JDBC操作事务
首先我们先用IDEA连接数据库
IDEA连接数据库
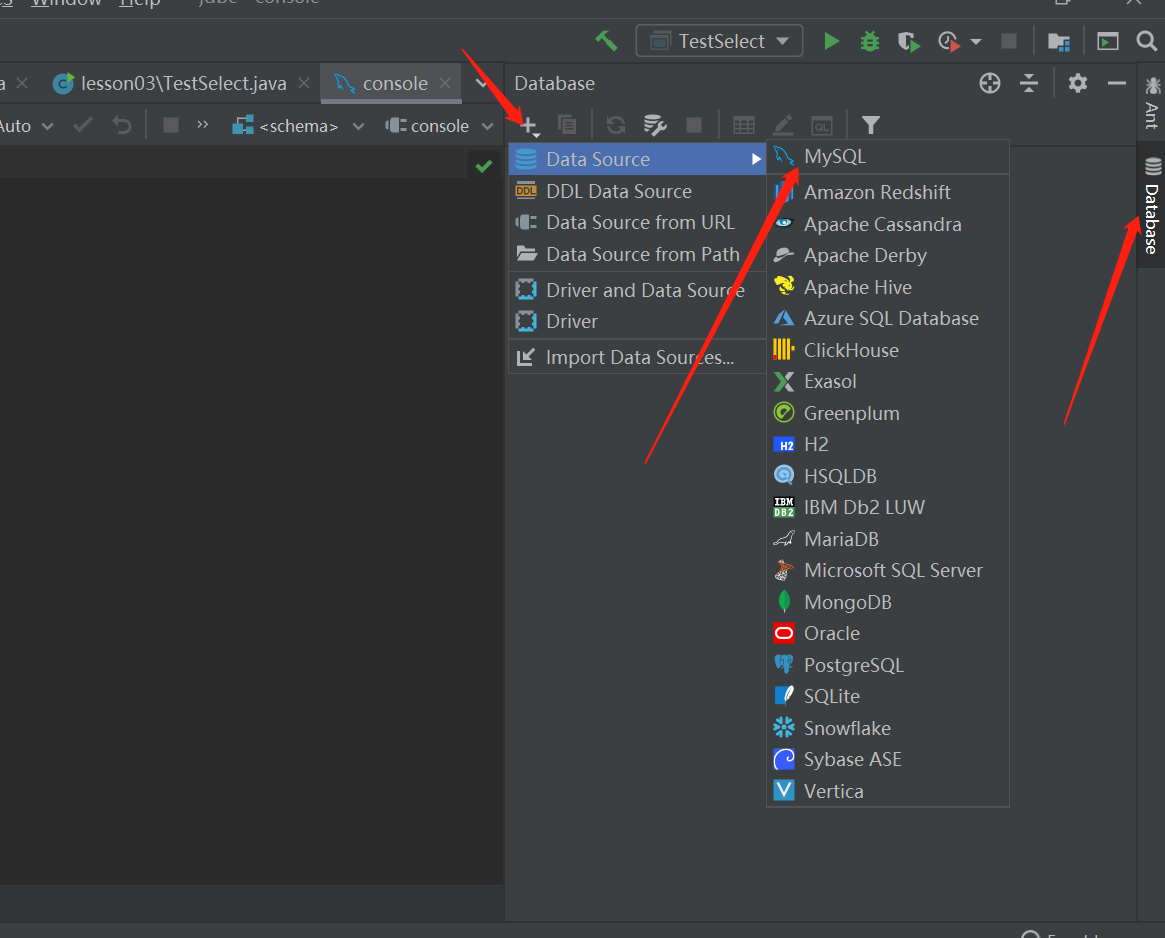
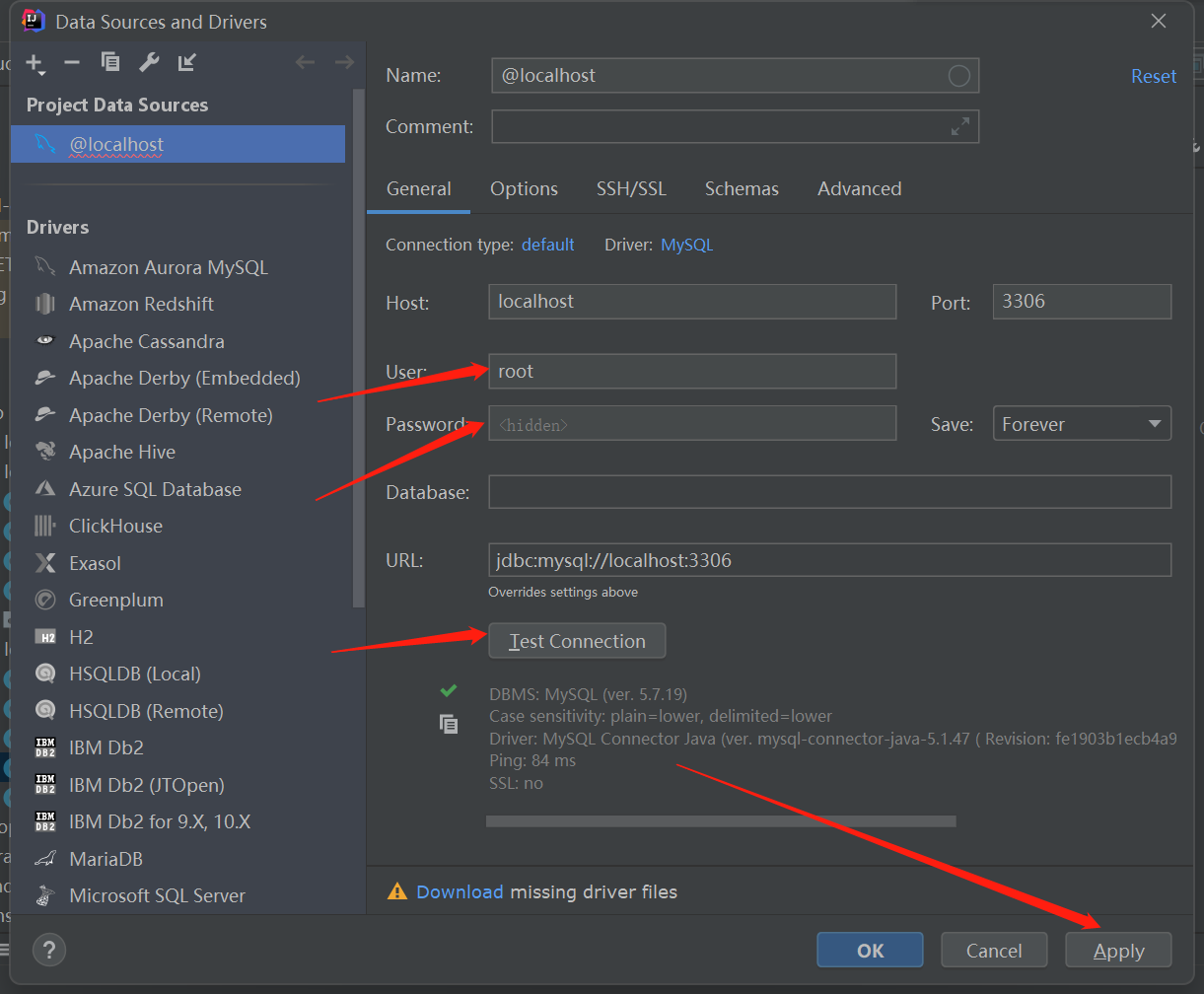
连接成功后可以选择数据库:
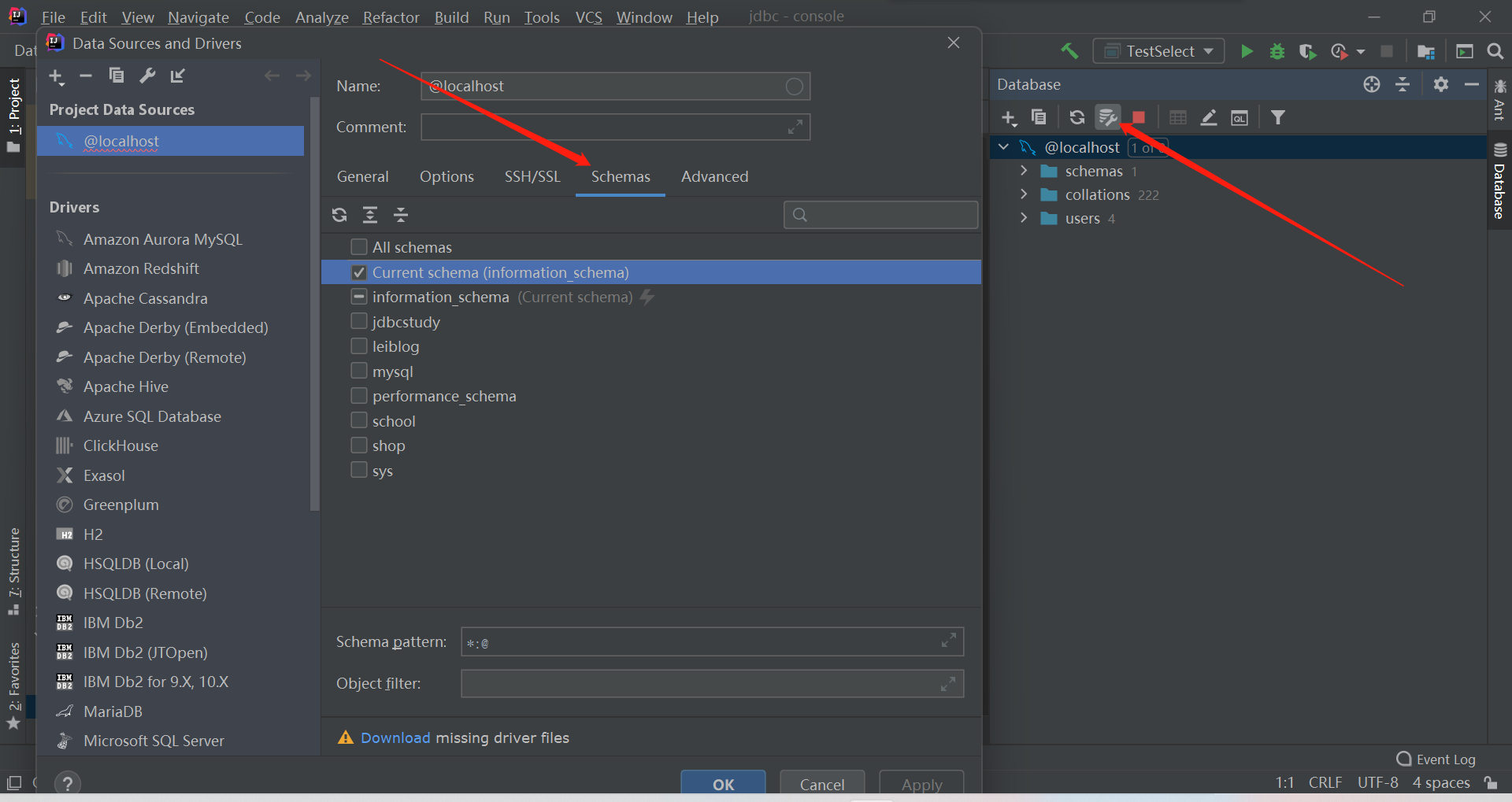
双击数据库,可进行一些操作

模拟转账成功:
public class TestTransaction1 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pst = null; ResultSet rs= null; try { conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //关闭数据库自动提交,自动会开启事务 conn.setAutoCommit(false); String sql1 = "update account set money = money-100 where name='A'"; pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql1); pst.executeUpdate(); String sql2 = "update account set money = money+100 where name='B'"; conn.prepareStatement(sql2); pst.executeUpdate(); //提交事务 conn.commit(); System.out.println("成功!"); } catch (SQLException e) { try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JdbcUtils.release(conn,pst,rs); } } }
模拟转账失败:
public class TestTransaction2 { public static void main(String[] args) { Connection conn = null; PreparedStatement pst = null; ResultSet rs= null; try { conn = JdbcUtils.getConnection(); //关闭数据库自动提交,自动会开启事务 conn.setAutoCommit(false); String sql1 = "update account set money = money-100 where name='A'"; pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql1); pst.executeUpdate(); int x =1/0;//报错 String sql2 = "update account set money = money+100 where name='B'"; conn.prepareStatement(sql2); pst.executeUpdate(); //提交事务 conn.commit(); System.out.println("成功!"); } catch (SQLException e) { try { conn.rollback(); } catch (SQLException e1) { e1.printStackTrace(); } e.printStackTrace(); }finally { JdbcUtils.release(conn,pst,rs); } } }






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 阿里最新开源QwQ-32B,效果媲美deepseek-r1满血版,部署成本又又又降低了!
· 开源Multi-agent AI智能体框架aevatar.ai,欢迎大家贡献代码
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧