A2-02-02.DML-Using MySQL DISTINCT to Eliminate Duplicates
转载自:http://www.mysqltutorial.org/mysql-distinct.aspx
Using MySQL DISTINCT to Eliminate Duplicates
Summary: in this tutorial, you will learn how to use MySQL DISTINCT clause with the SELECT statement to eliminate duplicate rows in a result set.
Introduction to MySQL DISTINCT clause
When querying data from a table, you may get duplicate rows. In order to remove these duplicate rows, you use the DISTINCT clause in the SELECT statement.
The syntax of using the DISTINCT clause is as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SELECT DISTINCT
columns
FROM
table_name
WHERE
where_conditions;
|
MySQL DISTINCT example
Let’s take a look a simple example of using the DISTINCT clause to select the unique last names of employees from the employees table.
First, we query the last names of employees from the employees table using the SELECT statement as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
SELECT
lastname
FROM
employees
ORDER BY lastname;
|
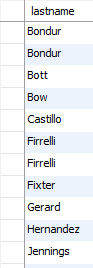
Some employees have the same last name Bondur,Firrelli etc.
To remove the duplicate last names, you add the DISTINCT clause to the SELECT statement as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
SELECT DISTINCT
lastname
FROM
employees
ORDER BY lastname;
|
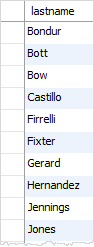
The duplicate last names are eliminated in the result set when we used the DISTINCT clause.
MySQL DISTINCT and NULL values
If a column has NULL values and you use the DISTINCT clause for that column, MySQL keeps one NULLvalue and eliminates the other because the DISTINCT clause treats all NULL values as the same value.
For example, in the customers table, we have many rows whose state column has NULL values. When we use the DISTINCT clause to query the customers’ states, we will see unique states and a NULL value as the following query:
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT DISTINCT
state
FROM
customers;
|
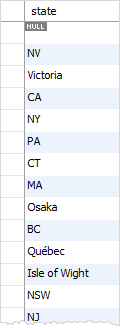
MySQL DISTINCT with multiple columns
You can use the DISTINCT clause with more than one column. In this case, MySQL uses the combination of all columns to determine the uniqueness of the row in the result set.
For example, to get the unique combination of city and state from the customers table, you use the following query:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT DISTINCT
state, city
FROM
customers
WHERE
state IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY state , city;
|
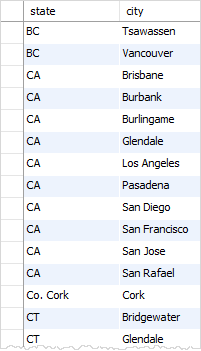
Without the DISTINCT clause, you will get the duplicate combination of state and city as follows:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT
state, city
FROM
customers
WHERE
state IS NOT NULL
ORDER BY state , city;
|
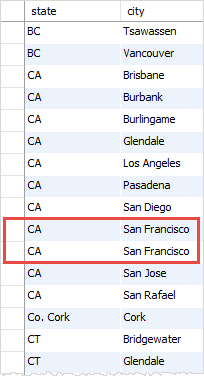
DISTINCT clause vs. GROUP BY clause
If you use the GROUP BY clause in the SELECT statement without using aggregate functions, the GROUP BY clause behaves like the DISTINCT clause.
The following statement uses the GROUP BY clause to select the unique states of customers from the customers table.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
SELECT
state
FROM
customers
GROUP BY state;
|
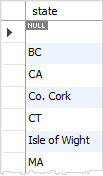
You can achieve the similar result by using the DISTINCT clause:
|
1
2
3
4
|
SELECT DISTINCT
state
FROM
customers;
|
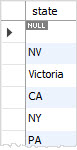
Generally speaking, the DISTINCT clause is a special case of the GROUP BY clause. The difference between DISTINCT clause and GROUP BY clause is that the GROUP BY clause sorts the result set whereas the DISTINCT clause does not.
If you add the ORDER BY clause to the statement that uses the DISTINCT clause, the result set is sorted and it is the same as the one returned by the statement that uses GROUP BY clause.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
SELECT DISTINCT
state
FROM
customers
ORDER BY state;
|
MySQL DISTINCT and aggregate function
You can use the DISTINCT clause with an aggregate function e.g., SUM, AVG, and COUNT, to remove duplicate rows before MySQL applies the aggregate function to the result set.
For example, to count the unique states of customers in the U.S., you use the following query:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
SELECT
COUNT(DISTINCT state)
FROM
customers
WHERE
country = 'USA';
|
![]()
MySQL DISTINCT with LIMIT clause
In case you use the DISTINCT clause with the LIMIT clause, MySQL stops searching immediately when it finds the number of unique rows specified in the LIMIT clause.
The following query selects the first 5 non-null unique states in the customers table.
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
SELECT DISTINCT
state
FROM
customers
WHERE
state IS NOT NULL
LIMIT 5;
|
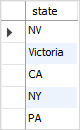
In this tutorial, we have shown you various ways of using MySQL DISTINCT clause such as eliminating duplicate rows and counting non-NULL values.


