A2-02-23.DML- MySQL INTERSECT
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-intersect/
MySQL INTERSECT
Summary: in this tutorial, we will introduce you to the SQL INTERSECT operator and show you how to simulate the MySQL INTERSECT operator.
Introduction to the SQL INTERSECT operator
The INTERSECT operator is a set operator that returns only distinct rows of two queries or more queries.
The following illustrates the syntax of the INTERSECT operator.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
(SELECT column_list
FROM table_1)
INTERSECT
(SELECT column_list
FROM table_2);
|
The INTERSECT operator compares the result of two queries and returns the distinct rows that are output by both left and right queries.
To use the INTERSECT operator for two queries, the following rules are applied:
- The order and the number of columns must be the same.
- The data types of the corresponding columns must be compatible.
The following diagram illustrates the INTERSECT operator.
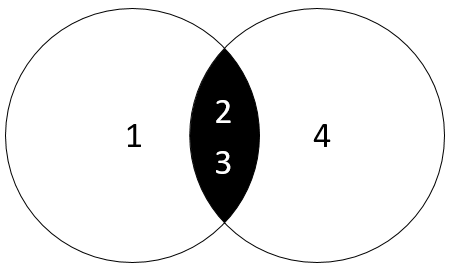
The left query produces a result set of (1,2,3).
The right query returns a result set of (2,3,4).
The INTERSECT operator returns the distinct rows of both result sets which include (2,3).
Unlike the UNION operator, the INTERSECT operator returns the intersection between two circles.
Note that SQL standard has three set operators that include UNION, INTERSECT, and MINUS.
MySQL INTERSECT simulation
Unfortunately, MySQL does not support the INTERSECT operator. However, you can simulate the INTERSECT operator.
Let’s create some sample data for the demonstration.
The following statements create tables t1 and t2, and then insert data into both tables.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
CREATE TABLE t1 (
id INT PRIMARY KEY
);
CREATE TABLE t2 LIKE t1;
INSERT INTO t1(id) VALUES(1),(2),(3);
INSERT INTO t2(id) VALUES(2),(3),(4);
|
The following query returns rows from the t1 table .
|
1
2
|
SELECT id
FROM t1;
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
id
----
1
2
3
|
The following query returns the rows from the t2 table:
|
1
2
|
SELECT id
FROM t2;
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
id
---
2
3
4
|
Simulate MySQL INTERSECT operator using DISTINCT operator and INNER JOIN clause.
The following statement uses DISTINCT operator and INNER JOIN clause to return the distinct rows in both tables:
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT DISTINCT
id
FROM t1
INNER JOIN t2 USING(id);
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
id
----
2
3
|
How it works.
- The
INNER JOINclause returns rows from both left and right tables. - The
DISTINCToperator removes the duplicate rows.
Simulate MySQL INTERSECT operator using IN operator and subquery
The following statement uses the IN operator and a subquery to return the intersection of the two result sets.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
SELECT DISTINCT
id
FROM
t1
WHERE
id IN (SELECT
id
FROM
t2);
|
|
1
2
3
4
|
id
----
2
3
|
How it works.
- The subquery returns the first result set.
- The outer query uses the IN operator to select only values that are in the first result set. The
DISTINCToperator ensures that only distinct values are selected.
In this tutorial, you have learned a couple of ways to simulate the INTERSECT operator in MySQL.

