A2-03-01.DDL-Manage Database in MySQL
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-create-drop-database.aspx
Manage Database in MySQL
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to manage databases in MySQL. You will learn how to create new databases, remove existing databases, and display all databases in the MySQL database server.
Let’s start creating a new database in MySQL.
Creating Database
Before doing anything else with the data, you need to create a database. A database is a container of data. It stores contacts, vendors, customers or any kind of data that you can think of. In MySQL, a database is a collection of objects that are used to store and manipulate data such as tables, database views, triggers, stored procedures, etc.
To create a database in MySQL, you use the CREATE DATABASE statement as follows:
|
1
|
CREATE DATABASE [IF NOT EXISTS] database_name;
|
Let’s examine the CREATE DATABASE statement in greater detail:
- Followed by the
CREATE DATABASEstatement is database name that you want to create. It is recommended that the database name should be as meaningful and descriptive as possible. - The
IF NOT EXISTSis an optional clause of the statement. TheIF NOT EXISTSclause prevents you from an error of creating a new database that already exists in the database server. You cannot have 2 databases with the same name in a MySQL database server.
For example, to create classicmodels database, you can execute the CREATE DATABASE statement as follows:
|
1
|
CREATE DATABASE classicmodels;
|
After executing this statement, MySQL returns a message to notify that the new database has been created successfully or not.
Displaying Databases
The SHOW DATABASES statement displays all databases in the MySQL database server. You can use the SHOW DATABASES statement to check the database that you’ve created or to see all the databases on the database server before you create a new database, for example:
|
1
|
SHOW DATABASES;
|
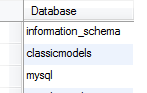
We have three databases in the MySQL database server. The information_schema and mysql are the default databases that are available when we install MySQL, and the classicmodels is the new database that we have created.
Selecting a database to work with
Before working with a particular database, you must tell MySQL which database you want to work with by using the USE statement.
|
1
|
USE database_name;
|
You can select the classicmodels sample database using the USE statement as follows:
|
1
|
USE classicmodels;
|
From now all operations such as querying data, create new tables or calling stored procedures which you perform, will take effects on the current database i.e., classicmodels .
Removing Databases
Removing database means you delete the database physically. All the data and associated objects inside the database are permanently deleted and this cannot be undone. Therefore, it is very important to execute this query with extra cautions.
To delete a database, you use the DROP DATABASE statement as follows:
|
1
|
DROP DATABASE [IF EXISTS] database_name;
|
Followed the DROP DATABASE is the database name that you want to remove. Similar to the CREATE DATABASE statement, the IF EXISTS is an optional part of the statement to prevent you from removing a database that does not exist in the database server.
If you want to practice with the DROP DATABASE statement, you can create a new database, make sure that it is created, and remove it. Let’s look at the following queries:
|
1
2
3
|
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS temp_database;
SHOW DATABASES;
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS temp_database;
|
The sequence of three statements is as follows:
- First, we created a database named
temp_databaseusing theCREATE DATABASEstatement. - Second, we displayed all databases using the
SHOW DATABASESstatement. - Third, we removed the
temp_databaseusing theDROP DATABASEstatement.
In this tutorial, you’ve learned various statements to manage databases in MySQL including creating a new database, removing an existing database, selecting a database to work with, and displaying all databases in a MySQL database server.

