A2-02-17.DML-MySQL Self Join
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-self-join/
MySQL Self Join
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL self join that joins a table to itself using join statement.
In the previous tutorials, you have learned how to join a table to the other tables using INNER JOIN, LEFT JOINor CROSS JOIN clause. However, there is a special case that you need join a table to itself, which is known as self join.
You use the self join when you want to combine rows with other rows in the same table. To perform the self join operation, you must use a table alias to help MySQL distinguish the left table from the right table of the same table in a single query.
MySQL self join examples
Let’s take a look at the employees table in the sample database.
In the employees table, we store not only employees data but also organization structure data. The reportsto column is used to determine the manager id of an employee.
To get the whole organization structure, you can join the employees table to itself using the employeeNumber and reportsTo columns. The employees table has two roles: one is Manager and the other is Direct Reports.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
SELECT
CONCAT(m.lastname, ', ', m.firstname) AS 'Manager',
CONCAT(e.lastname, ', ', e.firstname) AS 'Direct report'
FROM
employees e
INNER JOIN
employees m ON m.employeeNumber = e.reportsto
ORDER BY manager;
|
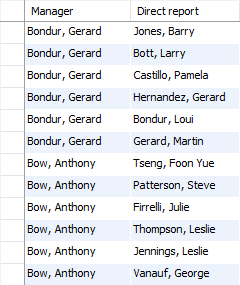
In the above output, you see only employees who have a manager. However, you don’t see the top manager because his name is filtered out due to the INNER JOIN clause. The top manager is the employee who does not have any manager or his manager no is NULL .
Let’s change the INNER JOIN clause to the LEFT JOIN clause in the query above to include the top manager. You also need to use the IFNULL function to display the top manager if the manger’s name is NULL .
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
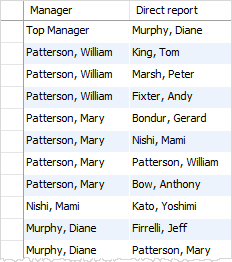
SELECT
IFNULL(CONCAT(m.lastname, ', ', m.firstname),
'Top Manager') AS 'Manager',
CONCAT(e.lastname, ', ', e.firstname) AS 'Direct report'
FROM
employees e
LEFT JOIN
employees m ON m.employeeNumber = e.reportsto
ORDER BY manager DESC;
|
By using the MySQL self join, you can display a list of customers who locate in the same city by joining the customers table to itself.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
SELECT
c1.city, c1.customerName, c2.customerName
FROM
customers c1
INNER JOIN
customers c2 ON c1.city = c2.city
AND c1.customername > c2.customerName
ORDER BY c1.city;
|
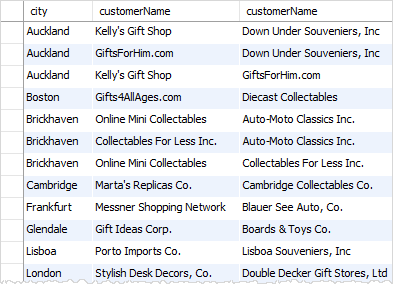
We joined the customers table to itself with the following join conditions:
c1.city = c2.cityto make sure that both customers have the same cityc.customerName > c2.customerNameto ensure that we don’t get the same customer.
In this tutorial, we have introduced you to MySQL self join that allows you to join a table to itself by using INNER JOIN or LEFT JOIN clauses.


