A2-02-05.DML-MySQL OR Operator
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-or/
MySQL OR Operator
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use the MySQL OR operator to combine Boolean expressions for filtering data.
Introduction to the MySQL OR operator
The MySQL OR operator combines two Boolean expressions and returns true when either condition is true.
The following illustrates the syntax of the OR operator.
|
1
|
boolean_expression_1 OR boolean_expression_2
|
Both boolean_expression_1 and boolean_expression_2 are Boolean expressions that return true, false, or NULL.
The following table shows the result of the OR operator.
| TRUE | FALSE | NULL | |
| TRUE | TRUE | TRUE | TRUE |
| FALSE | TRUE | FALSE | NULL |
| NULL | TRUE | NULL | NULL |
MySQL OR short-circuit evaluation
MySQL uses short-circuit evaluation for the OR operator. In other words, MySQL stops evaluating the remaining parts of the statement when it can determine the result.
See the following example.
|
1
|
SELECT 1 = 1 OR 1 / 0;
|
|
1
2
3
|
1 = 1 OR 1 / 0
--------------
1
|
Because the expression 1 = 1 always returns true, MySQL does not evaluate the 1 / 0. If it did, it would issue an error because of the division by zero error.
Operator precedence
When you use more than one logical operator in an expression, MySQL evaluates the OR operators after the AND operators. This is called operator precedence.
The operator precedence determines the order of evaluation of the operators. MySQL evaluates the operator with the higher precedence first.
See the following example.
|
1
|
SELECT true OR false AND false;
|
|
1
2
3
|
true OR false AND false
-----------------------
1
|
How it works
- First, MySQL evaluates the AND operator, therefore the expression
false AND falsereturns false. - Second, MySQL evaluates the OR operator hence the expression
true OR falsereturns true.
To change the order of evaluation, you use the parentheses, for example:
|
1
|
SELECT (true OR false) AND false;
|
|
1
2
3
|
(true OR false) AND false
-------------------------
0
|
How it works
- First, MySQL evaluates the expression in the parenthesis
(true OR false)returns true - Second, MySQL evaluates the remaining part of the statement,
true AND falsereturns false.
MySQL OR operator examples
We will use the customers table in the sample database for the demonstration.

For example, to get the customers who locate in the USA or France, you use the OR operator in the WHERE clause as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SELECT
customername, country
FROM
customers
WHERE
country = 'USA' OR country = 'France';
|
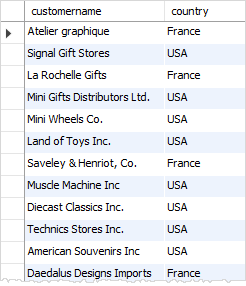
As you can see the result, the query returns customers who locate in either USA or France.
The following statement returns the customers who locate in the USA or France and have credit limit greater than 10000.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT
customername, country, creditLimit
FROM
customers
WHERE
(country = 'USA' OR country = 'France')
AND creditlimit > 100000;
|
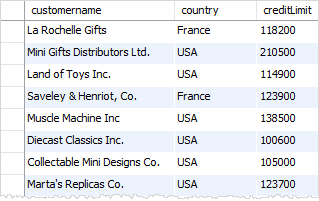
Notice that if you do not use the parentheses, the query will return the customers who locate in the USA or the customers who locate in France with the credit limit greater than 10000.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SELECT
customername, country, creditLimit
FROM
customers
WHERE
country = 'USA' OR country = 'France' AND creditlimit > 100000;
|

In this tutorial, you have learned how to use the MySQL OR operator to combine Boolean expressions for filtering data.


