A2-02-10.DML-MySQL ORDER BY: Sort a Result Set
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-order-by/
MySQL ORDER BY: Sort a Result Set
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to sort a result set using MySQL ORDER BY clause.
Introduction to MySQL ORDER BY clause
When you use the SELECT statement to query data from a table, the result set is not sorted in any orders. To sort the result set, you use the ORDER BY clause. The ORDER BY clause allows you to:
- Sort a result set by a single column or multiple columns.
- Sort a result set by different columns in ascending or descending order.
The following illustrates the syntax of the ORDER BY clause:
|
1
2
3
|
SELECT column1, column2,...
FROM tbl
ORDER BY column1 [ASC|DESC], column2 [ASC|DESC],...
|
The ASC stands for ascending and the DESC stands for descending. By default, the ORDER BY clause sorts the result set in ascending order if you don’t specify ASC or DESC explicitly.
Let’s practice with some examples of using the ORDER BY clause.
MySQL ORDER BY examples
See the following customers table in the sample database.

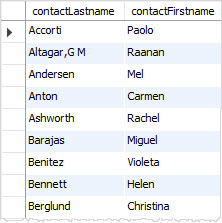
The following query selects contacts from the customers table and sorts the contacts by last name in ascending order.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT
contactLastname,
contactFirstname
FROM
customers
ORDER BY
contactLastname;
|
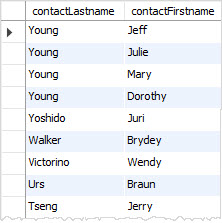
If you want to sort the contacts by last name in descending order, you specify the DESC after the contactLastname column in the ORDER BY clause as the following query:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT
contactLastname,
contactFirstname
FROM
customers
ORDER BY
contactLastname DESC;
|
If you want to sort the contacts by the last name in descending order and the first name in ascending order, you specify both DESC and ASC in the corresponding column as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
SELECT
contactLastname,
contactFirstname
FROM
customers
ORDER BY
contactLastname DESC,
contactFirstname ASC;
|
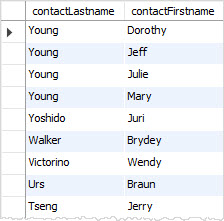
In the query above, the ORDER BY clause sorts the result set by the last name in descending order first and then sorts the sorted result set by the first name in ascending order to produce the final result set.
MySQL ORDER BY sort by an expression example
The ORDER BY clause also allows you to sort the result set based on an expression.
See the following orderdetails table.

The following query selects the order line items from the orderdetails table. It calculates the subtotal for each line item and sorts the result set based on the order number, order line number, and subtotal.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
SELECT
ordernumber,
orderlinenumber,
quantityOrdered * priceEach
FROM
orderdetails
ORDER BY
ordernumber,
orderLineNumber,
quantityOrdered * priceEach;
|

To make the query more readable, you can sort by the column alias as the following query:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
SELECT
ordernumber,
orderlinenumber,
quantityOrdered * priceEach AS subtotal
FROM
orderdetails
ORDER BY
ordernumber,
orderLineNumber,
subtotal;
|

We used subtotal as the column alias for the expression quantityOrdered * priceEach and sorted the result set based on the subtotal alias.
MySQL ORDER BY with custom sort order
The ORDER BY clause enables you to define your own custom sort order for the values in a column using the FIELD() function.
See the following orders table.
For example, if you want to sort the orders based on the following status by the following order:
- In Process
- On Hold
- Cancelled
- Resolved
- Disputed
- Shipped
You can use the FIELD function to map those values to a list of numeric values and use the numbers for sorting; See the following query:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
SELECT
orderNumber, status
FROM
orders
ORDER BY FIELD(status,
'In Process',
'On Hold',
'Cancelled',
'Resolved',
'Disputed',
'Shipped');
|
In this tutorial, we’ve shown you various techniques to sort a result set by using the MySQL ORDER BY clause.

