《机器学习Python实现_10_11_集成学习_xgboost_回归的简单实现》
一.损失函数
这一节对xgboost回归做介绍,xgboost共实现了5种类型的回归,分别是squarederror、logistic、poisson、gamma、tweedie回归,下面主要对前两种进行推导实现,剩余三种放到下一节
squarederror
即损失函数为平方误差的回归模型:
\[L(y,\hat{y})=\frac{1}{2}(y-\hat{y})^2
\]
所以一阶导和二阶导分别为:
\[\frac{\partial L(y,\hat{y})}{\partial \hat{y}}=\hat{y}-y\\
\frac{\partial^2 L(y,\hat{y})}{{\partial \hat{y}}^2}=1.0\\
\]
logistic
由于是回归任务,所以y也要套上sigmoid函数(用\(\sigma(\cdot)\)表示),损失函数:
\[L(y,\hat{y})=(1-\sigma(y))log(1-\sigma(\hat{y}))+\sigma(y)log(\sigma(\hat{y}))
\]
一阶导和二阶导分别为:
\[\frac{\partial L(y,\hat{y})}{\partial \hat{y}}=\sigma(\hat{y})-\sigma(y)\\
\frac{\partial^2 L(y,\hat{y})}{{\partial \hat{y}}^2}=\sigma(\hat{y})(1-\sigma(\hat{y}))\\
\]
二.代码实现
具体流程与gbdt的回归类似,只是每次要计算一阶、二阶导数信息,同时基学习器要替换为上一节的xgboost回归树
import os
os.chdir('../')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
from ml_models.ensemble import XGBoostBaseTree
from ml_models import utils
import copy
import numpy as np
"""
xgboost回归树的实现,封装到ml_models.ensemble
"""
class XGBoostRegressor(object):
def __init__(self, base_estimator=None, n_estimators=10, learning_rate=1.0, loss='squarederror'):
"""
:param base_estimator: 基学习器
:param n_estimators: 基学习器迭代数量
:param learning_rate: 学习率,降低后续基学习器的权重,避免过拟合
:param loss:损失函数,支持squarederror、logistic
"""
self.base_estimator = base_estimator
self.n_estimators = n_estimators
self.learning_rate = learning_rate
if self.base_estimator is None:
# 默认使用决策树桩
self.base_estimator = XGBoostBaseTree()
# 同质分类器
if type(base_estimator) != list:
estimator = self.base_estimator
self.base_estimator = [copy.deepcopy(estimator) for _ in range(0, self.n_estimators)]
# 异质分类器
else:
self.n_estimators = len(self.base_estimator)
self.loss = loss
def _get_gradient_hess(self, y, y_pred):
"""
获取一阶、二阶导数信息
:param y:真实值
:param y_pred:预测值
:return:
"""
if self.loss == 'squarederror':
return y_pred - y, np.ones_like(y)
elif self.loss == 'logistic':
return utils.sigmoid(y_pred) - utils.sigmoid(y), utils.sigmoid(y_pred) * (1 - utils.sigmoid(y_pred))
def fit(self, x, y):
y_pred = np.zeros_like(y)
g, h = self._get_gradient_hess(y, y_pred)
for index in range(0, self.n_estimators):
self.base_estimator[index].fit(x, g, h)
y_pred += self.base_estimator[index].predict(x) * self.learning_rate
g, h = self._get_gradient_hess(y, y_pred)
def predict(self, x):
rst_np = np.sum(
[self.base_estimator[0].predict(x)] +
[self.learning_rate * self.base_estimator[i].predict(x) for i in
range(1, self.n_estimators - 1)] +
[self.base_estimator[self.n_estimators - 1].predict(x)]
, axis=0)
return rst_np
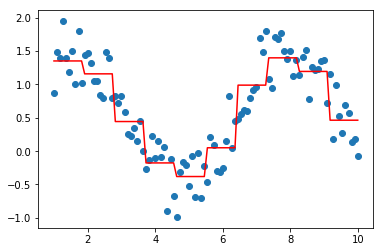
#测试
data = np.linspace(1, 10, num=100)
target = np.sin(data) + np.random.random(size=100) # 添加噪声
data = data.reshape((-1, 1))
model = XGBoostRegressor(loss='squarederror')
model.fit(data, target)
plt.scatter(data, target)
plt.plot(data, model.predict(data), color='r')
plt.show()
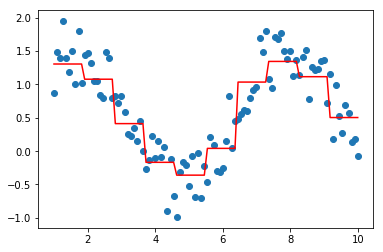
model = XGBoostRegressor(loss='logistic')
model.fit(data, target)
plt.scatter(data, target)
plt.plot(data, model.predict(data), color='r')
plt.show()
作者: 努力的番茄
出处: https://www.cnblogs.com/zhulei227/
关于作者:专注于机器学习、深度学习、强化学习、NLP等领域!
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出.


