打印机的打印队列,排在前面的最先打印。
Queue一般具有以下常见方法:
- enqueue:入列,向队列尾部增加一个元素
- dequeue:出列,移除队列头部的一个元素并返回被移除的元素
- front:获取队列的第一个元素
- isEmpty:判断队列是否为空
- size:获取队列中元素的个数
Javascript中的Array已经具备了Queue的一些特性,所以我们可以借助Array实现一个Queue类型:
<script type="text/javascript">
function Queue() {
var collection = [];
//返回队列所有元素
this.print = function () {
return collection;
}
//入列,向队列尾部增加一个元素
this.enqueue = function (element) {
collection.push(element);
}
//出列,移除队列头部的一个元素并返回被移除的元素
this.dequeue = function () {
return collection.shift();
}
//获取队列的第一个元素
this.front = function () {
return collection[0];
}
//判断队列是否为空
this.isEmpty = function () {
return collection.length === 0;
}
//清除队列
this.clear = function () {
items = [];
};
//获取队列中元素的个数
this.size = function () {
return collection.length;
}
}
var newQueue= new Queue();
newQueue.enqueue("第一个元素");
newQueue.enqueue("第二个元素");
newQueue.enqueue("第三个元素");
console.log("打印队列中元素个数:" + newQueue.size());
console.log("打印队列中第一个元素:" + newQueue.front());
console.log("打印队列中所有元素:" + newQueue.print());
console.log("打印队列中移除元素:" + newQueue.dequeue());
console.log("移除队列元素后再次打印队列中所有元素:" + newQueue.print());
console.log("判断队列中是否有元素:" + newQueue.isEmpty());
console.log("移除队列中所有元素:" + newQueue.clear());
console.log("移除后判断队列中是否有元素:" + newQueue.isEmpty());
</script>
Priority Queue(优先队列)
Queue还有个升级版本,给每个元素赋予优先级,优先级高的元素入列时将排到低优先级元素之前。区别主要是enqueue方法的实现:
<script type="text/javascript">
function PriorityQueue() {
var collection = [];
//返回队列所有元素
this.print = function () {
return collection;
}
//入列,向队列尾部增加一个元素
this.enqueue = function (element) {
collection.push(element);
}
//出列,移除队列头部的一个元素并返回被移除的元素
this.dequeue = function () {
return collection.shift();
}
//获取队列的第一个元素
this.front = function () {
return collection[0];
}
//判断队列是否为空
this.isEmpty = function () {
return collection.length === 0;
}
//清除队列
this.clear = function () {
items = [];
};
//获取队列中元素的个数
this.size = function () {
return collection.length;
}
//优先队列
this.priorityEnqueue = function (element) {
if (this.isEmpty()) {
collection.push(element);
} else {
var added = false;
for (var i = 0; i < collection.length; i++) {
if (element[1] < collection[i][1]) {
collection.splice(i, 0, element);
added = true;
break;
}
}
if (!added) {
collection.push(element);
}
}
}
}
var newQueue = new PriorityQueue();
newQueue.enqueue("第一个元素");
newQueue.enqueue("第二个元素");
newQueue.enqueue("第三个元素");
console.log("打印队列中元素个数:" + newQueue.size());
console.log("打印队列中第一个元素:" + newQueue.front());
console.log("打印队列中所有元素:" + newQueue.print());
console.log("打印队列中移除元素:" + newQueue.dequeue());
console.log("移除队列元素后再次打印队列中所有元素:" + newQueue.print());
console.log("判断队列中是否有元素:" + newQueue.isEmpty());
console.log("移除队列中所有元素:" + newQueue.clear());
console.log("移除后判断队列中是否有元素:" + newQueue.isEmpty());
newQueue.priorityEnqueue(['gannicus', 3]);
newQueue.priorityEnqueue(['spartacus', 1]);
newQueue.priorityEnqueue(['crixus', 2]);
newQueue.priorityEnqueue(['oenomaus', 4]);
console.log("优先队列中所有元素:" + newQueue.print());
</script>
Linked List(链表)
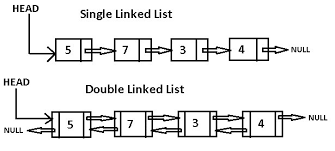
链表是一种链式数据结构,链上的每个节点包含两种信息:节点本身的数据和指向下一个节点的指针。链表和传统的数组都是线性的数据结构,存储的都是一个序列的数据,但也有很多区别,如下表:
| 比较维度 | 数组 | 链表 |
|---|---|---|
| 内存分配 | 静态内存分配,编译时分配且连续 | 动态内存分配,运行时分配且不连续 |
| 元素获取 | 通过Index获取,速度较快 | 通过遍历顺序访问,速度较慢 |
| 添加删除元素 | 因为内存位置连续且固定,速度较慢 | 因为内存分配灵活,只有一个开销步骤,速度更快 |
| 空间结构 | 可以是一维或者多维数组 | 可以是单向、双向或者循环链表 |
一个单向链表通常具有以下方法:
- size:返回链表中节点的个数
- head:返回链表中的头部元素
- add:向链表尾部增加一个节点
- remove:删除某个节点
- indexOf:返回某个节点的index
- elementAt:返回某个index处的节点
- addAt:在某个index处插入一个节点
- removeAt:删除某个index处的节点
单向链表的Javascript实现:
<script type="text/javascript"> /** * 链表中的节点 */ function Node(element) { // 节点中的数据 this.element = element; // 指向下一个节点的指针 this.next = null; } function LinkedList() { var length = 0; var head = null; //返回链表中节点的个数 this.size = function () { return length; } //返回链表中的头部元素 this.head = function () { return head; } //向链表尾部增加一个节点 this.add = function (element) { var node = new Node(element); if (head == null) { head = node; } else { var currentNode = head; while (currentNode.next) { currentNode = currentNode.next; } currentNode.next = node; } length++; } //删除某个节点 this.remove = function (element) { var currentNode = head; var previousNode; if (currentNode.element === element) { head = currentNode.next; } else { while (currentNode.element !== element) { previousNode = currentNode; currentNode = currentNode.next; } previousNode.next = currentNode.next; } length--; } this.isEmpty = function () { return length === 0; } //返回链表所有节点 this.value = function () { var currentNode = head; var nodeList = []; if (currentNode==null) { return undefined } else { while (currentNode.next) { nodeList.push(currentNode.element); currentNode = currentNode.next; } nodeList.push(currentNode.element); } return nodeList; } //返回某个节点的index this.indexOf = function (element) { var currentNode = head; var index = -1; while (currentNode) { index++; if (currentNode.element === element) { return index; } currentNode = currentNode.next; } return -1; } //返回某个index处的节点 this.elementAt = function (index) { var currentNode = head; var count = 0; while (count < index) { count++; currentNode = currentNode.next; } return currentNode.element; } //在某个index处插入一个节点 this.addAt = function (index, element) { var node = new Node(element); var currentNode = head; var previousNode; var currentIndex = 0; if (index > length) { return false; } if (index === 0) { node.next = currentNode; head = node; } else { while (currentIndex < index) { currentIndex++; previousNode = currentNode; currentNode = currentNode.next; } node.next = currentNode; previousNode.next = node; } length++; } //删除某个index处的节点 this.removeAt = function (index) { var currentNode = head; var previousNode; var currentIndex = 0; if (index < 0 || index >= length) { return null; } if (index === 0) { head = currentIndex.next; } else { while (currentIndex < index) { currentIndex++; previousNode = currentNode; currentNode = currentNode.next; } previousNode.next = currentNode.next; } length--; return currentNode.element; } } var newLinkedList = new LinkedList(); newLinkedList.indexOf("第一个节点"); newLinkedList.add("第一个节点"); newLinkedList.add("第二个节点"); newLinkedList.add("第三个节点"); newLinkedList.add("第四个节点"); newLinkedList.add("第五个节点"); newLinkedList.add("第六个节点"); newLinkedList.add("第七个节点"); newLinkedList.add("第八个节点"); console.log("打印链表中所有元素:" + newLinkedList.value()); newLinkedList.remove("第一个节点"); newLinkedList.remove("第三个节点"); console.log("打印删除后链表中所有元素:" + newLinkedList.value()); </script>
单链表
talk is easy, show the code, 下面用 JavaScript 实现一个相对完整的单链表,并提供以下方法供调用:
- push(element) // 链表尾部插入节点
- pop() // 链表尾部删除节点
- shift() // 删除头部节点、
- unshift(element) // 插入头部节点
- find(index) // 查找指定位置节点
- insert(element, index) // 指定位置插入节点
- edit(element, index) // 修改指定位置节点
- delete(index) // 链表删除指定位置节点
- cycle() // 使链表首尾成环
function initList() { class Node { constructor(item) { this.element = item } } class List { constructor() { this.head = null this.size = 0 this.last = null } /** * 链表查找元素 * @param index 查找的位置 */ find(index) { let current = this.head for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) { current = current.next } return current } /** * 链表尾部插入元素 * @param element 插入的元素 */ push(element) { let newNode = new Node(element) if (this.size === 0) { this.head = newNode this.head.next = null this.last = this.head } else { this.last.next = newNode this.last = newNode newNode.next = null } this.size += 1 } /** * 链表尾部删除元素 * @param element 删除的位置 */ pop(element) { this.last.next = null } /** * 链表头部删除元素 */ shift() { if (this.size === 0) return this.head = this.head.next if (this.size === 1) this.last = null this.size -= 1 } /** * 链表头部插入元素 * @param element 插入的元素 */ unshift(element) { let newNode = new Node(element) newNode.next = this.head this.head = newNode if (this.size === 0) this.last = this.head this.size += 1 } /** * 链表插入元素 * @param element 插入的位置, index 插入的位置 */ insert(element, index) { if (index < 0 || index > this.size) { console.error('超出链表节点范围') return } let newNode = new Node(element) if (this.size === 0) { // 空链表 newNode.next = null this.head = newNode this.last = newNode } else if (index === 0) { // 插入头部 newNode.next = this.head this.head = newNode } else if (index == this.size) { //插入尾部 newNode.next = null this.last.next = newNode this.last = newNode } else { // 中间插入 let preNode = this.find(index - 1) newNode.next = preNode.next preNode.next = newNode } this.size += 1 } /* *链表编辑元素 * @param element 编辑的元素,index 元素位置 */ edit(element, index) { let current = this.find(index) current.element = element } /* *链表删除元素 * @param index 删除元素位置 */ delete(index) { let current = this.find(index) if (index === 0) { // 删除头节点 this.head = this.head.next } else if (index === ((this.size) - 1)) { // 删除尾节点 let preNode = this.find(index - 1) preNode.next = null } else { // 删除中间节点 let preNode = this.find(index - 1) let nextNode = preNode.next.next let removeNode = preNode.next preNode.next = nextNode } this.size -= 1 } /* *链表使首尾成环 */ cycle() { this.last.next = this.head } } return new List() } let list = initList()
双向链表
双向链表的特点就是添加了指向上一个节点的指针(prev),比较单链表来说,稍微复杂一些,也更强大,这里把上面的单链表修改一下。
function initList() { class Node { constructor(item) { this.element = item this.next = null this.prev = null } } class List { constructor() { this.head = null this.size = 0 this.last = null } /** * 链表查找元素 * @param index 查找的位置 */ find(index) { let current = this.head for (let i = 0; i < index; i++) { current = current.next } return current } /** * 链表尾部插入元素 * @param element 插入的元素 */ push(element) { let newNode = new Node(element) if (this.size === 0) { this.head = newNode this.head.next = null this.last = this.head } else { this.last.next = newNode newNode.next = null newNode.prev = this.last this.last = newNode } this.size += 1 } /** * 链表尾部删除元素 * @param element 删除的位置 */ pop() { if (this.size === 0) return if (this.size === 1) { this.head = null this.last = null } else { this.last.prev.next = null this.last = this.last.prev } this.size -= 1 } /** * 链表头部删除元素 */ shift() { if (this.size === 0) return if (this.size === 1) { this.head = null this.last = null } else { this.head = this.head.next this.head.prev = null } this.size -= 1 } /** * 链表头部插入元素 * @param element 插入的元素 */ unshift(element) { let newNode = new Node(element) if (this.size === 0) { this.head = newNode this.head.next = null this.last = this.head } else { this.head.prev = newNode newNode.next = this.head this.head = newNode } this.size += 1 } /** * 链表插入元素 * @param element 插入的位置, index 插入的位置 */ insert(element, index) { if (index < 0 || index > this.size) { console.error('超出链表节点范围') return } let newNode = new Node(element) if (this.size === 0) { // 空链表 this.head = newNode this.head.next = null this.last = this.head } else if (index === 0) { // 插入头部 this.head.pre = newNode newNode.next = this.head this.head = newNode } else if (index == this.size - 1) { //插入尾部 newNode.next = null newNode.prev = this.last this.last.next = newNode this.last = newNode } else { // 中间插入 let prevNode = this.find(index - 1) newNode.next = prevNode.next prevNode.next = newNode newNode.prev = prevNode newNode.next.prev = newNode } this.size += 1 } /* *链表编辑元素 * @param element 编辑的元素,index 元素位置 */ edit(element, index) { let current = this.find(index) current.element = element } /* *链表删除元素 * @param index 删除元素位置 */ delete(index) { let current = this.find(index) if (index === 0) { // 删除头节点 this.head = this.head.next this.prev = null } else if (index === ((this.size) - 1)) { // 删除尾节点 let preNode = this.find(index - 1) preNode.next = null } else { // 删除中间节点 let preNode = this.find(index - 1) let nextNode = preNode.next.next let removeNode = preNode.next preNode.next = nextNode nextNode.prev = preNode } this.size -= 1 } /* *链表使首尾成环 */ cycle() { this.last.next = this.head this.head.prev = this.last } } return new List() } let list = new initList()
循环链表
循环链表可以是单链表也可以是双向链表,它的特点是最后一个节点的 next 指针指向的是 head 节点
而不是 null,上面代码已经提供了 cycle 方法来实现。
判断链表有环
主要有这些方法:
-
遍历链表,使每一个节点与之前节点比较,若有重复则为有环链表
-
定义一个 Map 对象,遍历链表到每一个节点,若 Map 中没有次节点 ID,则将节点 ID 为 key, 存入 Map ,每个节点判断一次,如果某个节点的 ID存在,证明链表成环
-
双指针法,举个例子来说,两个人在操场跑步,速度不同时,总会在某些时刻相遇,就是因为跑到是圆的(环),利用这个原理,定义一个循环和两个指向头节点的指针,一个每次移动一个节点,一个移动两个节点,如果是成环的链表,某个时刻必然会遇到同一个节点。
链表在前端开发中的应用
-
链表的特性表明其擅长修改,不擅查找,所以对于需要大量修改的操作,可以考虑用链表实现,但是前端往往处理的数据量不会大,所以这种场景的实际意义不是很大,个人感觉在框架的底层优化上,使用较多,业务开发中,数组够用。
-
链表因为是随机存储的,所以比较省内存,但是对动态语言 JavaScript 解释器来说,有自动的垃圾回收机制来管理内存,所以链表的这个优势就不明显了。
-
链表特殊的结构,感觉适合做轮播图(双向循环链表)、双向导航列表等
Set(集合)
集合是数学中的一个基本概念,表示具有某种特性的对象汇总成的集体。在ES6中也引入了集合类型Set,Set和Array有一定程度的相似,不同的是Set中不允许出现重复的元素而且是无序的。
一个典型的Set应该具有以下方法:
- values:返回集合中的所有元素
- size:返回集合中元素的个数
- has:判断集合中是否存在某个元素
- add:向集合中添加元素
- remove:从集合中移除某个元素
- union:返回两个集合的并集
- intersection:返回两个集合的交集
- difference:返回两个集合的差集
- subset:判断一个集合是否为另一个集合的子集
使用Javascript可以将Set进行如下实现,为了区别于ES6中的Set命名为MySet:
function MySet() { var collection = []; this.has = function (element) { return (collection.indexOf(element) !== -1); } this.values = function () { return collection; } this.size = function () { return collection.length; } this.add = function (element) { if (!this.has(element)) { collection.push(element); return true; } return false; } this.remove = function (element) { if (this.has(element)) { index = collection.indexOf(element); collection.splice(index, 1); return true; } return false; } this.union = function (otherSet) { var unionSet = new MySet(); var firstSet = this.values(); var secondSet = otherSet.values(); firstSet.forEach(function (e) { unionSet.add(e); }); secondSet.forEach(function (e) { unionSet.add(e); }); return unionSet; } this.intersection = function (otherSet) { var intersectionSet = new MySet(); var firstSet = this.values(); firstSet.forEach(function (e) { if (otherSet.has(e)) { intersectionSet.add(e); } }); return intersectionSet; } this.difference = function (otherSet) { var differenceSet = new MySet(); var firstSet = this.values(); firstSet.forEach(function (e) { if (!otherSet.has(e)) { differenceSet.add(e); } }); return differenceSet; } this.subset = function (otherSet) { var firstSet = this.values(); return firstSet.every(function (value) { return otherSet.has(value); }); } }
最后,推荐大家使用Fundebug,一款很好用的BUG监控工具~
Hash Table(哈希表/散列表)
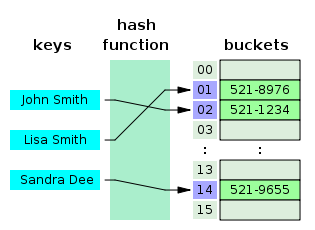
Hash Table是一种用于存储键值对(key value pair)的数据结构,因为Hash Table根据key查询value的速度很快,所以它常用于实现Map、Dictinary、Object等数据结构。如上图所示,Hash Table内部使用一个hash函数将传入的键转换成一串数字,而这串数字将作为键值对实际的key,通过这个key查询对应的value非常快,时间复杂度将达到O(1)。Hash函数要求相同输入对应的输出必须相等,而不同输入对应的输出必须不等,相当于对每对数据打上唯一的指纹。
一个Hash Table通常具有下列方法:
- put()增加元素
- remove()移除元素
- get()获取元素
简易版本的Hash Table的Javascript实现
class HashTable{ constructor(){ this.table = [] // 散列表 } /* 散列函数1:冲突相对比较 */ loseloseHashCode(key){ // 通过ASCII码转换生成key let hash = 0 for (let i = 0; i< key.length; i++) { hash += key[i].charCodeAt() // 计算key的ASCII码,当使用2个不同的键值,通过散列函数生成一致的散列键值,这样会发生哈希碰撞,导致数据覆盖 } return hash%37 // loseloseHashCode方法计算关键码的公式,即 ASCII码取余37 } /* 新增元素 */ put(key,value){ const position = this.loseloseHashCode(key) // 元素在散列表里的地址 this.table[position] = value } /* 移除元素 */ remove(key){ this.table[this.loseloseHashCode(key)] = undefined } /* 获取元素 */ get(key){ return this.table[this.loseloseHashCode(key)] } }
function betterHash (str, arr) { var H = 37; var total = 0; for (var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) { total += H * total + str.chatCodeAt(i); } total = total % arr.length; return parseInt(total); } function get (key) { return this.table[this.betterHash(key, this.table)]; }
质数37是一个比较好的数字适合我们的哈希算法来参与哈希键值运算,并且使生成的键值在哈希表中均匀分布。
以对象实现哈希表
// 创建构造函数HashTable function HashTable() { // 初始化哈希表的记录条数size var size = 0; // 创建对象用于接受键值对 var res = {}; // 添加关键字,无返回值 this.add = function (key, value) { //判断哈希表中是否存在key,若不存在,则size加1,且赋值 if (!this.containKey(key)) { size++; } // 如果之前不存在,赋值; 如果之前存在,覆盖。 res[key] = value; }; // 删除关键字, 如果哈希表中包含key,并且delete返回true则删除,并使得size减1 this.remove = function (key) { if (this.containKey(key) && (delete res[key])) { size--; } }; // 哈希表中是否包含key,返回一个布尔值 this.containKey = function (key) { return (key in res); }; // 哈希表中是否包含value,返回一个布尔值 this.containValue = function (value) { // 遍历对象中的属性值,判断是否和给定value相等 for (var prop in res) { if (res[prop] === value) { return true; } } return false; }; // 根据键获取value,如果不存在就返回null this.getValue = function (key) { return this.containKey(key) ? res[key] : null; }; // 获取哈希表中的所有value, 返回一个数组 this.getAllValues = function () { var values = []; for (var prop in res) { values.push(res[prop]); } return values; }; // 根据值获取哈希表中的key,如果不存在就返回null this.getKey = function (value) { for (var prop in res) { if (res[prop] === value) { return prop; } } // 遍历结束没有return,就返回null return null; }; // 获取哈希表中所有的key,返回一个数组 this.getAllKeys = function () { var keys = []; for (var prop in res) { keys.push(prop); } return keys; }; // 获取哈希表中记录的条数,返回一个数值 this.getSize = function () { return size; }; // 清空哈希表,无返回值 this.clear = function () { size = 0; res = {}; }; }
Tree(树)
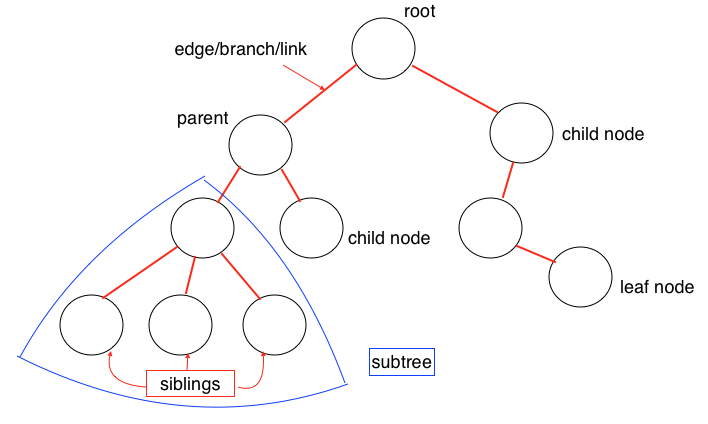
Tree的数据结构和自然界中的树极其相似,有根、树枝、叶子,如上图所示。Tree是一种多层数据结构,与Array、Stack、Queue相比是一种非线性的数据结构,在进行插入和搜索操作时很高效。在描述一个Tree时经常会用到下列概念:
-
Root(根):代表树的根节点,根节点没有父节点
-
Parent Node(父节点):一个节点的直接上级节点,只有一个
-
Child Node(子节点):一个节点的直接下级节点,可能有多个
-
Siblings(兄弟节点):具有相同父节点的节点
-
Leaf(叶节点):没有子节点的节点
-
Edge(边):两个节点之间的连接线
-
Path(路径):从源节点到目标节点的连续边
-
Height of Node(节点的高度):表示节点与叶节点之间的最长路径上边的个数
-
Height of Tree(树的高度):即根节点的高度
-
Depth of Node(节点的深度):表示从根节点到该节点的边的个数
-
Degree of Node(节点的度):表示子节点的个数
以二叉查找树为例,展示树在Javascript中的实现。在二叉查找树中,即每个节点最多只有两个子节点,而左侧子节点小于当前节点,而右侧子节点大于当前节点,如图所示:
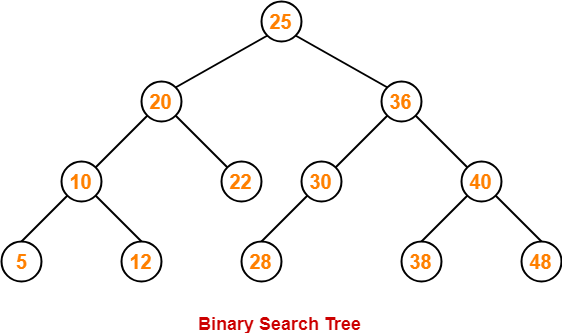
二叉查找树应该具有以下常用方法:
- add:向树中插入一个节点
- findMin:查找树中最小的节点
- findMax:查找树中最大的节点
- find:查找树中的某个节点
- isPresent:判断某个节点在树中是否存在
- remove:移除树中的某个节点
以下是二叉查找树的Javascript实现:
class Node { constructor(data, left = null, right = null) { this.data = data; this.left = left; this.right = right; } } class BST { constructor() { this.root = null; } add(data) { const node = this.root; if (node === null) { this.root = new Node(data); return; } else { const searchTree = function (node) { if (data < node.data) { if (node.left === null) { node.left = new Node(data); return; } else if (node.left !== null) { return searchTree(node.left); } } else if (data > node.data) { if (node.right === null) { node.right = new Node(data); return; } else if (node.right !== null) { return searchTree(node.right); } } else { return null; } }; return searchTree(node); } } findMin() { let current = this.root; while (current.left !== null) { current = current.left; } return current.data; } findMax() { let current = this.root; while (current.right !== null) { current = current.right; } return current.data; } find(data) { let current = this.root; while (current.data !== data) { if (data < current.data) { current = current.left } else { current = current.right; } if (current === null) { return null; } } return current; } isPresent(data) { let current = this.root; while (current) { if (data === current.data) { return true; } if (data < current.data) { current = current.left; } else { current = current.right; } } return false; } remove(data) { const removeNode = function (node, data) { if (node == null) { return null; } if (data == node.data) { // node没有子节点 if (node.left == null && node.right == null) { return null; } // node没有左侧子节点 if (node.left == null) { return node.right; } // node没有右侧子节点 if (node.right == null) { return node.left; } // node有两个子节点 var tempNode = node.right; while (tempNode.left !== null) { tempNode = tempNode.left; } node.data = tempNode.data; node.right = removeNode(node.right, tempNode.data); return node; } else if (data < node.data) { node.left = removeNode(node.left, data); return node; } else { node.right = removeNode(node.right, data); return node; } } this.root = removeNode(this.root, data); } }
测试一下:
const bst = new BST();
|
打印结果:
1
|
二叉树的遍历,遍历方式:
前序遍历:先遍历根结点,然后左子树,再右子树
中序遍历:先遍历左子树,然后根结点,再右子树
后续遍历:先遍历左子树,然后右子树,再根结点
//前序遍历 function ProOrderTraverse(biTree) { if (biTree == null) return; console.log(biTree.data); ProOrderTraverse(biTree.lChild); ProOrderTraverse(biTree.rChild); } //中序遍历 function InOrderTraverse(biTree) { if (biTree == null) return; InOrderTraverse(biTree.lChild); console.log(biTree.data); InOrderTraverse(biTree.rChild); } //后续遍历 function PostOrderTraverse(biTree) { if (biTree == null) return; PostOrderTraverse(biTree.lChild); PostOrderTraverse(biTree.rChild); console.log(biTree.data); }
二叉树的非递归遍历
深度优先遍历(主要利用栈的先进后出)
广度优先遍历(主要利用队列的先进先出)
//深度优先非递归 function DepthFirstSearch(biTree) { let stack = []; stack.push(biTree); while (stack.length != 0) { let node = stack.pop(); console.log(node.data); if (node.rChild) { stack.push(node.rChild); } if (node.lChild) { stack.push(node.lChild); } } } //广度优先非递归 function BreadthFirstSearch(biTree) { let queue = []; queue.push(biTree); while (queue.length != 0) { let node = queue.shift(); console.log(node.data); if (node.lChild) { queue.push(node.lChild); } if (node.rChild) { queue.push(node.rChild); } } }
Trie(字典树,读音同try)
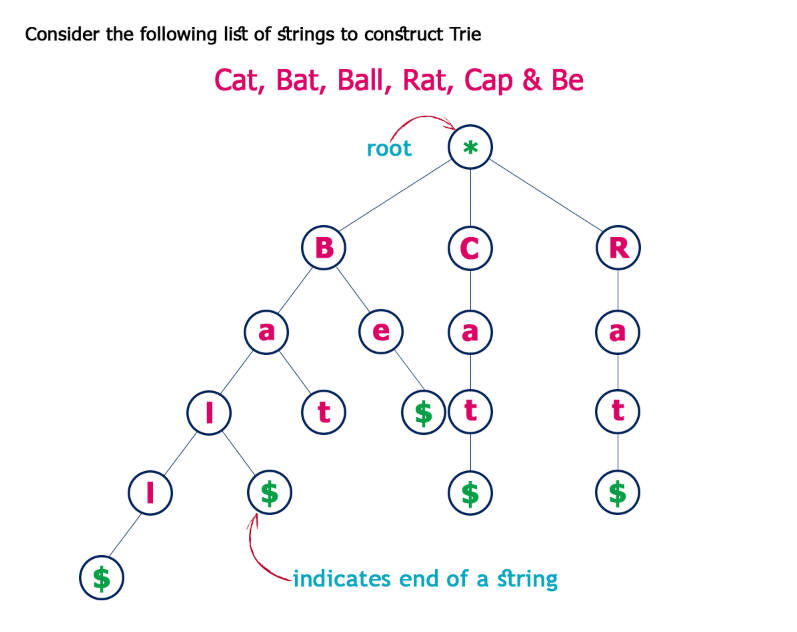
Trie也可以叫做Prefix Tree(前缀树),也是一种搜索树。Trie分步骤存储数据,树中的每个节点代表一个步骤,trie常用于存储单词以便快速查找,比如实现单词的自动完成功能。 Trie中的每个节点都包含一个单词的字母,跟着树的分支可以可以拼写出一个完整的单词,每个节点还包含一个布尔值表示该节点是否是单词的最后一个字母。
Trie一般有以下方法:
- add:向字典树中增加一个单词
- isWord:判断字典树中是否包含某个单词
- print:返回字典树中的所有单词
/** * Trie的节点 */ function Node() { this.keys = new Map(); this.end = false; this.setEnd = function () { this.end = true; }; this.isEnd = function () { return this.end; } } function Trie() { this.root = new Node(); this.add = function (input, node = this.root) { if (input.length === 0) { node.setEnd(); return; } else if (!node.keys.has(input[0])) { node.keys.set(input[0], new Node()); return this.add(input.substr(1), node.keys.get(input[0])); } else { return this.add(input.substr(1), node.keys.get(input[0])); } } this.isWord = function (word) { let node = this.root; while (word.length > 1) { if (!node.keys.has(word[0])) { return false; } else { node = node.keys.get(word[0]); word = word.substr(1); } } return (node.keys.has(word) && node.keys.get(word).isEnd()) ? true : false; } this.print = function () { let words = new Array(); let search = function (node = this.root, string) { if (node.keys.size != 0) { for (let letter of node.keys.keys()) { search(node.keys.get(letter), string.concat(letter)); } if (node.isEnd()) { words.push(string); } } else { string.length > 0 ? words.push(string) : undefined; return; } }; search(this.root, new String()); return words.length > 0 ? words : null; } }
Graph(图)
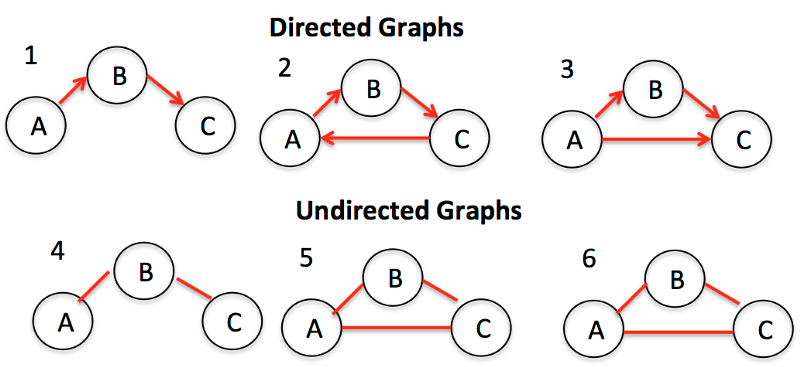
Graph是节点(或顶点)以及它们之间的连接(或边)的集合。Graph也可以称为Network(网络)。根据节点之间的连接是否有方向又可以分为Directed Graph(有向图)和Undrected Graph(无向图)。Graph在实际生活中有很多用途,比如:导航软件计算最佳路径,社交软件进行好友推荐等等。
Graph通常有两种表达方式:
Adjaceny List(邻接列表):
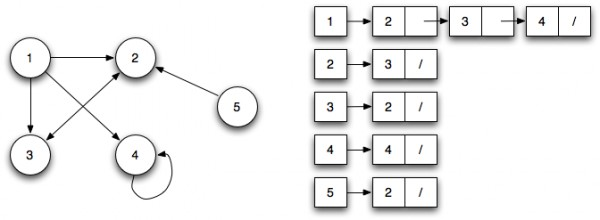
邻接列表可以表示为左侧是节点的列表,右侧列出它所连接的所有其他节点。
和 Adjacency Matrix(邻接矩阵):
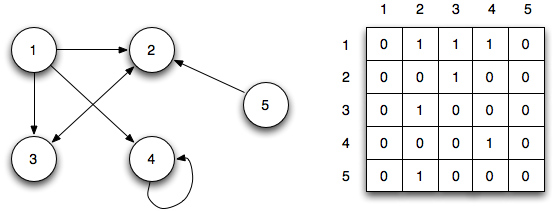
邻接矩阵用矩阵来表示节点之间的连接关系,每行或者每列表示一个节点,行和列的交叉处的数字表示节点之间的关系:0表示没用连接,1表示有连接,大于1表示不同的权重。
访问Graph中的节点需要使用遍历算法,遍历算法又分为广度优先和深度优先,主要用于确定目标节点和根节点之间的距离,
图的相关术语
1.有一条边相连的顶点叫相邻顶点;
2.一个顶点的度就是该顶点的相邻顶点数;
3.路径指顶点组成的连续序列;
4.简单路径没有重复顶点;
5.有向图和无向图
图的表示
邻接矩阵
array[i][j] ===1代表i节点和j节点相邻,否则不相邻
邻接表
相当于把每个节点的相邻节点一一列举出来。
关联矩阵
形式和邻接矩阵一样,只是把邻接矩阵的直接维度换成对应的边,适用于边比顶点多的情况。
创建图类
接下来就采用邻接表的方式创建上面的图并且采用字典来表示:
创建字典类
function Dictionary() { var items = {}; //set(key,value)向字典里添加新元素,这里主要用来添加边 this.set = function (key, value) { items[key] = value; } //has(key)如果存在就返回true,否则false this.has = function (key) { return key in items; } //get(key)通过key查找特定的数值并返回,这里主要用来查找顶点对应的边数组 this.get = function (key) { return this.has(key) ? items[key] : undefined; } }
创建图类
function Graph() { var vertices = []; //用来储存顶点 var adjList = new Dictionary(); //用来储存边 //创建initializeColor用来初始化各个顶点的颜色,为遍历过程中的标记做准备 var initializeColor = function () { var color = []; for (var i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) { color[vertices[i]] = 'white'; } return color; } //addVertex(key)用来添加顶点 this.addVertex = function (v) { vertices.push(v); adjList.set(v, []); } //addEdge(key,value)用来添加边v-w this.addEdge = function (v, w) { adjList.get(v).push(w); adjList.get(w).push(v); } //toString()把邻接表转化成字符串的形式,便于输出显示 this.toString = function () { var s = ''; for (var i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) { s += vertices[i] + '->'; var neighbors = adjList.get(vertices[i]); for (var j = 0; j < neighbors.length; j++) { s += neighbors[j] + ' '; } s += '\n'; } return s; } }
创建实例
var graph = new Graph(); var myVertices = ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I']; //添加顶点 for (var i = 0; i < myVertices.length; i++) { graph.addVertex(myVertices[i]); } //逐一加入边 graph.addEdge('A', 'B'); graph.addEdge('A', 'C'); graph.addEdge('A', 'D'); graph.addEdge('C', 'G'); graph.addEdge('C', 'D'); graph.addEdge('D', 'G'); graph.addEdge('D', 'H'); graph.addEdge('B', 'E'); graph.addEdge('B', 'F'); graph.addEdge('E', 'I'); console.log(graph.toString());
输出的结果为:
A->B C D
B->A E F
C->A G D
D->A C G H
E->B I
F->B
G->C D
H->D
I->E
图的遍历
广度优先遍历
采用队列的方式,先添加节点的先被探索;
采用三种颜色来反应节点的状态:
白色:还没被访问;
灰色:被访问但未被探索;
黑色:被访问且探索过;
思路:
首先搜索节点A,探索A节点的相邻节点B,C,D,把其加入队列中,再逐一出队列进行探索,从而实现广度遍历。
添加bfs方法
//广度优先遍历,在Graph()类中添加以下方法
this.bfs = function (v, callback) { var color = initializeColor(); //初始化节点,都标记为白色 var queue = []; //创建队列用来顶点的入队; queue.push(v); //访问的节点入队列 while (!queue.length == 0) { //如果队列非空就执行以下 var u = queue.shift(); //节点出队列 var neighbors = adjList.get(u); //探索节点对应的边 color[u] = 'grey'; //把搜索过的节点变成灰色 for (var i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) { var w = neighbors[i]; if (color[w] === 'white') { //如果探索到的子节点是白色就逐一变灰并入队列 color[w] = 'grey'; queue.push(w); } } color[u] = 'black'; //节点完成搜索和探索的过程,直接变黑 if (callback) { callback(u); //回调函数,可以用来输出 } } }
创建bfs实例
//bfs实例
function printNode(value) { console.log('Visited vertex:' + value); } graph.bfs(myVertices[0], printNode);
bfs输出结果
Visited vertex:A
Visited vertex:B
Visited vertex:C
Visited vertex:D
Visited vertex:E
Visited vertex:F
Visited vertex:G
Visited vertex:H
Visited vertex:I
使用BFS寻找最短路径
this.BFS = function (v) { var color = initializeColor(), queue = [], d = [], //用来储存从v到u的距离 pred = []; //用来储存节点的前溯点 queue.push(v); for (var i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) { d[vertices[i]] = 0; //初始化 pred[vertices[i]] = null; } while (!queue.length == 0) { var u = queue.shift(); var neighbors = adjList.get(u); color[u] = 'grey'; for (i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) { var w = neighbors[i]; if (color[w] === 'white') { color[w] = 'grey'; d[w] = d[u] + 1; //从头节点到w的距离 pred[w] = u; queue.push(w); } } color[u] = 'black'; } return { distance: d, predecessers: pred } }
创建BFS实例
//BFS实例 var shortestPathA = graph.BFS(myVertices[0]);//需要输入头节点myVertices[0] //console.log(shortestPathA); //搜索路径BFS var fromVertex = myVertices[0]; for (var i = 1; i < myVertices.length; i++) { var toVertex = myVertices[i]; var path = []; //path用来储存路径 for (var v = toVertex; v !== fromVertex; v = shortestPathA.predecessers[v]) { path.push(v); } path.push(fromVertex); var s = path.pop(); while (!path.length == 0) { s += '-' + path.pop(); } console.log(s) }
BFS输出结果
A-B
A-C
A-D
A-B-E
A-B-F
A-C-G
A-D-H
A-B-E-I
深度优先遍历
采用栈的方式,先添加节点的先被探索;
由递归实现。
思路:
从节点A开始,探索到A的相邻节点B,C,D压入栈中(这里的代码采用for循环,所以没有实质上的栈,但是用栈更容易理解),接着搜索B,探索到B的相邻节点E,F压入栈中,以此递归。
添加dfs方法
this.dfs = function (callback) { var color = initializeColor(); for (var i = 0; i < vertices.length; i++) { if (color[vertices[i]] === 'white') { dfsVisit(vertices[i], color, callback)//调用递归函数 } } } var dfsVisit = function (u, color, callback) { color[u] = 'grey'; if (callback) { callback(u); } var neighbors = adjList.get(u); for (var i = 0; i < neighbors.length; i++) { var w = neighbors[i]; if (color[w] === 'white') { dfsVisit(w, color, callback); } } color[u] = 'black'; }
创建dfs实例
graph.dfs(printNode);
dfs输出结果
Visited vertex:A
Visited vertex:B
Visited vertex:E
Visited vertex:I
Visited vertex:F
Visited vertex:C
Visited vertex:G
Visited vertex:D
Visited vertex:H