Nginx Web服务(一)
一、Nginx原理介绍
1.1:什么是Nginx
Nginx是一个开源的,支持高性能、高并发的WWW服务和代理服务软件
1.2:Nginx的功能特点及应用场合
① 支持高并发:能支持几万并发连接,特别是针对静态小文件业务
② 资源消耗少:在3万并发连接的情况下,开始10个nginx的线程消耗不到200M
③ 可以做HTTP的反向代理及加速缓存,即负载均衡,内置对RS节点的服务器健康检查
④ 具备squid等专业代理软件的缓存功能
⑤ 支持异步网络IO事件模型
1.3:同步与异步的简单介绍
① 同步:发送出去一直等待,直到被处理(效率低 安全性高)
② 异步:发送出去不管有没有被处理,直接进行下一个请求(效率高 安全性低)
1.4:epoll模型和select模型的区别
Nginx所使用的模型就是异步epoll模型,所以他的效率高速度快,Apache使用的模型就是select模型
PS:(在生产环境中大多数高并发的软件都是使用的epoll的异步模型)
| 指标 | select | epoll |
| 性能 | 随着连接数的增加,性能是急剧下降的,处理成千上万的连接数性能很差 | 随着连接数的增加,性能基本上不会发生变化,处理成千上万的连接数,性能很好 |
| 连接数 | 连接数有限制,处理的最大连接数不能超过1024,如要超过1024个连接数,需要修改FD_SETSIZE宏,并重新编译 | 连接数没有限制 |
| 内在处理机制 | 线性轮询 | 回调callback |
| 开发的复杂性 | 低 | 中 |
二、Nginx代理原理介绍
2.1:正向/反向代理原理图
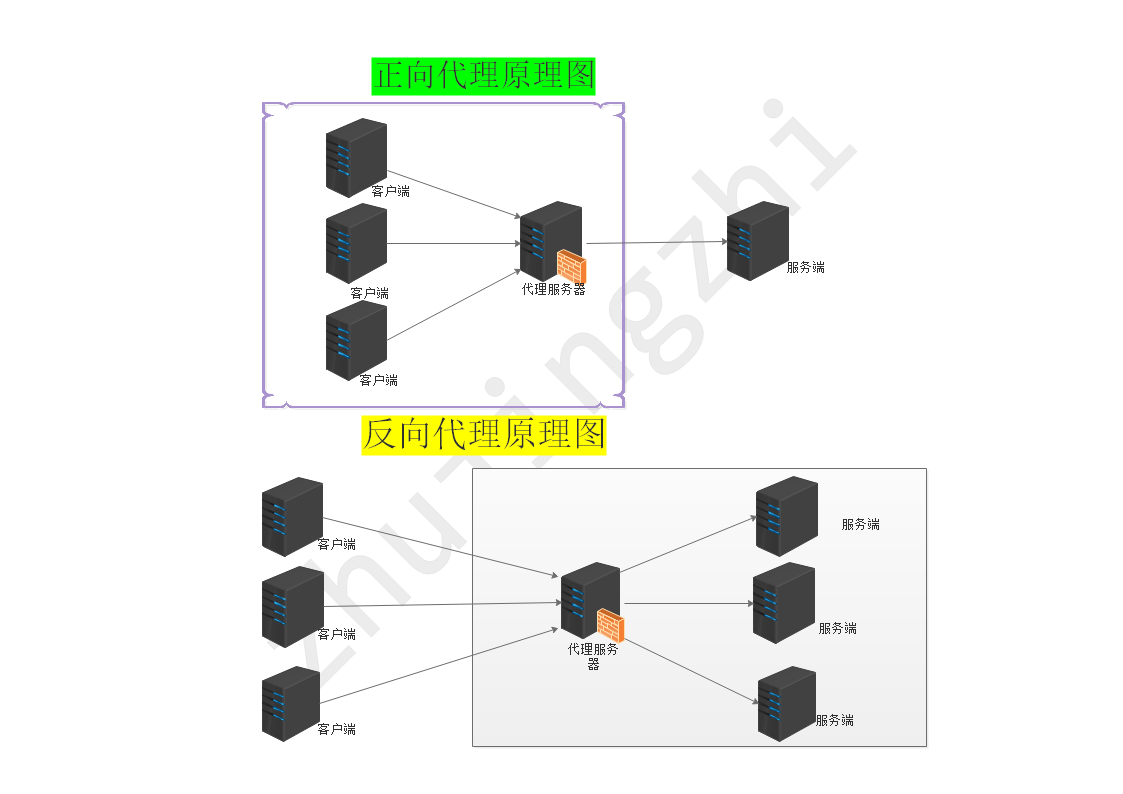
2.2:正向代理原理阐述
正向代理:客户端<-->代理-->服务端
正向代理就是客户端和服务器之间的中间服务器,为了从服务器取到内容,客户端向代理服务器发送一个请求并指定目标服务器,然后代理服务器向服务器转交请求并将获得的内容回给客户端,客户端必须设置正向代理服务器,当然前提是你要知道正向代理服务器的IP地址和程序端口
其实举个例子就是
A(客户端)想租C(服务端)的房子,但是A(客户端)并不认识C(服务端)租不到。
B(代理)认识C(服务端)能租这个房子所以你找了B(代理)帮忙租到了这个房子。
这个过程中C(服务端)不认识A(客户端)只认识B(代理)
C(服务端)并不知道A(客户端)租了房子,只知道房子租给了B(代理)。
这个样做的目的是
① 访问本无法访问的服务器(Over the wall访问谷歌,但是Over the wall的技术不仅仅是使用了传统的正向代理技术还有其他的技术)
② 缓存(Cache)作用
③ 客户端访问授权(可以限制指定的客户端访问)
④ 隐藏访问者的行踪(抓肉鸡)
2.3:反向代理原理阐述
反向代理:客户端-->代理<-->服务端
反向代理正好与正向代理相反,对于客户端而言代理服务器就是提供访问业务的服务器,并且客户端不需要进行任何的特别的设置,客户端向反向代理的命名空间中的内容发送普通请求,接着反向代理将判断向何处(提供访问业务的服务器)转发请求,并将获得的内容返回给客户端
举例说明
A(客户端)想租一个房子,B(代理)就把这个房子租给了他。
这时候实际上C(服务端)才是房东。
B(代理)是中介把这个房子租给了A(客户端)。
这个过程中A(客户端)并不知道这个房子到底谁才是房东
他都有可能认为这个房子就是B(代理)的
使用反向代理的目的
① 保护和隐藏原始的资源服务器
② 实现服务器集群的负载均衡,实现客户端高速访问
PS:网上有人说NGINX不能做正向代理,其实是不对的。NGINX也可以做正向代理,不过用的人比较少了。
三、Nginx安装
3.1:编译安装
nginx的版本在不断的更新中,以后我能可以去http://nginx.org/ 去下载最新的稳点版 yum -y install wget (可以使用rpm -qa wget 看看有没有安装,没有安装在执行yum安装) yum -y install pcre pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel (为了使用nginx的伪静态功能,centos7 默认已经安装了) mkdir -p /server/software (创建一个通用的存放软件的目录) cd /server/software wget -q http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz tar xf nginx-1.12.2.tar.gz -C /opt/ cd /opt/nginx-1.12.2 useradd nginxs -s /sbin/nologin -M ./configure --user=nginxs --group=nginxs --with-http_ssl_module --with-http_stub_status_module --prefix=/data/nginx-1.12.2/ # 配置 ================================解释======================================= --user=nginxs # 指定安装的用户 --group=nginxs # 指定安装的组 --with-http_ssl_module # 开启https --with-http_stub_status_module # 开启nginx的status监测 --prefix=/data/nginx-1.12.2/ # 指定安装目录 ================================解释======================================= make && make install # 编译 安装 ln -s /data/nginx-1.12.2/ /data/nginx # 创建软连接 为了工作中方便 /data/nginx/sbin/nginx # 启动nginx netstat -lntup | grep nginx # 检查是否启动成功 客户端测试 curl -v 192.168.163.129(服务器地址)
3.2:yum安装
yum -y install pcre pcre-devel openssl openssl-devel (为了使用nginx的伪静态功能,centos7 默认已经安装了) yum -y install epel-resease (centos的默认yum源没有nginx的包,所以我们要在第三方yum源安装) yum -y install nginx systemctl start nginx # 启动 netstat -lntup | grep nginx # 检查是否启动成功
客户端测试 curl -v 192.168.163.129(服务器地址)
四、Nginx常用模块
4.1:常用模块及功能介绍
核心模块官网地址:http://nginx.org/en/docs/ngx_core_module.html
http模块官网地址:http://nginx.org/en/docs/
核心模块:nginx的核心模块负责nginx的全局应用,主要是对应主配置文件的Main区块和Events区块区域,这里有很多的Nginx的全局参数配置
http标准模块:这些标准模块,虽然不是nginx软件所必须的,但是都是很常用的
ngx_http_core_module # 包括一些核心的http参数配置,对应http区块部分 ngx_http_access_module # 访问控制模块,用来控制网站用户对nginx的访问 ngx_http_gzip_module # 压缩模块,对nginx的返回数据进行压缩 ngx_http_fastcgi_module # fastcgi模块,和动态应用相关的模块,如php ngx_http_proxy_module # proxy代理模块 ngx_http_upstream_module # 负载均衡模块,可以实现网站的负载均衡及节点检查 ngx_http_rewrite_module # URL地址重写模块 ngx_http_limit_conn_module # 限制用户并发连接数及请求模块 ngx_http_limit_req_module # 根据定义的key限制nginx请求过程的速率 ngx_http_log_module # 访问日志模块,以指定的格式记录访问日志 ngx_http_auth_basic_module # Web认证模块,设置web用户通过账号密码访问nginx ngx_http_ssl_module # ssl模块 用于加密的http连接 ngx_http_stub_status_module # 记录nginx基本的访问状
五、Nginx配置文件说明
5.1:nginx的配置文件(/etc/nginx.conf)基本解析说明
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf.default | egrep -v "#|^$" # 对配置文件进行最小化
worker_processes 1; # worker的进程数(和CPU的核心数一致最好)
events { # 事件区块的开始
worker_connections 1024; # 每个worker的最大连接数
} # 事件区块的结束
http { # http区块的开始
include mime.types; # 设定mime类型,类型由mime.type文件定义
default_type application/octet-stream; # 默认类型
sendfile on; # 开启高效的传输模式
keepalive_timeout 65; # 超时时间
server { # server区块的开始
listen 80; # 监听的端口
server_name localhost; # 域名地址
location / { # 站点的根目录
root html; # 存放网站html文件的目录
index index.html index.htm; # 打开网站的默认文件
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; # 错误文件地址,出现错误访问这个下面的html
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
六、Nginx两种代理的配置
6.1:正向代理
应用在nginx的server段,不要server_name,需要添加一个resolver。
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; # 配置错误日志默认级别error
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
# 配置DNS解析IP地址,比如 Google Public DNS,以及超时时间(5秒)
resolver 8.8.8.8; # 必需
resolver_timeout 5s;
# 监听端口
listen 8080;
access_log /home/reistlin/logs/proxy.access.log;
error_log /home/reistlin/logs/proxy.error.log;
location / {
# 配置正向代理参数
proxy_pass $scheme://$host$request_uri;
# 解决如果URL中带"."后Nginx 503错误
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
# 配置缓存大小
proxy_buffers 256 4k;
# 关闭磁盘缓存读写减少I/O
proxy_max_temp_file_size 0;
# 代理连接超时时间
proxy_connect_timeout 30;
# 配置代理服务器HTTP状态缓存时间
proxy_cache_valid 200 302 10m;
proxy_cache_valid 301 1h;
proxy_cache_valid any 1m;
}
}
}
client端:
一次代理,直接在shell执行:
#export http_proxy=http://192.168.163.132:8080
永久使用:
#vim .bashrc
export http_proxy=http://192.168.163.132:8080
#source .bashrc
6.2:反向代理
反向代理的配置
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 2; #启动进程,通常设置成和cpu的数量相等
events {
worker_connections 1024; #单个后台worker process进程的最大并发链接数
}
http {
include mime.types; #设定mime类型,类型由mime.type文件定义
default_type application/octet-stream;
#sendfile 指令指定 nginx 是否调用 sendfile 函数(zero copy)来输出文件,对于普通应用,
#必须设为 on,如果用来进行下载等应用磁盘IO重负载应用,可设置为 off,以平衡磁盘与网络I/O处理速度,降低系统的uptime.
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65; #连接超时时间
server {
listen 80; #侦听80端口
server_name localhost; # 定义使用www.xx.com访问
charset utf-8;
location / {
root html;
add_header Cache-Control no-store;
add_header 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin' '*';
index index.html index.htm;
}
location /request/ {
root /request; # 网站的资源路径
#请求替换地址 例如要请求http://localhost:8888/login/ 也就是请求http://localhost/request/
proxy_pass http://localhost:8888/login/;
proxy_redirect off;
proxy_set_header Host $host; #请求主机头字段,否则为服务器名称。
# 后端的Web服务器可以通过X-Forwarded-For获取用户真实IP
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
client_max_body_size 10m; #允许客户端请求的最大单文件字节数
client_body_buffer_size 128k; #缓冲区代理缓冲用户端请求的最大字节数
proxy_connect_timeout 300; #nginx跟后端服务器连接超时时间(代理连接超时)
proxy_send_timeout 300; #后端服务器数据回传时间(代理发送超时)
proxy_read_timeout 300; #连接成功后,后端服务器响应时间(代理接收超时)
proxy_buffer_size 4k; #设置代理服务器(nginx)保存用户头信息的缓冲区大小
proxy_buffers 4 32k; #proxy_buffers缓冲区,网页平均在32k以下的话,这样设置
proxy_busy_buffers_size 64k; #高负荷下缓冲大小(proxy_buffers*2)
proxy_temp_file_write_size 64k; #设定缓存文件夹大小,大于这个值,将从upstream服务器传
proxy_headers_hash_max_size 1024; #存放http报文头的哈希表容量上限,默认为512个字符
proxy_headers_hash_bucket_size 128; #设置头部哈希表大小 默认为64
}
location ~ ^/html5/ {
rewrite /html5(.*)$ $1 break; #该指令根据表达式来重定向URI, 路径中存在/html5/的
expires -1; #缓存
root D:\html5; #前端静态文件物理路径 通过http://localhost/html5/来访问D盘html5下的文件夹
}
}
}
七、Nginx虚拟主机配置
6.1:什么是虚拟主机
在web服务里面就是一个独立的网站站点,这个站点对应独立的域名,具有独立的程序及资源目录,可以独立的对外提供服务
6.2:虚拟主机的类型
① 基于域名的虚拟主机
相同的IP端口不同的域名提供不同的资源,最常用的
② 基于端口的虚拟主机
相同的IP不同的端口提供不同的资源(局域网最常用的)
③ 基于IP的虚拟主机
相同端口不同的IP提供不同的资源(最不常用,一般也不会用到)
6.3:虚拟主机的配置(在nginx.conf配置文件中添加server区块)
① 基于域名的虚拟主机
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/www; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name bbs.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/bbs; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 80;
server_name blos.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/blos; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
② 基于端口的虚拟主机
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80; # 端口也不一样
server_name www.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/www; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 81; # 端口也不一样
server_name bbs.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/bbs; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 82; # 端口也不一样
server_name blos.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/blos; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
③ 基于IP的虚拟主机
vim /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 192.168.163.129:80; # 端口一样IP不一样
server_name www.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/www; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 192.168.163.130:80; # 端口一样IP不一样
server_name bbs.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/bbs; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
listen 192.168.163.131:80; # 端口一样IP不一样
server_name blos.zhujingzhi.org; # 域名不一样
location / {
root html/blos; # 记得添加网站的资源目录
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
PS:修改完配置文件(因为nginx支持reload方法)所以我们要重新的平滑重启下 在重启之前一定nginx -t 检查下语法,在配置基于IP的虚拟主机的时候IP一定是存在的,不然会出现语法错误
八、Nginx状态模块使用
7.1:nginx status 状态模块配置(--with-http_stub_status_module参数)
# 在编译安装的时候指定--with-http_stub_status_module参数就是开启了状态监测模块
# 主配置文件
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; # 我们把server区块分离出来了放到了/etc/nginx/conf.d/下,然后用include导入
}
# 状态监测配置文件(这个就是要配置的状态监测的server区块写到.conf里面在主配置文件中导入)
cat >> /etc/nginx/conf.d/status.conf <<EOF
> # status
> server {
> listen 80;
> server_name status.zhujingzhi.org;
> location / {
> stub_status on; # 开启状态监测
> access_log off; # 拒绝写日志
> allow 192.168.163.0/24; # 允许访问的地址
> deny all; # 决绝访问
> }
> }
> EOF
7.2:输出结果详细解析
没有域名解析,我们要添加hosts文件(只针对测试环境) vim /etc/hosts 127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4 ::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6 192.168.163.132 status.zhujingzhi.org # 我们添加的 curl status.zhujingzhi.org # 访问状态监测的地址 # 得到的结果 Active connections: 1 server accepts handled requests 27 27 27 Reading: 0 Writing: 1 Waiting: 0 # 结果的解释 Active connections: 表示Nginx正处理的活动连接数 server:表示Nginx启动到现在共处理了多少个连接 accepts:表示Nginx启动到现在共处理成功创建的握手次数 handled requests:表示共处理了多少次请求 Reading:表示读取到客户端的Header信息数 Writing:表示返回给客户端的Header信息数 Waiting:表示已经处理完正在等候下一次请求指令的驻留连接数,在开启keeplive的情况下,这个值等于active-(reading+writing)
PS:为了安全起见,这个状态信息要防止外部用户查看
7.3:利用监控系统监控nginx的状态(扩展)
九、Nginx日志详情
8.3:访问日志内容解析(access.log)
访问日志
参数
log_format:用来定义日志的格式
access_log:用来注定日志文件的路径及使用的何种日志格式记录日志
# 默认的日志格式(放在http标签内)
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
# 日志格式参数说明
$remote_addr # 记录客户端访问网站的地址
$remote_user # 远程客户端用户的名称
$time_local # 记录访问时间与时区
$request # 用户的http请求起始行信息
$status # http状态码,记录请求返回的状态
$body_bytes_sent # 服务器发送给客户端的响应body字节数
$http_referer # 记录此次请求是从哪个链接访问过来的可以根据refer进行防盗链的设置
$http_user_agent # 记录客户端的访问信息,例如:浏览器,手机客户端等
$http_x_forwarded_for # 当前端有代理服务器时,设置Web节点记录客户端地址的配置,此参数生效的前提是代理服务器上也要进行配置x_forwarded_for设置
访问日志配置文件设置
在server区块中添加access_log /etc/log/access.log main; 这里的main表示的是在http标签中设置的日志格式的main 这个可以是main1、main2 等不同的格式记录日志
8.4:错误日志内容解析(error.log)
错误日志 属于核心功能模块ngx_core_module参数,该参数的名字为error_log,可以放在main区块中全局配置,也可以放在不同的虚拟主机中单独记录虚拟主机的错误信息 语法 error_log file level; error_log # 固定的参数 file # 日志的文件 level # 日志的级别 日志的级别包含:debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg ,级别越高记录的信息越少,生产中一般使用warn|error|crit 这个三个级别 PS:千万不要使用info 会产生大量的I/O
8.1:配置文件配置日志
访问日志配置
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; # 配置错误日志默认级别error
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"'; # 默认格式,可以自定义
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main; # 启动访问日志
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.zhujingzhi.org;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
错误日志配置
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; # 配置错误日志默认级别error
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.zhujingzhi.org;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
}
十、Nginx日志切割
9.1:日志切割的方式
9.2:日志切割脚本+crontab计划任务
9.3:常用的日志收集工具(rsyslog、awstats、flume、ELK、storm)
十一、Nginx认证访问
10.1:为什么要配置认证访问
有些时候我们用nginx要做内部的网站访问,或者是用nginx来做文件服务器给内部人员使用,为了安全我们就要用到认证机制,保证数据的安全
10.2:配置日志访问的方法
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
error_log /var/log/nginx/error.log; # 配置错误日志默认级别error
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80; #监听端口为80
server_name www.zhujingzhi.com; #虚拟主机网址
location / {
root html/bbs; # 虚拟主机网站根目录
index index.html index.htm; # 虚拟主机首页
auth_basic "secret"; # 虚拟主机认证命名
auth_basic_user_file /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db; # 虚拟主机用户名密码认证数据库
}
location /status {
stub_status on; # 开启网站监控状态
access_log /usr/local/nginx/logs/www1_status.log; # 监控日志
auth_basic "NginxStatus";
}
}
}
我们还要生成用户名密码文件
通过htpasswd命令生成用户名及对应密码数据库文件
htpasswd -c /usr/local/nginx/passwd.db nginxtest
十二、Nginx Location
location指令的作用是可以根据用户请求的URI来执行不同的应用,其实就是根据用户的请求的网站的地址URL匹配,匹配成功即进行相关的操作(相当于if...else语句,女孩子你有钱我就嫁给你 O(∩_∩)O哈哈~)
① location语法
location[=|~|~*|^~]uri{
.....
}
location # 指令
[=|~|~*|^~|!~|!~|@] # 匹配标识
uri # 匹配的网站地址
{...} # 匹配URI后要执行的配置段
====================================================================================
匹配标识解释
= # 精确匹配
~ # 开头表示区分大小写的正则匹配
~* # 开头表示不区分大小写的正则匹配
^~ # 常规的字符串匹配检查之后,不做正则表达式的检查
!~和!~* # 分别为区分大小写不匹配及不区分大小写不匹配 的正则
/ # 通用匹配,任何请求都会匹配到。
@ # "@" 定义一个命名的 location,使用在内部定向时,例如 error_page, try_files
location = / {
# 只匹配"/".
[ configuration A ]
}
location / {
# 匹配任何请求,因为所有请求都是以"/"开始
# 但是更长字符匹配或者正则表达式匹配会优先匹配
[ configuration B ]
}
location /documents/ {
# 匹配以documents开头的地址
[ configuration C ]
}
location ^~ /images/ {
# 匹配任何以 /images/ 开始的请求,并停止匹配 其它location
[ configuration D ]
}
location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
# 匹配以 gif, jpg, or jpeg结尾的请求.
# 但是所有 /images/ 目录的请求将由 [Configuration C]处理.
[ configuration E ]
}
② 配置location
主配置文件
cat /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
include /etc/nginx/conf.d/*.conf; # 导入虚拟主机文件
}
# 虚拟主机文件配置location
cat /etc/nginx/conf.d/www.conf
# www
server {
listen 80;
server_name www.zhujingzhi.org;
location / {
return 401;
#root html/www;
#index index.html index.htm;
}
location = /{
return 402;
}
location /documents/ {
return 403;
}
location ^~ /images/ {
return 404;
}
location ~* .(gif|jpg|jpeg)$ {
return 405;
}
}
客户端测试
为了测试我们要加hosts文件
cat /etc/hosts
127.0.0.1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost4 localhost4.localdomain4
::1 localhost localhost.localdomain localhost6 localhost6.localdomain6
192.168.163.132 status.zhujingzhi.org www.zhujingzhi.org
使用curl 测试 返回我们配置在location中的return返回值
curl -s -o /dev/null -I -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.zhujingzhi.org
402
curl -s -o /dev/null -I -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.zhujingzhi.org/
402
curl -s -o /dev/null -I -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.zhujingzhi.org/index.html
401
curl -s -o /dev/null -I -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.zhujingzhi.org/documents/document.html
403
curl -s -o /dev/null -I -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.zhujingzhi.org/images/1.png
404
curl -s -o /dev/null -I -w "%{http_code}\n" http://www.zhujingzhi.org/documents/2.jpg
405
③ 结论
用户请求的URI 完整的URL 匹配的返回值 / http://www.zhujingzhi.org/ 402 /index.html http://www.zhujingzhi.org/index.html 401 /documents/document.html http://www.zhujingzhi.org/documents/document.html 403 /images/1.png http://www.zhujingzhi.org/images/1.png 404 /documents/2.jpg http://www.zhujingzhi.org/documents/2.jpg 405 location 优先级 1、Directives with the = prefix that match the query exactly. If found, searching stops. 2、All remaining directives with conventional strings, longest match first. If this match used the ^~ prefix, searching stops. 3、Regular expressions, in order of definition in the configuration file. 4、If #3 yielded a match, that result is used. Else the match from #2 is used. 1、=前缀的指令严格匹配这个查询。如果找到,停止搜索。 2、所有剩下的常规字符串,最长的匹配。如果这个匹配使用^〜前缀,搜索停止。 3、正则表达式,在配置文件中定义的顺序。 4、如果第3条规则产生匹配的话,结果被使用。否则,使用第2条规则的结果。
十三、Nginx rewrite
-------------------------------------------
个性签名:在逆境中要看到生活的美,在希望中别忘记不断奋斗
如果觉得这篇文章对你有小小的帮助的话,记得在右下角点个“推荐”哦,博主在此感谢!
万水千山总是情,打赏一分行不行,所以如果你心情还比较高兴,也是可以扫码打赏博主,哈哈哈(っ•̀ω•́)っ✎⁾⁾!


也可以关注我的微信公众号,不定时更新技术文章(kubernetes,Devops,Python)等





