A2-02-03.DML- Filter Rows Using MySQL WHERE
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-where/
Filter Rows Using MySQL WHERE
Summary: you will learn how to use MySQL WHERE clause in the SELECT statement to filter rows in the result set.
Introduction to MySQL WHERE clause
If you use the SELECT statement to query the data from tables without the WHERE clause, you will get all rows in the tables that may be not necessary. The tables accumulate data from business transactions all times. It does not make sense to get all rows from a table especially for big tables like employees, sales orders, purchase orders, production orders, etc., because we often want to analyze a set of data at a time e.g, sales of this quarter, sales of this year compared to last year, etc.
The WHERE clause allows you to specify exact rows to select based on a particular filtering expression or condition.
You will also learn how to use LIMIT clause to constrain the number of rows returned by the SELECTstatement.
MySQL WHERE clause examples
We will continue with the employees table data in the sample database as shown in the picture below.
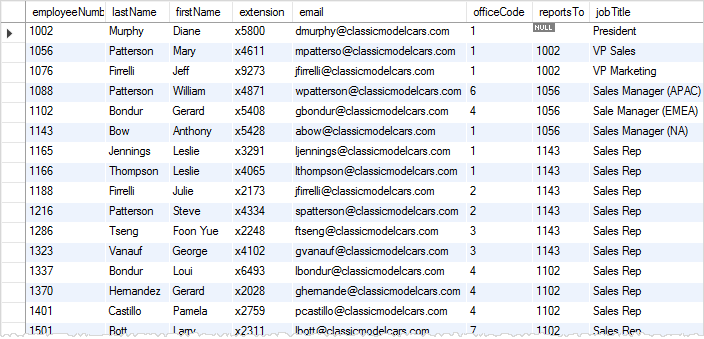
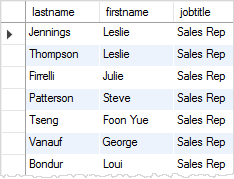
Suppose, we just want to get sales rep employees from the employees table, we use the following query:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SELECT
lastname, firstname, jobtitle
FROM
employees
WHERE
jobtitle = 'Sales Rep';
|

Even though the WHERE clause appears at the end of the statement, MySQL evaluates the expression in the WHERE clause first to select the matching rows. It chooses the rows that have job title as Sales Rep
|
1
|
jobtitle = 'Sales Rep';
|
MySQL then selects the columns from the selection list in the SELECT clause. The highlighted area contains the columns and rows in the final result set.
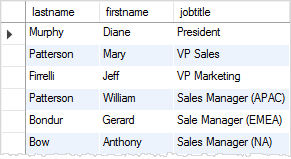
You can form a simple condition like the query above, or a very complex one that combines multiple expressions with logical operators such as AND, OR, etc. For example, to find all sales rep in the office code 1, you use the following query:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SELECT
lastname, firstname, jobtitle
FROM
employees
WHERE
jobtitle = 'Sales Rep' AND officeCode = 1;
|

The following table lists the comparison operators that you can use to form filtering expressions in the WHERE clause.
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Equal to. You can use it with almost any data types. |
| <> or != | Not equal to. |
| < | Less than. You typically use it with numeric and date/time data types. |
| > | Greater than. |
| <= | Less than or equal to |
| >= | Greater than or equal to |
The following query uses the not equal to operator to get all employees who are not the sales rep:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SELECT
lastname, firstname, jobtitle
FROM
employees
WHERE
jobtitle <> 'Sales Rep';
|
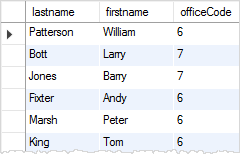
The following query gets every employee that have office code is greater than 5:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
SELECT
lastname, firstname, officeCode
FROM
employees
WHERE officecode > 5;
|
What about employee with office code less than or equal 4 (<=4):
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
SELECT
lastname, firstname, officeCode
FROM
employees
WHERE officecode <= 4;
|
More on MySQL WHERE clause…
There are also some useful operators that you can use in the WHERE clause to form complex conditions such as:
- BETWEEN selects values within a range of values.
- LIKE matches value based on pattern matching.
- IN specifies if the value matches any value in a list.
- IS NULL checks if the value is NULL.
The WHERE clause is used not only with the SELECT statement but also other SQL statements to filter rows such as DELETE and UPDATE.
In this tutorial, we’ve shown you how to use MySQL WHERE clause to filter rows based on conditions.

