springboot与swagger2的集成
springboot与swagger2的集成
1、出现的背景
随着互联网技术的发展,现在的网站架构基本都由原来的后端渲染变成了:前端渲染、先后端分离的形态,而前端和后端的唯一联系,变成了API接口;
API文档变成了前后端开发人员联系的纽带,变得越来越重要。包括app开发人员和后端直接的交流都是基于api文档。
手写接口文档
手写Api文档的几个痛点:
- 文档需要更新的时候,需要再次发送一份给前端,也就是文档更新交流不及时。
- 接口返回结果不明确
- 不能直接在线测试接口,通常需要使用工具,比如postman
- 接口文档太多,不好管理
- swagger就是一款让你更好的书写API文档的框架。
2、什么是swagger2
编写和维护接口文档是每个程序员的职责,根据Swagger2可以快速帮助我们编写最新的API接口文档,再也不用担心开会前仍忙于整理各种资料了,间接提升了团队开发的沟通效率。
3、swagger2常用注解:
swagger通过注解表明该接口会生成文档,包括接口名、请求方法、参数、返回信息的等等。
@Api:修饰整个类,描述Controller的作用
@ApiOperation:描述一个类的一个方法,或者说一个接口
@ApiParam:单个参数描述
@ApiModel:用对象来接收参数
@ApiProperty:用对象接收参数时,描述对象的一个字段
@ApiResponse:HTTP响应其中1个描述
@ApiResponses:HTTP响应整体描述
@ApiIgnore:使用该注解忽略这个API
@ApiError :发生错误返回的信息
@ApiImplicitParam:一个请求参数
@ApiImplicitParams:多个请求参数
@Api:用在请求的类上,表示对类的说明
tags="说明该类的作用,可以在UI界面上看到的注解"
value="该参数没什么意义,在UI界面上也看到,所以不需要配置"
@ApiOperation:用在请求的方法上,说明方法的用途、作用
value="说明方法的用途、作用"
notes="方法的备注说明"
@ApiImplicitParams:用在请求的方法上,表示一组参数说明
@ApiImplicitParam:用在@ApiImplicitParams注解中,指定一个请求参数的各个方面
name:参数名
value:参数的汉字说明、解释
required:参数是否必须传
paramType:参数放在哪个地方
· header --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestHeader
· query --> 请求参数的获取:@RequestParam
· path(用于restful接口)--> 请求参数的获取:@PathVariable
· body(不常用)
· form(不常用)
dataType:参数类型,默认String,其它值dataType="Integer"
defaultValue:参数的默认值
@ApiResponses:用在请求的方法上,表示一组响应
@ApiResponse:用在@ApiResponses中,一般用于表达一个错误的响应信息
code:数字,例如400
message:信息,例如"请求参数没填好"
response:抛出异常的类
@ApiModel:用于响应类上,表示一个返回响应数据的信息
(这种一般用在post创建的时候,使用@RequestBody这样的场景,
请求参数无法使用@ApiImplicitParam注解进行描述的时候)
@ApiModelProperty:用在属性上,描述响应类的属性
4、SpringBoot 集成 Swagger2
1)、第一步:导入pom
<!-- Swagger -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger-ui</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.springfox</groupId>
<artifactId>springfox-swagger2</artifactId>
<version>2.8.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- END Swagger -->
2)、编写SwaggerConfig.java配置类
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import springfox.documentation.builders.ApiInfoBuilder;
import springfox.documentation.builders.PathSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.builders.RequestHandlerSelectors;
import springfox.documentation.service.ApiInfo;
import springfox.documentation.spi.DocumentationType;
import springfox.documentation.spring.web.plugins.Docket;
import springfox.documentation.swagger2.annotations.EnableSwagger2;
@Configuration
@EnableSwagger2
public class SwaggerConfig {
@Bean
public Docket createRestApi() {
return new Docket(DocumentationType.SWAGGER_2)
.apiInfo(apiInfo())
.select()
.apis(RequestHandlerSelectors.basePackage("hello"))
.paths(PathSelectors.any())
.build();
}
private ApiInfo apiInfo() {
return new ApiInfoBuilder()
//页面标题
.title("Spring Boot中使用Swagger2构建RESTful APIs")
//描述
.description("欢迎来到java思维导图社区学习")
.termsOfServiceUrl("http://www.java-mindmap.com/")
//版本号
.version("1.0")
.build();
}
}
3)、编写测试的controller
package com.springboot.example.Controller;
import com.springboot.example.Service.StudentService;
import com.springboot.example.entity.Student;
import io.swagger.annotations.Api;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiImplicitParam;
import io.swagger.annotations.ApiOperation;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* Created by Administrator on 2017/9/13.
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("api")
@Api("swaggerDemoController相关的api")
public class SwaggerDemoController {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
private static final Logger logger= LoggerFactory.getLogger(SwaggerDemoController.class);
@ApiOperation(value = "根据id查询学生信息", notes = "查询数据库中某个的学生信息")
@ApiImplicitParam(name = "id", value = "学生ID", paramType = "path", required = true, dataType = "Integer")
@RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Student getStudent(@PathVariable int id) {
logger.info("开始查询某个学生信息");
return studentService.selectStudentById(id);
}
}
4)、启动项目 访问
访问路径:http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui.html
5)、查看页面的效果
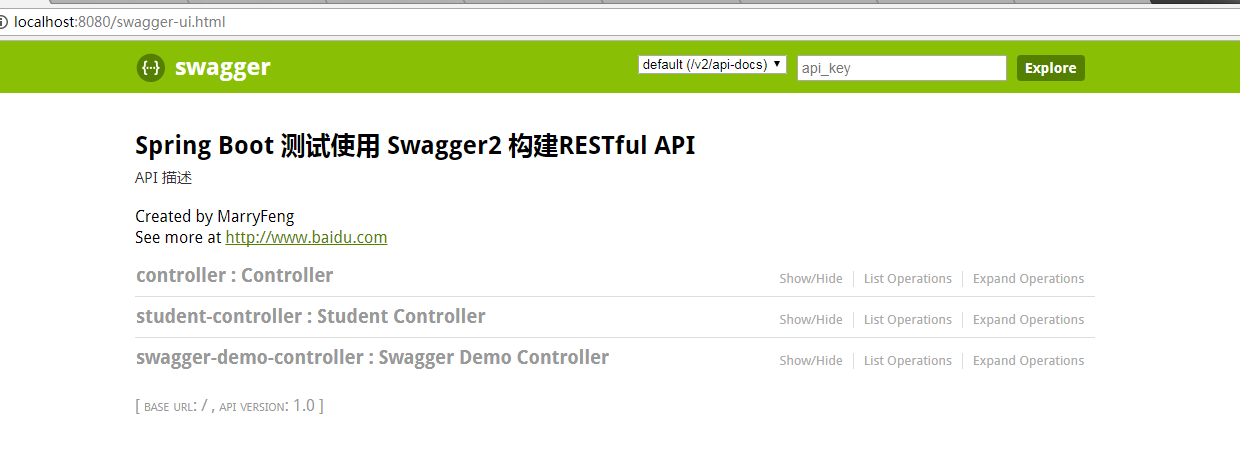

至此 SpringBoot 集成 Swagger2 完成!!!!!!
致敬:2020年的自己
--------------------------------------------
即使不为了什么远大理想,为了好好生活,你也得努力奋斗啊,不然别说什么风花雪月了,柴米油盐也能让你一筹莫展。

