java基础1(二)
Bean的xml配置
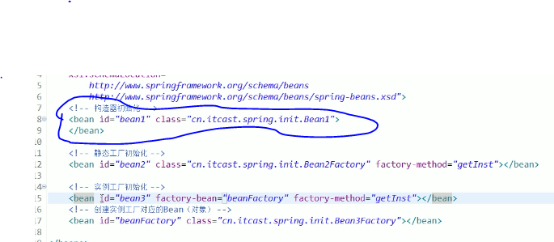
1.bean的初始化方式
三种方式: 默认构造器,静态工厂初始化(了解)和实例工厂初始化(了解)

2.springbean的作用域
Bean默认作用域是单实例的
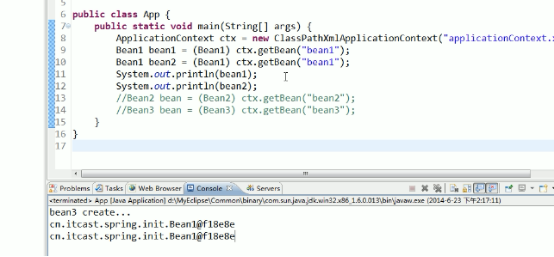
可以设置非单实例

作用域介绍:

比如:将作用域设置request时,原理是在request对象创建好后调用,request.setAttribute(“bean4”,ctx.getBean(“bean4”))。

Bean的生命周期

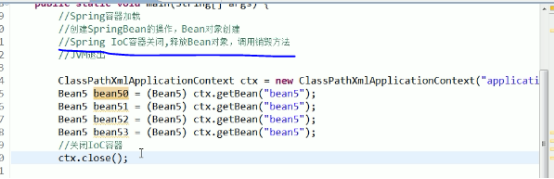
注意: spring的bean容器关闭后才会调用销毁方法。
2.Bean的属性注入
两种方式: 构造器注入和属性注入

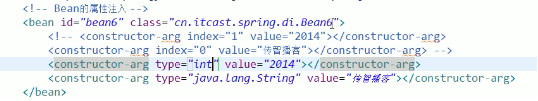
1) 构造器注入
配置文件
Java类

- bean的初始化使用有参数构造器时,需要同时给属性赋值,这时就叫做bean的属性注入,bean的初始化方式还是构造方法
2)setter注入

配置实例

复杂属性注入
- list注入
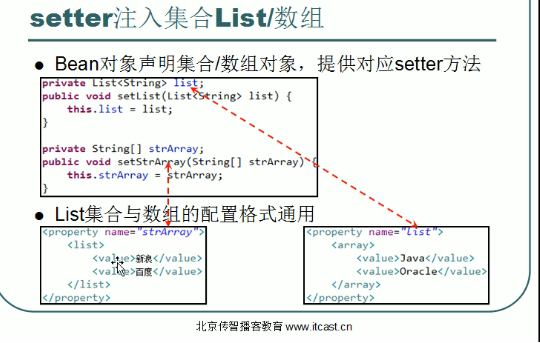
2.map属性注入
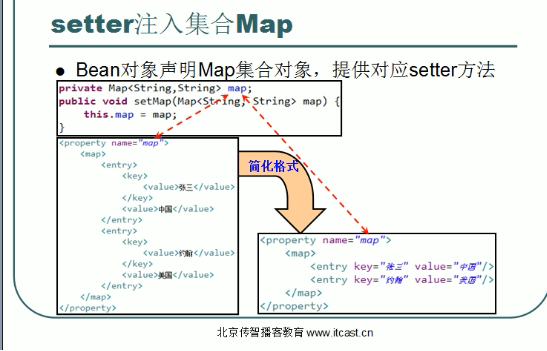
Property注入

3)团队开发

Bean的注解配置
@Autowired和qualifier(“”)注解可以使用Resource替代.


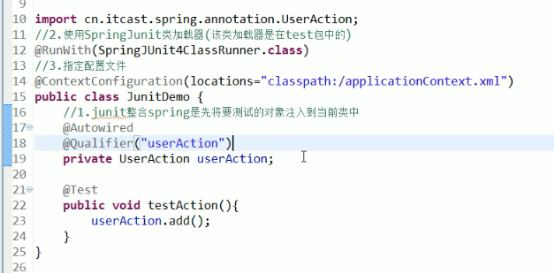
Spring整合junit
Classpath: 指定项目的根路径
@RunWith: 使用springJunit类加载器
@ContextConfiguration: 指定配置文件
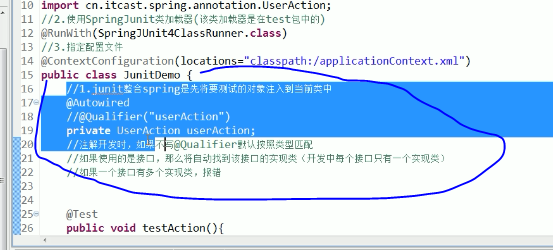
注意: @Autowired根据类型自动注入,如果类型是接口,那么会默认找到实现类.如果有多个实现类则会抱错
AOP



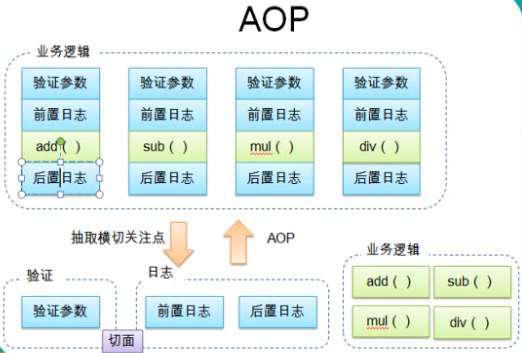
aop代码实例
1)applicationContext-aop.xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 自动扫描的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.aop"></context:component-scan> <!-- 使 AspectJ 的注解起作用 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> </beans>
2)LoggingAspect.java类

package com.atguigu.spring.aop; import java.util.Arrays; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * AOP 的 helloWorld * 1. 加入 jar 包 * com.springsource.net.sf.cglib-2.2.0.jar * com.springsource.org.aopalliance-1.0.0.jar * com.springsource.org.aspectj.weaver-1.6.8.RELEASE.jar * spring-aspects-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar * * 2. 在 Spring 的配置文件中加入 aop 的命名空间。 * * 3. 基于注解的方式来使用 AOP * 3.1 在配置文件中配置自动扫描的包: <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.aop"></context:component-scan> * 3.2 加入使 AspjectJ 注解起作用的配置: <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> * 为匹配的类自动生成动态代理对象. * * 4. 编写切面类: * 4.1 一个一般的 Java 类 * 4.2 在其中添加要额外实现的功能. * * 5. 配置切面 * 5.1 切面必须是 IOC 中的 bean: 实际添加了 @Component 注解 * 5.2 声明是一个切面: 添加 @Aspect * 5.3 声明通知: 即额外加入功能对应的方法. * 5.3.1 前置通知: @Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))") * @Before 表示在目标方法执行之前执行 @Before 标记的方法的方法体. * @Before 里面的是切入点表达式: * * 6. 在通知中访问连接细节: 可以在通知方法中添加 JoinPoint 类型的参数, 从中可以访问到方法的签名和方法的参数. * * 7. @After 表示后置通知: 在方法执行之后执行的代码. */ //通过添加 @Aspect 注解声明一个 bean 是一个切面! @Aspect @Component public class LoggingAspect { //切面方法针对那些方法使用切面,@Before前置通知 @Before("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(int, int))") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(args)); } @After("execution(* com.atguigu.spring.aop.*.*(..))") public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends"); } }
3)main.java执行类

package com.atguigu.spring.aop; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { // ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = new ArithmeticCalculatorImpl(); // // arithmeticCalculator = // new ArithmeticCalculatorLoggingProxy(arithmeticCalculator).getLoggingProxy(); // // int result = arithmeticCalculator.add(11, 12); // System.out.println("result:" + result); // // result = arithmeticCalculator.div(21, 3); // System.out.println("result:" + result); ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext-aop.xml"); ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator"); System.out.println(arithmeticCalculator.getClass().getName()); int result = arithmeticCalculator.add(11, 12); System.out.println("result:" + result); result = arithmeticCalculator.div(21, 3); System.out.println("result:" + result); } }
效果如下图:

前置通知:

方法签名:


注解声明切面实例:
1.applicationContext.xml文件

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <!-- 配置自动扫描的包 --> <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring.aop"></context:component-scan> <!-- 配置自动为匹配 aspectJ 注解的 Java 类生成代理对象 --> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> </beans>
2.定义类日志切面

package com.atguigu.spring.aop; import java.util.Arrays; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; /** * 可以使用 @Order 注解指定切面的优先级, 值越小优先级越高 */ @Order(2) @Aspect @Component public class LoggingAspect { /** * 定义一个方法, 用于声明切入点表达式. 一般地, 该方法中再不需要添入其他的代码. * 使用 @Pointcut 来声明切入点表达式. * 后面的其他通知直接使用方法名来引用当前的切入点表达式. */ @Pointcut("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))") public void declareJointPointExpression(){} /** * 在 com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator 接口的每一个实现类的每一个方法开始之前执行一段代码 */ @Before("declareJointPointExpression()") public void beforeMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); Object [] args = joinPoint.getArgs(); System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(args)); } /** * 在方法执行之后执行的代码. 无论该方法是否出现异常 */ @After("declareJointPointExpression()") public void afterMethod(JoinPoint joinPoint){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends"); } /** * 在方法法正常结束受执行的代码 * 返回通知是可以访问到方法的返回值的! */ @AfterReturning(value="declareJointPointExpression()", returning="result") public void afterReturning(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends with " + result); } /** * 在目标方法出现异常时会执行的代码. * 可以访问到异常对象; 且可以指定在出现特定异常时在执行通知代码 */ @AfterThrowing(value="declareJointPointExpression()", throwing="e") public void afterThrowing(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception e){ String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName(); System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " occurs excetion:" + e); } /** * 环绕通知需要携带 ProceedingJoinPoint 类型的参数. * 环绕通知类似于动态代理的全过程: ProceedingJoinPoint 类型的参数可以决定是否执行目标方法. * 且环绕通知必须有返回值, 返回值即为目标方法的返回值 */ /* @Around("execution(public int com.atguigu.spring.aop.ArithmeticCalculator.*(..))") public Object aroundMethod(ProceedingJoinPoint pjd){ Object result = null; String methodName = pjd.getSignature().getName(); try { //前置通知 System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " begins with " + Arrays.asList(pjd.getArgs())); //执行目标方法 result = pjd.proceed(); //返回通知 System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends with " + result); } catch (Throwable e) { //异常通知 System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " occurs exception:" + e); throw new RuntimeException(e); } //后置通知 System.out.println("The method " + methodName + " ends"); return result; } */ }
3.定义校验切面

package com.atguigu.spring.aop; import java.util.Arrays; import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Order(1) @Aspect @Component public class VlidationAspect { @Before("com.atguigu.spring.aop.LoggingAspect.declareJointPointExpression()") public void validateArgs(JoinPoint joinPoint){ System.out.println("-->validate:" + Arrays.asList(joinPoint.getArgs())); } }
4.arithmeticCalculator类

package com.atguigu.spring.aop; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component("arithmeticCalculator") public class ArithmeticCalculatorImpl implements ArithmeticCalculator { @Override public int add(int i, int j) { int result = i + j; return result; } @Override public int sub(int i, int j) { int result = i - j; return result; } @Override public int mul(int i, int j) { int result = i * j; return result; } @Override public int div(int i, int j) { int result = i / j; return result; } }
5.Main.java类

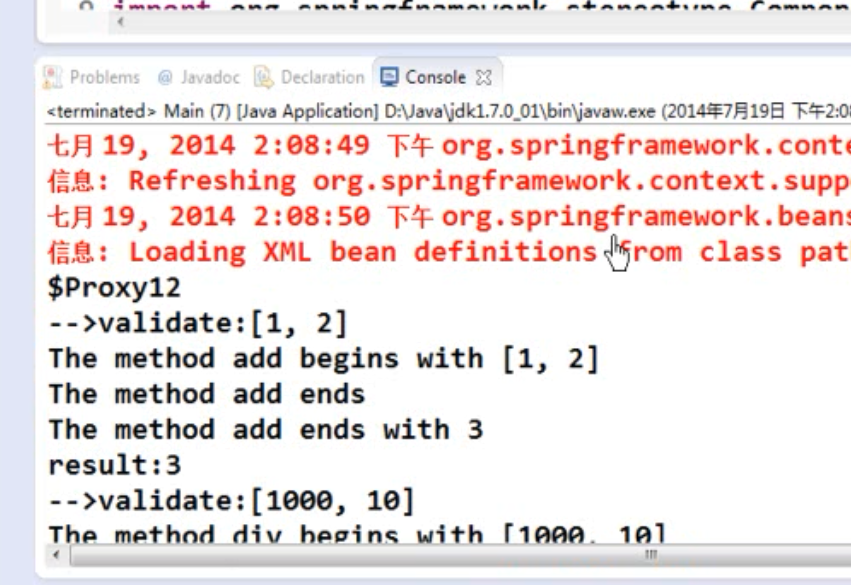
package com.atguigu.spring.aop; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; public class Main { public static void main(String[] args) { ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml"); ArithmeticCalculator arithmeticCalculator = (ArithmeticCalculator) ctx.getBean("arithmeticCalculator"); System.out.println(arithmeticCalculator.getClass().getName()); int result = arithmeticCalculator.add(1, 2); System.out.println("result:" + result); result = arithmeticCalculator.div(1000, 10); System.out.println("result:" + result); } }
方法执行截图:
spring声明式事务
xml文件:

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-4.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring"></context:component-scan> <!-- 导入资源文件 --> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"/> <!-- 配置 C3P0 数据源 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"></property> <property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.jdbcUrl}"></property> <property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driverClass}"></property> <property name="initialPoolSize" value="${jdbc.initPoolSize}"></property> <property name="maxPoolSize" value="${jdbc.maxPoolSize}"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置 Spirng 的 JdbcTemplate --> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 配置 NamedParameterJdbcTemplate, 该对象可以使用具名参数, 其没有无参数的构造器, 所以必须为其构造器指定参数 --> <bean id="namedParameterJdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.namedparam.NamedParameterJdbcTemplate"> <constructor-arg ref="dataSource"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!-- 配置事务管理器 --> <bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> <!-- 启用事务注解 --> <tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/> </beans>
代码如下:
package com.atguigu.spring.tx; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation; import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional; @Service("bookShopService") public class BookShopServiceImpl implements BookShopService { @Autowired private BookShopDao bookShopDao; //添加事务注解 //1.使用 propagation 指定事务的传播行为, 即当前的事务方法被另外一个事务方法调用时 //如何使用事务, 默认取值为 REQUIRED, 即使用调用方法的事务 //REQUIRES_NEW: 事务自己的事务, 调用的事务方法的事务被挂起. //2.使用 isolation 指定事务的隔离级别, 最常用的取值为 READ_COMMITTED //3.默认情况下 Spring 的声明式事务对所有的运行时异常进行回滚. 也可以通过对应的 //属性进行设置. 通常情况下去默认值即可. //4.使用 readOnly 指定事务是否为只读. 表示这个事务只读取数据但不更新数据, //这样可以帮助数据库引擎优化事务. 若真的事一个只读取数据库值的方法, 应设置 readOnly=true //5.使用 timeout 指定强制回滚之前事务可以占用的时间. // @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW, // isolation=Isolation.READ_COMMITTED, // noRollbackFor={UserAccountException.class}) @Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW, isolation=Isolation.READ_COMMITTED, readOnly=false, timeout=3) @Override public void purchase(String username, String isbn) { try { Thread.sleep(5000); } catch (InterruptedException e) {} //1. 获取书的单价 int price = bookShopDao.findBookPriceByIsbn(isbn); //2. 更新数的库存 bookShopDao.updateBookStock(isbn); //3. 更新用户余额 bookShopDao.updateUserAccount(username, price); } }
事务传播行为


在web中应该怎么使用spring
1.思路整理
1. Spring 如何在 WEB 应用中使用 ?
1). 需要额外加入的 jar 包:
spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
spring-webmvc-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar
2). Spring 的配置文件, 没有什么不同
3). 如何创建 IOC 容器 ?
①. 非 WEB 应用在 main 方法中直接创建
②. 应该在 WEB 应用被服务器加载时就创建 IOC 容器:
在 ServletContextListener#contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) 方法中创建 IOC 容器.
③. 在 WEB 应用的其他组件中如何来访问 IOC 容器呢 ?
在 ServletContextListener#contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) 方法中创建 IOC 容器后, 可以把其放在
ServletContext(即 application 域)的一个属性中.
④. 实际上, Spring 配置文件的名字和位置应该也是可配置的! 将其配置到当前 WEB 应用的初始化参数中较为合适.
2. Spring 如何整合 Struts2 ?
2.web.xml配置

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5"> <!--配置servletContext的初始化参数--> <context-param> <param-name>configLocation</param-name> <param-value>applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!--配置servletContext监听器,用于初始化ioc容器--> <listener> <listener-class>com.atguigu.spring.struts2.listeners.SpringServletContextListener</listener-class> </listener> <!--配置servletContext--> <servlet> <description></description> <display-name>TestServlet</display-name> <servlet-name>TestServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>com.atguigu.spring.struts2.servlets.TestServlet</servlet-class> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>TestServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/TestServlet</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app>
3.SpringServletContextListener

package com.atguigu.spring.struts2.listeners; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent; import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext; /** * Application Lifecycle Listener implementation class SpringServletContextListener * */ public class SpringServletContextListener implements ServletContextListener { /** * Default constructor. */ public SpringServletContextListener() { // TODO Auto-generated constructor stub } /** * @see ServletContextListener#contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent) */ public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent arg0) { //1. 获取 Spring 配置文件的名称. ServletContext servletContext = arg0.getServletContext(); String config = servletContext.getInitParameter("configLocation"); //1. 创建 IOC 容器 ApplicationContext ctx = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(config); //2. 把 IOC 容器放在 ServletContext 的一个属性中. servletContext.setAttribute("ApplicationContext", ctx); } /** * @see ServletContextListener#contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent) */ public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent arg0) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub } }
4.applicationContext.xml

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="person" class="com.atguigu.spring.struts2.beans.Person"> <property name="username" value="atguigu"></property> </bean> </beans>
5.testservelt.java ---测试类

package com.atguigu.spring.struts2.servlets; import java.io.IOException; import javax.servlet.ServletContext; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import com.atguigu.spring.struts2.beans.Person; /** * Servlet implementation class TestServlet */ public class TestServlet extends HttpServlet { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; /** * @see HttpServlet#doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) */ protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { //1. 从 application 域对象中得到 IOC 容器的引用 ServletContext servletContext = getServletContext(); ApplicationContext ctx = (ApplicationContext) servletContext.getAttribute("ApplicationContext"); //2. 从 IOC 容器中得到需要的 bean Person person = ctx.getBean(Person.class); person.hello(); } }
在web中使用spring
4). 在 WEB 环境下使用 Spring ①. 需要额外加入的 jar 包: spring-web-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar spring-webmvc-4.0.0.RELEASE.jar ②. Spring 的配置文件, 和非 WEB 环境没有什么不同 ③. 需要在 web.xml 文件中加入如下配置: <!-- 配置 Spring 配置文件的名称和位置 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!-- 启动 IOC 容器的 ServletContextListener --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener>
web.xml文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd" id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5"> <!-- 配置 Spring 配置文件的名称和位置 --> <context-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:applicationContext.xml</param-value> </context-param> <!-- 启动 IOC 容器的 ServletContextListener --> <listener> <listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class> </listener> <!-- 配置 Struts2 的 Filter --> <filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.ng.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping> </web-app>
Xml文件操作
Schema约束
w3c中http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance,这个是w3预定义的命名空间。客户可以根据这个名称空间创建自己的约束文档。就像w3定义了一个标准接口一样,实现这个接口可以具备自定义约束文档的能力,比如:<complexType>这个标签就是w3预定义的标签,用于客户实现自己的约束文档。用户做完自己的约束文档后就可以在实例文档中使用这个约束文档,创建对应的配置文件。
即定义自己的约束文档然后使用的过程是:
自定义约束文档: 引入w3预定义命名空间,使用其内的标签定义自己的约束标签。
实例文档: 引入预定义命名空间,引入自定义明明空间和位置。使用自定义标签进行配置,从而完成配置文件作用。

使用实例:
如下:
1)xmls引入自定义命名空间 2)xmlns:xsi:引入预定义命名空间 3)xsi:schemalocation:引入自定义空间位置
Xml解析


posted on 2019-03-31 11:46 zhulibin2012 阅读(133) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报




