A2-03-14.DDL-MySQL Temporary Table
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-temporary-table/
MySQL Temporary Table
Summary: in this tutorial, we will discuss MySQL temporary table and show you how to create, use and drop temporary tables.
Introduction to MySQL temporary table
In MySQL, a temporary table is a special type of table that allows you to store a temporary result set, which you can reuse several times in a single session.
A temporary table is very handy when it is impossible or expensive to query data that requires a single SELECT statement with the JOIN clauses. In this case, you can use a temporary table to store the immediate result and use another query to process it.
A MySQL temporary table has the following specialized features:
- A temporary table is created by using
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLEstatement. Notice that theTEMPORARYkeyword is added between theCREATEandTABLEkeywords. - MySQL removes the temporary table automatically when the session ends or the connection is terminated. Of course, you can use the
DROP TABLEstatement to remove a temporary table explicitly when you are no longer use it. - A temporary table is only available and accessible to the client that creates it. Different clients can create temporary tables with the same name without causing errors because only the client that creates the temporary table can see it. However, in the same session, two temporary tables cannot share the same name.
- A temporary table can have the same name as a normal table in a database. For example, if you create a temporary table named
employeesin the sample database, the existingemployeestable becomes inaccessible. Every query you issue against theemployeestable is now referring to the temporaryemployeestable. When you drop theemployeestemporary table, the permanentemployeestable is available and accessible again.
For example, in case the connection to the database server is lost and you reconnect to the server automatically, you cannot differentiate between the temporary table and the permanent one. Then, you may issue a DROP TABLE statement to remove the permanent table instead of the temporary table, which is not expected.
Creating a MySQL temporary table
To create a temporary table, you just need to add the TEMPORARY keyword to the CREATE TABLEstatement. For example, the following statement creates a temporary table that stores the top 10 customers by revenue:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE top10customers
SELECT p.customerNumber,
c.customerName,
ROUND(SUM(p.amount),2) sales
FROM payments p
INNER JOIN customers c ON c.customerNumber = p.customerNumber
GROUP BY p.customerNumber
ORDER BY sales DESC
LIMIT 10;
|
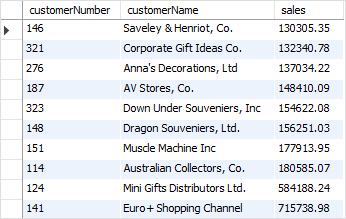
Now, you can query data from the top10customers temporary table like querying from a permanent table:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT
customerNumber,
customerName,
sales
FROM
top10customers
ORDER BY sales;
|
Removing a MySQL temporary table
You can use the DROP TABLE statement to remove temporary tables however it is good practice to add the TEMPORARY keyword as follows:
|
1
|
DROP TEMPORARY TABLE table_name;
|
The DROP TEMPORARY TABLE statement removes a temporary table only, not a permanent table. It helps you avoid the mistake of removing a permanent table when you name your temporary table the same as the name of the permanent table
For example, to remove the top10customers temporary table, you use the following statement:
|
1
|
DROP TEMPORARY TABLE top10customers;
|
Notice that if you try to remove a permanent table with the DROP TEMPORARY TABLE statement, you will get an error message saying that the table that you are trying drop is unknown.
If you develop an application that uses a connection pooling or persistent connections, it is not guaranteed that the temporary tables are removed automatically when your application is terminated.
Because the database connection that the application uses may be still open and placed in a connection pool for other clients to use. Therefore, it is a good practice to always remove the temporary tables whenever you are no longer use them.
In this tutorial, you have learned about the MySQL temporary tables and how to manage temporary tables such as creating and removing a new temporary table.


