C语言学习笔记之 文件操作
文件操作
目录

文件指针
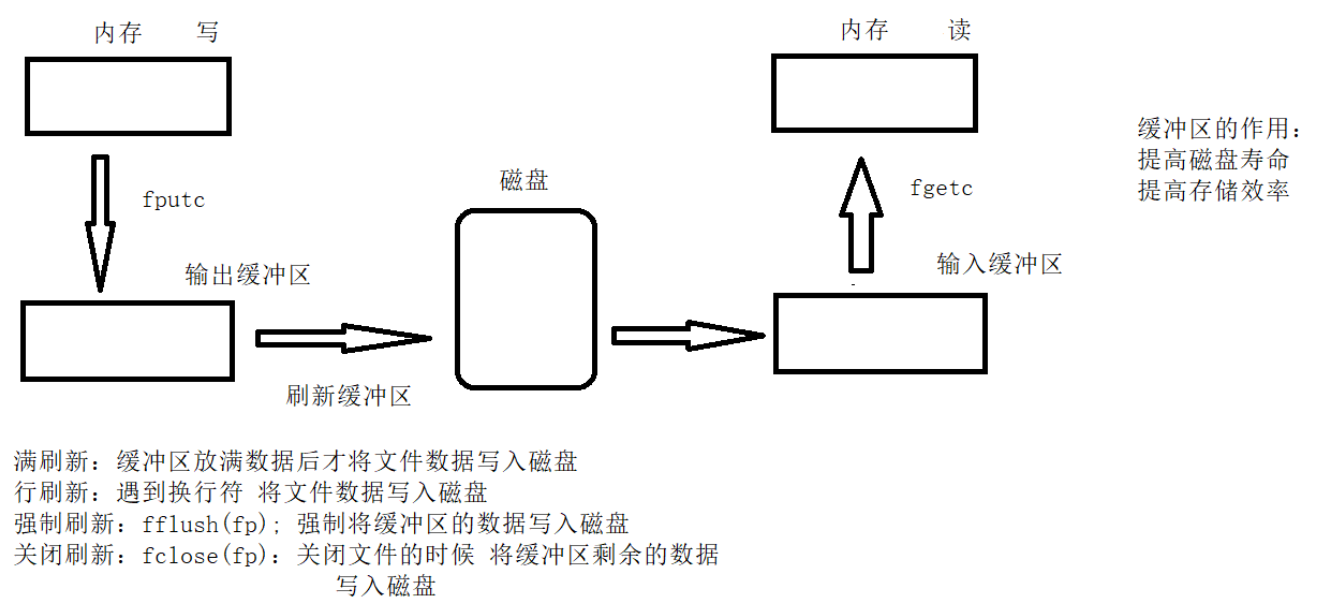
操作系统通过 函数(API) 操作文件,而函数通过文件指针识别不同文件
函数 --> 文件指针 --> 文件

打开和关闭文件
fopen打开文件
#include <stdio.h>
FILE *fopen(const char *filename,const char *mode);
功能:打开文件
参数:
filename:文件名
mode:打开文件的模式
返回值:
成功:文件指针
失败:NULL
mode的赋值:

r只读,w只写,b二进制文件,a追加,+可读可写
附:
FILE的定义:
struct _iobuf {
char *_ptr;
int _cnt;
char *_base;
int _flag;
int _file;
int _charbuf;
int _bufsiz;
char *_tmpfname;
};
typedef struct _iobuf FILE;
fclose关闭文件
#include <stdio.h>
int fclose(FILE *stream);
功能:关闭fopen打开的文件,将缓冲区的数据写入文件中,
并释放系统提供的文件资源
参数:
stream:文件指针
返回:
成功:0
失败:-1
例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp = NULL;
fp = fopen("./tes","rb");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
exit(1);
}
printf("打开成功\n");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
# 当test文件存在时
打开成功
# 当不存在时
fopen: No such file or directory
文件读写
fputc往文件写一个字符
#include <stdio.h>
int fputc(int ch,FILE *stream);
功能:将ch转换为unsigned char后写入stream文件中
参数:
ch:字符
stream:文件指针
返回:
成功:成功写入文件的字符
失败:返回-1
例:
fgetc读取一个字符
#include <stdio.h>
int fgetc(FILE *stream);
功能:从stream指定的文件里读取一个字符
参数:
stream:文件指针
返回:
成功:读取到的字符
失败:-1
判断文件结束
EOF 宏 -1 文本文件
feof 函数 文本文件和二进制文件
int feof(FILE *stream);
功能:检测是否读到了文件结尾。判断的是最后一次“读操作的
内容”,不是当前位置内容(上一个内容)
参数:
stream:文件指针
返回:
非0值:已经到文件结尾
0:未到文件结尾
例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
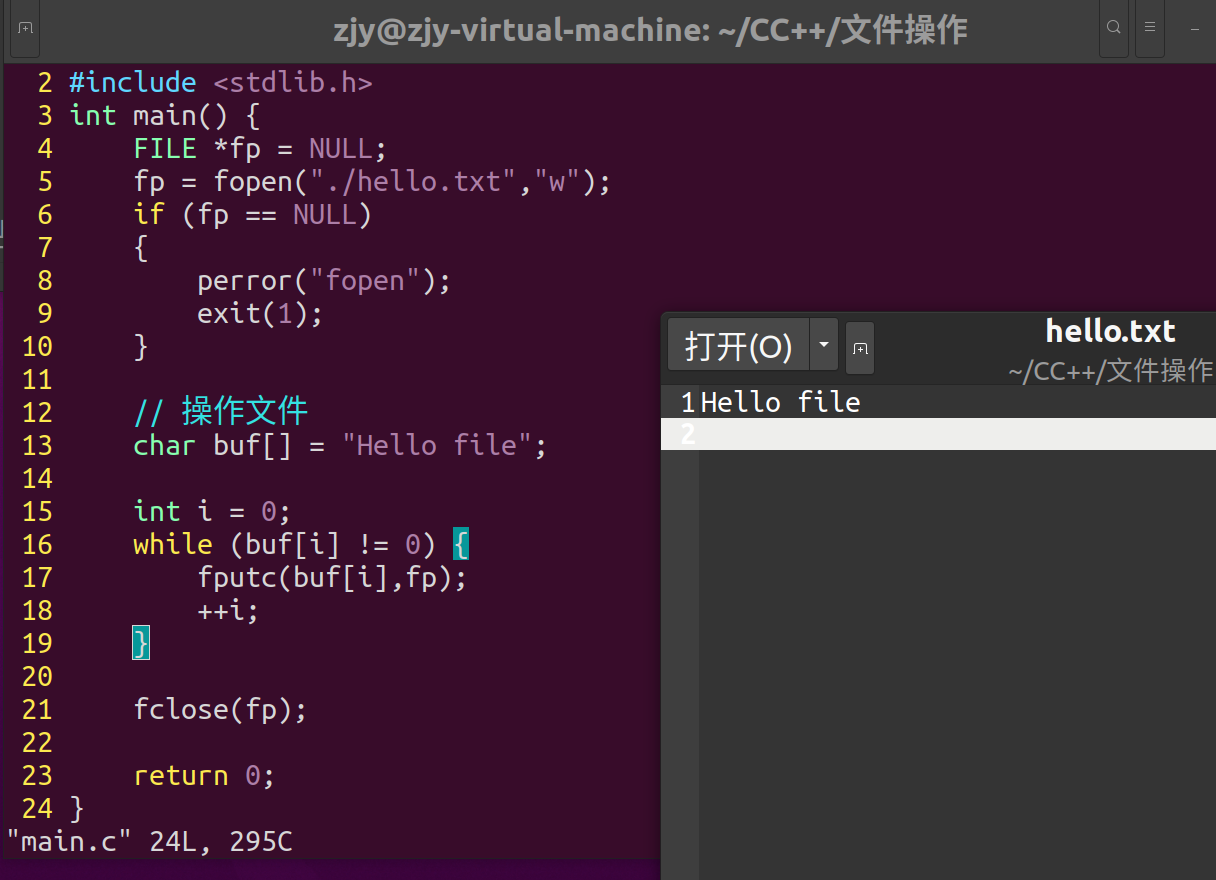
int main() {
FILE *fp = NULL;
fp = fopen("./hello.txt","r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
exit(1);
}
// 操作文件
while (1) {
char ch = 0;
ch = fgetc(fp);
// 判断文件末尾
// EOF
// if (ch == EOF)
// {
// break;
// }
if (feof(fp)) {
break;
}
printf("%c",ch);
}
printf("\n");
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
Hello file
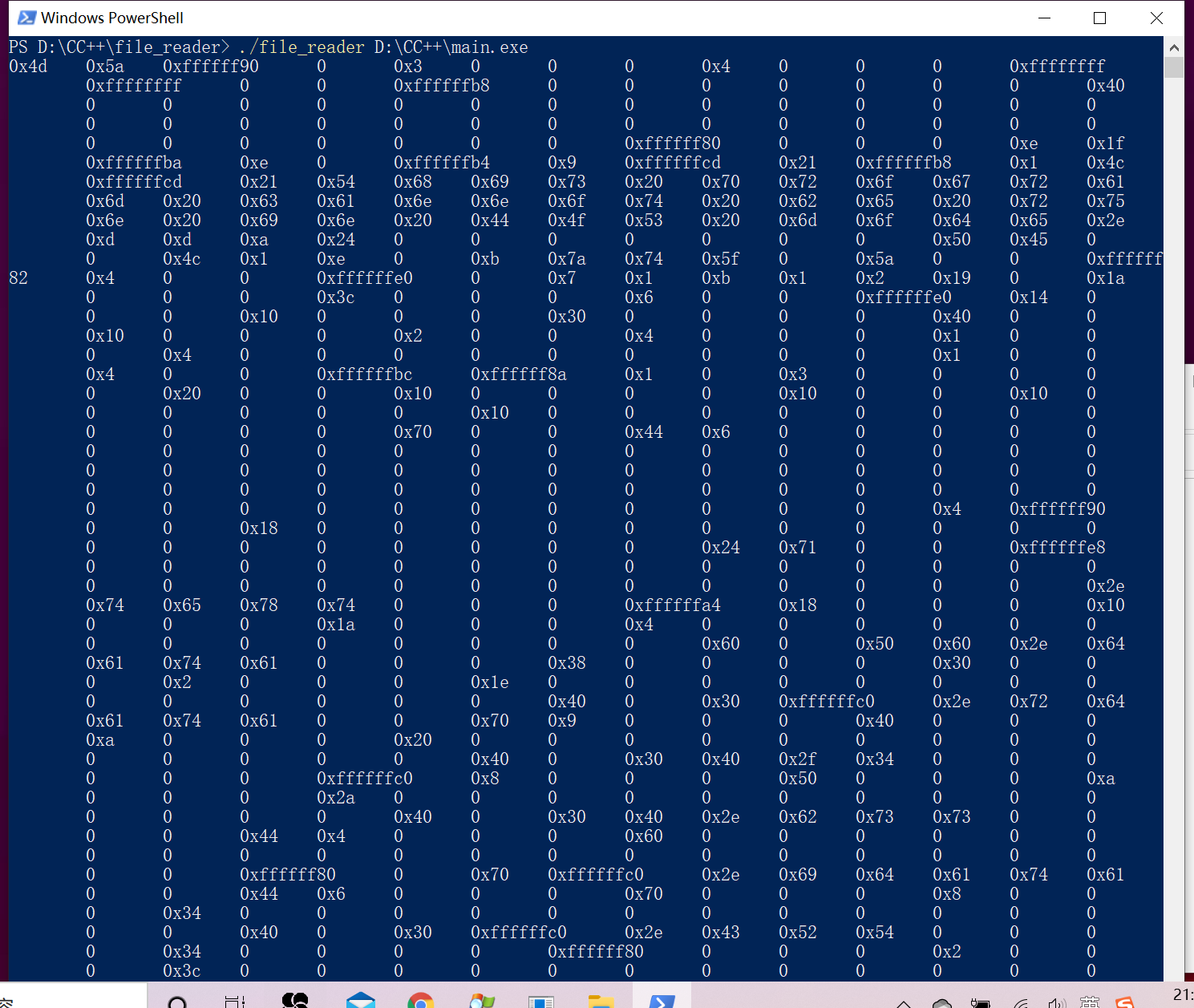
实例1:二进制文件读取器
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc < 2)
{
printf("ERROR:参数过少。。。");
exit(1);
}
else if (argc > 2)
{
printf("ERROR:参数过多。。。");
exit(1);
}
else
{
FILE *fp = NULL;
fp = fopen(argv[1], "rb");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
exit(1);
}
while (1)
{
char ch = 0;
ch = fgetc(fp);
if (feof(fp))
{
printf("\n");
break;
}
printf("%-#x\t", ch);
}
}
return 0;
}
效果:
fputs写入字符串
int fputs(const char *str,FILE *stream);
功能:将str字符串写入stream文件中
参数:
str:字符串
stream:文件指针
返回:
成功:0
失败:-1
例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp = NULL;
fp = fopen("./hello.txt","w");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
exit(1);
}
// 操作文件
char *buf[] = {"大漠孤烟直\n","长河落日园"};
for (size_t i = 0; i < sizeof(buf)/sizeof(buf[0]); ++i) {
fputs(buf[i],fp);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
# hello.txt
大漠孤烟直
长河落日园
fgets获取一行
#include <stdio.h>
char *fgets(char *str,int size,FILE *stream);
功能:从stream文件中读取字符,写入str中,
直到出现换行符、文件结尾或已经读了size-1个字符为止,
最后会自动加上'\0'
参数:
str:字符串
size:最大读取字符串的长度
stream:文件指针
返回:
成功:字符串
读到文件尾或出错:NULL
例:四则运算解题神器
题目:
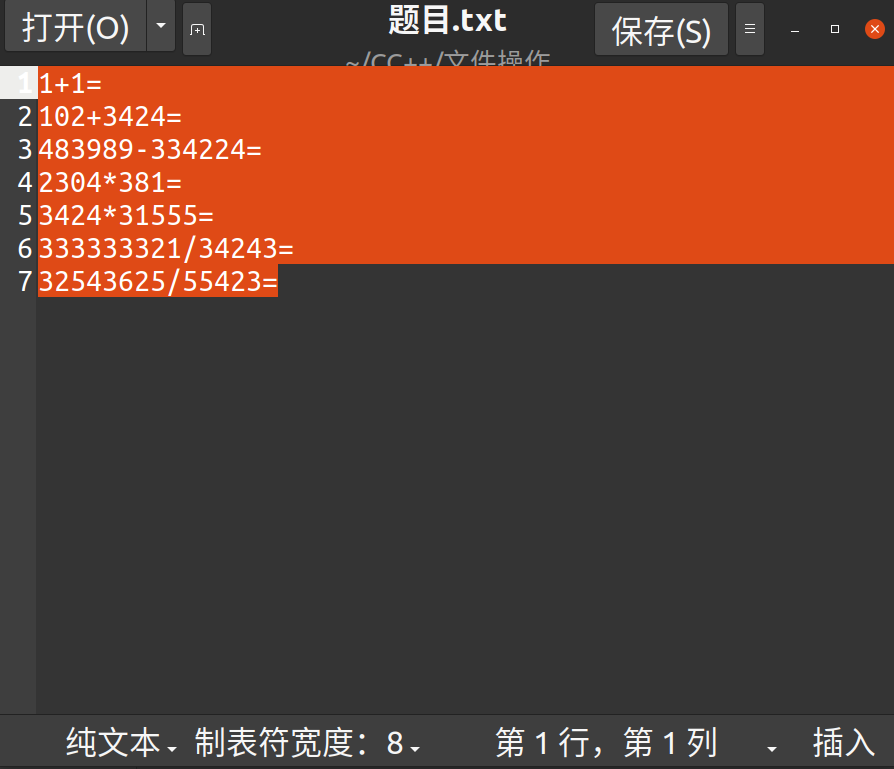
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp = fopen("题目.txt","r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
exit(1);
}
char buf[128] = "";
while (fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),fp))
{
int num1 = 0, num2 = 0;
char ch = 0;
// 解包
sscanf(buf, "%d%c%d=", &num1, &ch, &num2);
// 计算
int sum = 0;
switch (ch)
{
case '+':
sum = num1 + num2;
break;
case '-':
sum = num1 - num2;
break;
case '*':
sum = num1 * num2;
case '/':
sum = num1 / num2;
break;
}
printf("%d%c%d = %d\n",num1,ch,num2,sum);
}
if (fp != NULL)
{
fclose(fp);
fp = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
1+1 = 2
102+3424 = 3526
483989-334224 = 149765
2304*381 = 6
3424*31555 = 0
333333321/34243 = 9734
32543625/55423 = 587
文件高级操作
文件重命名和删除

文件的块读写
将内存中的数据原样输出在文件
fwrite
#include <stdio.h>
size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream)
功能:把 ptr 所指向的数组中的数据写入到stream 中
参数:
ptr:指向要被写入的元素数组的指针。
size:要被写入的每个元素的大小,以字节为单位。
nmemb:元素的个数,每个元素的大小为 size 字节
stream:文件指针
返回:
如果成功,该函数返回一个 size_t 对象,
表示元素的总数,该对象是一个整型数据类型。
如果该数字与 nmemb 参数不同,则会显示一个错误
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct {
char name[16];
int age;
float score;
}stu;
int main() {
stu student[3] = {
{"小李",13,100},
{"小红",14,119},
{"小明",15,120}
};
FILE *fp = fopen("./student.txt","w");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
exit(1);
}
fwrite(student,sizeof(stu),3,fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
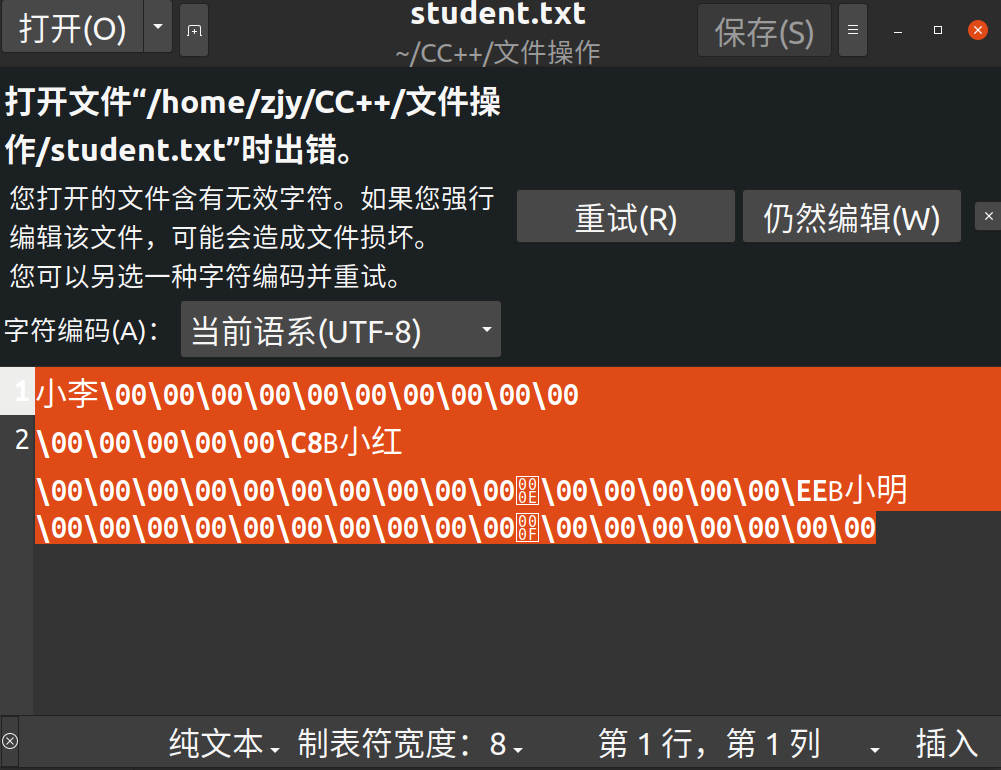
fread
size_t fread(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, FILE *stream);
功能:从给定流 stream 读取数据到 ptr 所指向的数组中
参数:
ptr:指向带有最小尺寸 size*nmemb 字节的内存块的指针
size:要读取的每个元素的大小,以字节为单位
nmemb:元素的个数,每个元素的大小为 size 字节
stream:文件指针
返回:
成功读取的元素总数会以 size_t 对象返回,
size_t 对象是一个整型数据类型。
如果总数与 nmemb 参数不同,
则可能发生了一个错误或者到达了文件末尾
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef struct {
char name[16];
int age;
float score;
}stu;
int main() {
stu student[3];
FILE *fp = fopen("./student.txt","r");
if (fp == NULL)
{
perror("fopen");
exit(1);
}
int n = fread(student,sizeof(stu),3,fp);
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
printf("name = %s, age = %d, score = %.2f\n",student[i].name,student[i].age,student[i].score);
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
name = 小李, age = 13, score = 100.00
name = 小红, age = 14, score = 119.00
name = 小明, age = 15, score = 120.00
格式化读写
fprintf

fscanf

复位流指针

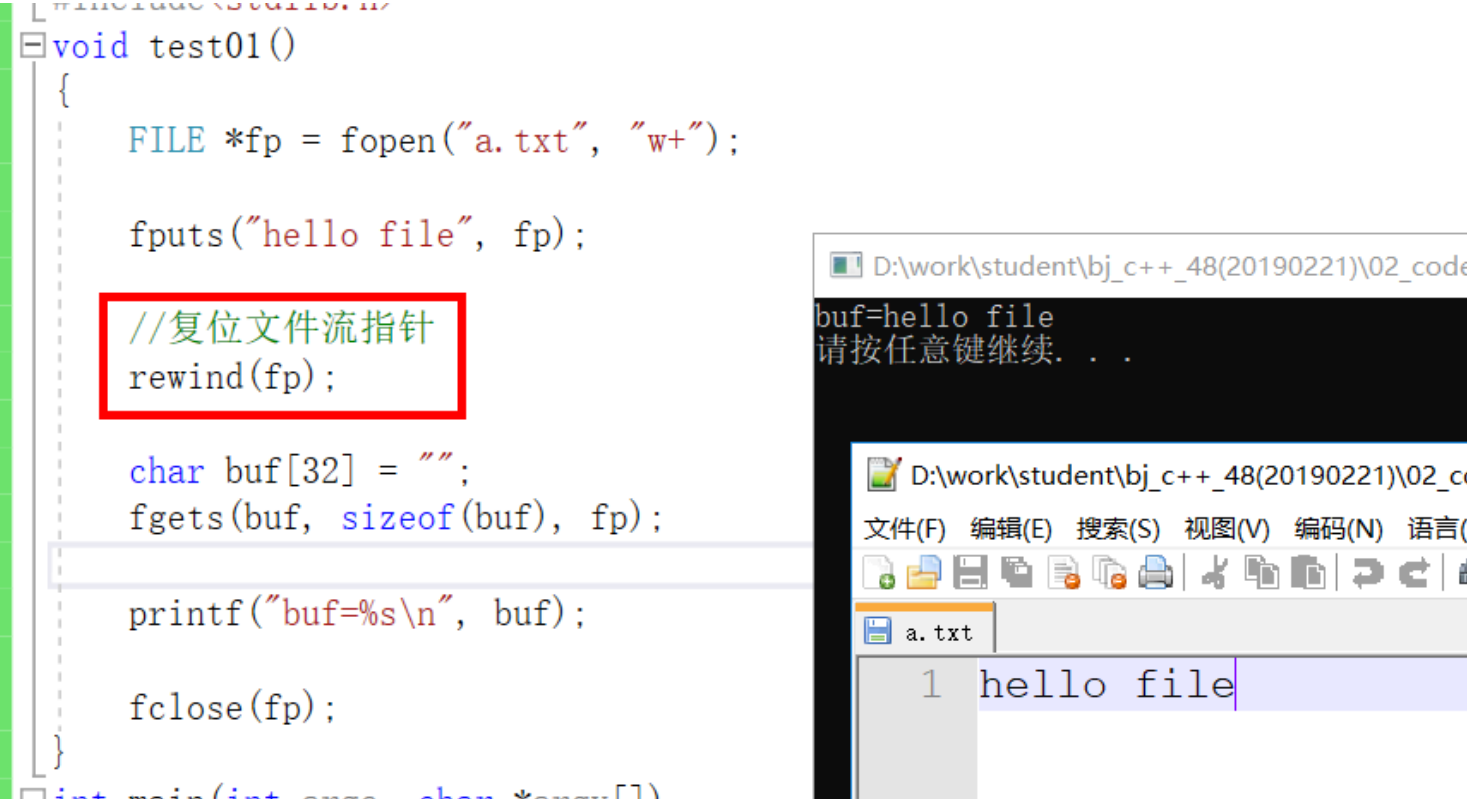
设置文件流指针

成功:0;失败:-1

ftell返回文件流指针距离文件首部的偏移量(字节)

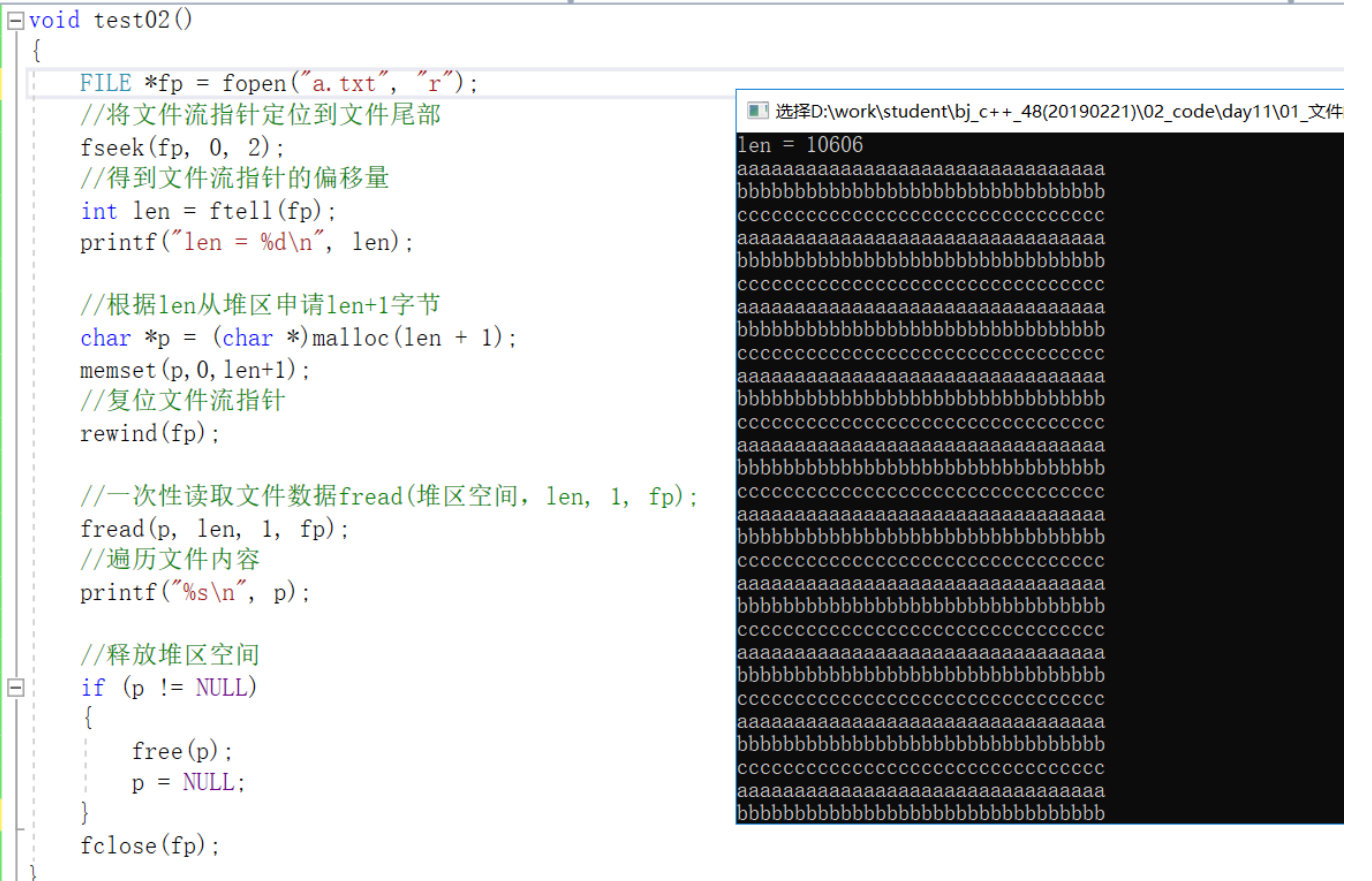
获取文件状态



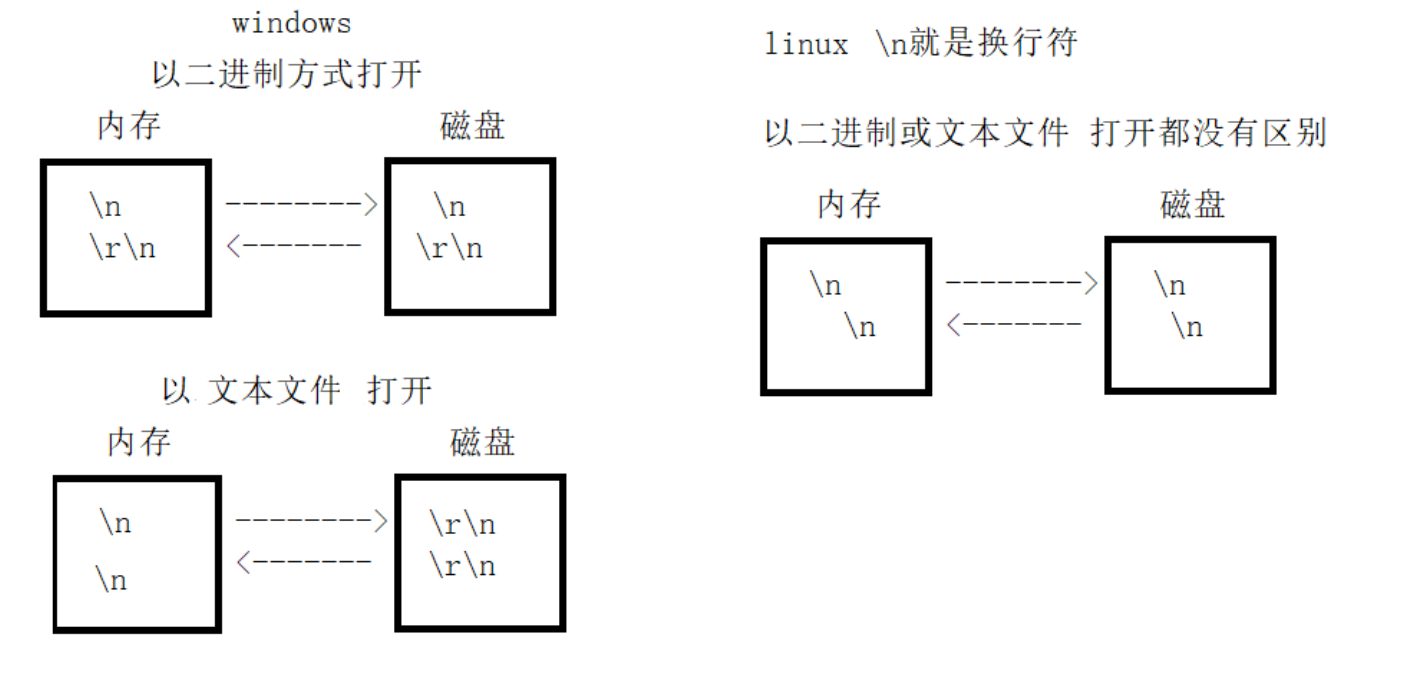
缓冲区