线段树

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; #define endl "\n" //转换成斜率,画图知斜率最大一定是出现在相邻两点之间 //太妙了 const int N = 2e5 + 5; int a[N]; ll Tree[N * 4]; void build(int now, int l, int r) { if (l == r) { Tree[now] = a[l] - a[l - 1]; return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; build(now * 2, l, mid); build(now * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r); Tree[now] = max(Tree[now * 2], Tree[now * 2 + 1]); } void modify(int now, int l, int r, int pos, int v) { if (l == r) { Tree[now] = v; return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; if (pos <= mid)modify(now * 2, l, mid, pos, v); else modify(now * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r, pos, v); Tree[now] = max(Tree[now * 2], Tree[now * 2 + 1]); } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); int n; while(cin>>n){ for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i]; build(1, 2, n); int T = 1; cin >> T; while (T--) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; a[x] = y; if (x > 1)modify(1, 2, n, x, a[x] - a[x - 1]); if (x < n)modify(1, 2, n, x + 1, a[x + 1] - a[x]); double ans = Tree[1]; cout << fixed << setprecision(2) << ans << endl; } } return 0; }
当区间只有01两种状态时,使用异或操作,lazy标记也用异或操作实现

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; #define endl "\n" const int N = 1e5 + 5; struct TreeNode { int sum, ok; }Tree[4*N]; void pushdown(int now,int l,int r) { int mid = (l + r) >> 1; Tree[now * 2].sum = mid - l + 1 - Tree[now*2].sum; Tree[now * 2 + 1].sum = r - mid - Tree[now*2+1].sum; Tree[now * 2].ok ^= 1; Tree[now * 2 + 1].ok ^= 1; Tree[now].ok = 0; } void pushup(int now) { Tree[now].sum = Tree[now * 2].sum + Tree[now * 2 + 1].sum; } void modify(int now, int l, int r, int x, int y) { if (x <= l && y >= r) { Tree[now].ok ^= 1; Tree[now].sum = r - l + 1 - Tree[now].sum; return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; if(Tree[now].ok)pushdown(now, l, r); if (x <= mid)modify(now * 2, l, mid, x, y); if (y > mid)modify(now * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r, x, y); pushup(now); } ll qurey(int now, int l, int r, int x, int y) { if (x <= l && y >= r)return Tree[now].sum; if(Tree[now].ok)pushdown(now, l, r); int mid = (l + r) >> 1; ll res = 0; if (x <= mid)res += qurey(now * 2, l, mid, x, y); if (y > mid)res += qurey(now * 2 + 1, mid + 1, r, x, y); pushup(now); return res; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; while (m--) { int op; cin >> op; if (op == 1) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; cout << qurey(1, 1, n, x, y) << endl; } else { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; modify(1, 1, n, x, y); } } return 0; }
异或操作无法通过公式展开,对二进制每一位开一个线段树,求和就是将所有元素对每一位的1的个数乘上对应2的n次方求和

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; #define endl "\n" //二维线段树,对二进制每一位开一个线段树,这样就可以用lazy优化异或操作 const int N = 1e5 + 5; int a[N]; struct TreeNode { ll sum, ok; }Tree[N * 4][25]; void pushup(int now, int now_bit) { Tree[now][now_bit].sum = Tree[now * 2][now_bit].sum + Tree[now * 2 + 1][now_bit].sum; } //Tree[now][now_bit].ok为1才pushdown,为1代表之前已经修改过了,这是pushdown下传信息,再去修改或者询问,用的时候再pushdown,这样子优化 void pushdown(int now, int now_bit, int l, int r) { //不能直接这样子写,因为可能之前就有标记,如果之前有标记,再打标记相当于什么都不做 //Tree[now * 2][now_bit].ok = Tree[now * 2 + 1][now_bit].ok = 1; int mid = (l + r) >> 1; Tree[now * 2][now_bit].sum = mid - l + 1 - Tree[now * 2][now_bit].sum; Tree[now * 2 + 1][now_bit].sum = r - mid - Tree[now * 2 + 1][now_bit].sum; Tree[now * 2][now_bit].ok ^= 1; Tree[now * 2 + 1][now_bit].ok ^= 1; Tree[now][now_bit].ok = 0; } void build(int now, int now_bit, int l, int r) { if (l == r) { Tree[now][now_bit].sum = ((a[l] >> now_bit) & 1); return; } int mid = (l + r) >> 1; build(now * 2, now_bit, l, mid); build(now * 2 + 1, now_bit, mid + 1, r); pushup(now, now_bit); } ll qurey(int now, int now_bit, int l, int r, int x, int y) { if (l >= x && r <= y)return Tree[now][now_bit].sum; if (Tree[now][now_bit].ok)pushdown(now, now_bit, l, r); int mid = (l + r) >> 1; ll res = 0; if (x <= mid)res += qurey(now * 2, now_bit, l, mid, x, y); if (y > mid)res += qurey(now * 2 + 1, now_bit, mid + 1, r, x, y); return res; } void modify(int now, int now_bit, int l, int r, int x, int y) { if (l >= x && r <= y) { Tree[now][now_bit].sum = r - l + 1 - Tree[now][now_bit].sum; Tree[now][now_bit].ok ^= 1; return; } if (Tree[now][now_bit].ok)pushdown(now, now_bit, l, r); int mid = (l + r) >> 1; if (x <= mid)modify(now * 2, now_bit, l, mid, x, y); if (y > mid)modify(now * 2 + 1, now_bit, mid + 1, r, x, y); pushup(now, now_bit); } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); int n, m; cin >> n >> m; for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)cin >> a[i]; for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i++)build(1, i, 1, n); while (m--) { int op; cin >> op; if (op == 1) { int x, y; cin >> x >> y; ll res = 0; for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i++) { res += qurey(1, i, 1, n, x, y) * (1LL << i); } cout << res << endl; } else { int x, y, k; cin >> x >> y >> k; for (int i = 0; i <= 20; i++) { if ((k >> i) & 1)modify(1, i, 1, n, x, y); } } } return 0; }

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; typedef long long ll; #define endl "\n" //一个区间最不管长度多长,都只能对取模后的l,r产生1的贡献值,因为op==3时询问的是有多少个区间 //通过unique和erase离散化建立线段树 const int N = 1e5 + 5; vector<int>vec; struct Node { int op, l, r, x; }a[N]; struct BIT { int c[4 * N]; void modify(int x, int k) { for (; x <= N; x += x & (-x)) { c[x] += k; } } int qurey(int x) { int ans = 0; for (; x; x -= x & (-x)) { ans += c[x]; } return ans; } }Tree; //获得离散后x是第几大的 int get_idx(int x) { return lower_bound(vec.begin(), vec.end(), x) - vec.begin() + 1; } int main() { ios::sync_with_stdio(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0); int n, k; cin >> n >> k; if (n == 0) { cout << "fafa"; return 0; } for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { cin >> a[i].op; if (a[i].op == 1) { cin >> a[i].l >> a[i].r; vec.push_back(a[i].l); vec.push_back(a[i].r); } else if (a[i].op == 2) { cin >> a[i].l >> a[i].r; vec.push_back(a[i].l); vec.push_back(a[i].r); } else { cin >> a[i].x; //这里需要push_back当前x的值 //不然离散化后不会被覆盖到 vec.push_back(a[i].x); } } //离散化 sort(vec.begin(), vec.end()); vec.erase(unique(vec.begin(), vec.end()), vec.end()); if (k == 0) { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (a[i].op == 1) { int l = get_idx(a[i].l); int r = get_idx(a[i].r); Tree.modify(l, 1); Tree.modify(r + 1, -1); } else if (a[i].op == 2) { int l = get_idx(a[i].l); int r = get_idx(a[i].r); Tree.modify(l, -1); Tree.modify(r + 1, 1); } else { int ans = get_idx(a[i].x); cout << Tree.qurey(ans) << endl; } } } else { for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) { if (a[i].op == 1) { int len = a[i].r - a[i].l + 1; if (len >= k) { Tree.modify(1, 1); Tree.modify(k + 1, -1); } else { int mod_l = a[i].l % k + 1; int mod_r = a[i].r % k + 1; if (mod_l <= mod_r) { Tree.modify(mod_l, 1); Tree.modify(mod_r + 1, -1); } else { Tree.modify(1, 1); Tree.modify(mod_r + 1, -1); Tree.modify(mod_l, 1); Tree.modify(k + 1, -1); } } } else if (a[i].op == 2) { int len = a[i].r - a[i].l + 1; if (len >= k) { Tree.modify(1, -1); Tree.modify(k + 1, 1); } else { int mod_l = a[i].l % k + 1; int mod_r = a[i].r % k + 1; if (mod_l <= mod_r) { Tree.modify(mod_l, -1); Tree.modify(mod_r + 1, 1); } else { Tree.modify(1, -1); Tree.modify(mod_r + 1, 1); Tree.modify(mod_l, -1); Tree.modify(k + 1, 1); } } } else { cout << Tree.qurey(a[i].x % k + 1) << endl; } } } return 0; }

op1-->-x-1
op2-->x+1
由线性代数知识推每次操作要乘的矩阵,线段树维护一个矩阵信息
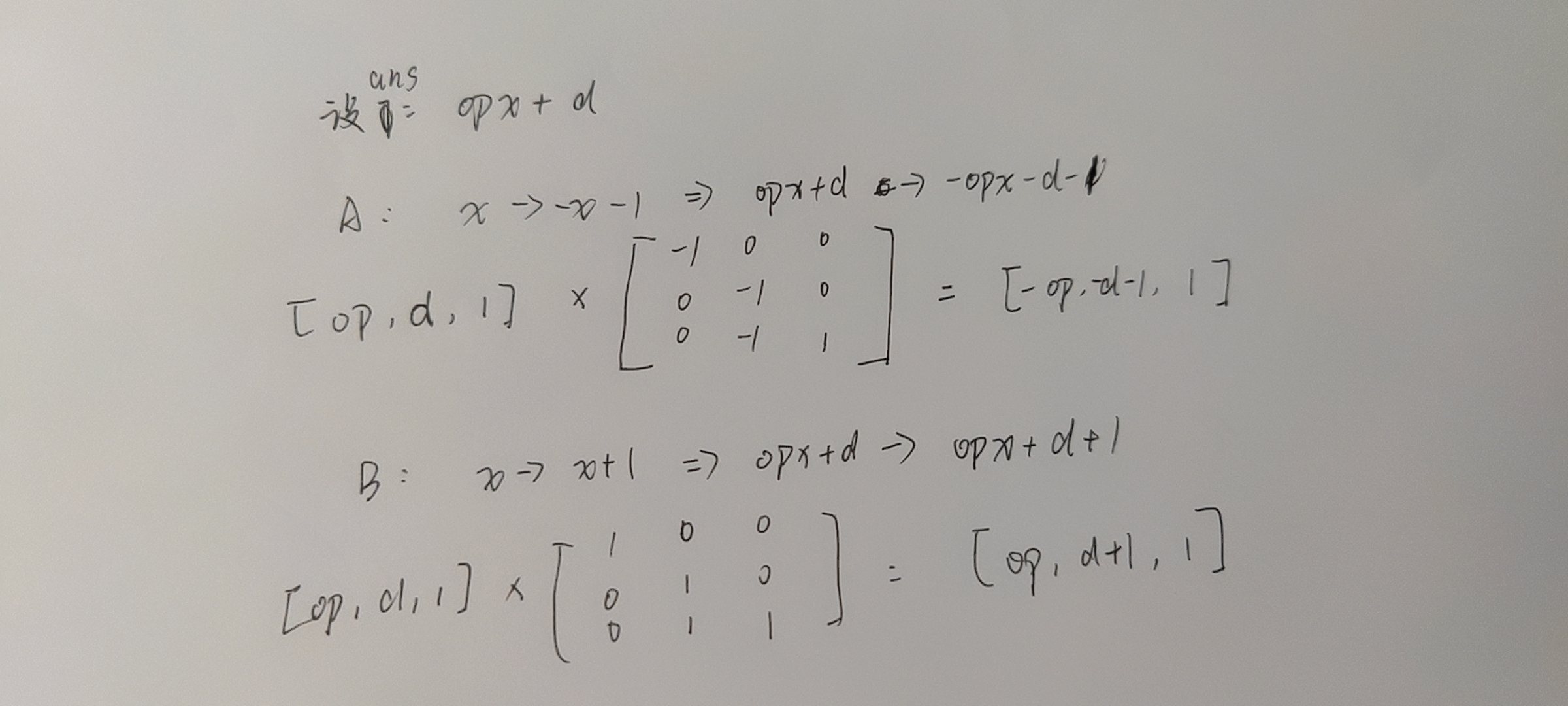
[op,d,1] 就是代表一个f(x)=kx+b的方程,根据线性代数知识用矩阵表示该方程 -> f(x)=op*x+d , 最后一个1只是凑矩阵用的 ,f代表该矩阵,因为刚开始就是x,所以op=1,d=0

#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define endl "\n" typedef long long ll; const int sz=3; const int N=2e5+5; string s; struct mat { ll m[sz][sz]; mat() { memset(m, 0, sizeof m); } mat operator-(const mat& T) const { mat res; for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < sz; ++j) { res.m[i][j] = (m[i][j] - T.m[i][j]); } return res; } mat operator+(const mat& T) const { mat res; for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < sz; ++j) { res.m[i][j] = (m[i][j] + T.m[i][j]); } return res; } mat operator*(const mat& T) const { mat res; int r; for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) for (int k = 0; k < sz; ++k) { r = m[i][k]; for (int j = 0; j < sz; ++j) res.m[i][j] += T.m[k][j] * r ; } return res; } mat operator^(ll x) const { mat res, bas; for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) res.m[i][i] = 1; for (int i = 0; i < sz; ++i) for (int j = 0; j < sz; ++j) bas.m[i][j] = m[i][j]; while (x) { if (x & 1) res = res * bas; bas = bas * bas; x >>= 1; } return res; } }A,B,f,Tree[4*N],unit; void build(int now,int l,int r){ if(l==r){ if(s[l-1]=='A')Tree[now]=A; else Tree[now]=B; return; } int mid=(l+r)>>1; build(now*2,l,mid); build(now*2+1,mid+1,r); Tree[now]=Tree[now*2]*Tree[now*2+1]; } mat qurey(int now,int l,int r,int x,int y){ if(x<=l&&y>=r)return Tree[now]; int mid=(l+r)>>1; mat ans=unit; if(x<=mid)ans=ans*qurey(now*2,l,mid,x,y); if(y>mid)ans=ans*qurey(now*2+1,mid+1,r,x,y); return ans; } int main(){ ios::sync_with_stdio(false),cin.tie(0),cout.tie(0); int n,q;cin>>n>>q>>s; int last=0; A.m[0][0]=A.m[1][1]=A.m[2][1]=-1; A.m[2][2]=B.m[2][1]=1; f.m[0][0]=f.m[0][2]=1; for(int i=0;i<3;i++)B.m[i][i]=1,unit.m[i][i]=1; build(1,1,n); while(q--){ int l,r;cin>>l>>r; string now;cin>>now; int rl=(last^l)%n+1,rr=(last^r)%n+1; l=min(rl,rr);r=max(rl,rr); mat calc=f*qurey(1,1,n,l,r); ll len=now.size(),t=0; for(int i=0;i<len;i++)t=t*2+(now[i]-'0'); ll mod=1ll<<len; last=((t*calc.m[0][0]%mod+mod)%mod+calc.m[0][1]%mod+mod)%mod; for(int i=len-1;i>=0;i--){ if((last>>i)&1)cout<<1; else cout<<0; } cout<<endl; if(last<0)break; } return 0; }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号