elasticsearch安装
安装包准备,将安装包上传到opt目录下,解压,文件夹重命名
tar -zxvf elasticsearch-x.x.x.tar.gz
mv elasticsearch-x.x.x es
设置内核参数
vi /etc/sysctl.conf
增加以下参数
vm.max_map_count=655360
执行以下命令确保配置生效。
sysctl -p
设置资源参数
vi /etc/security/limits.conf
# 修改如下
* soft nproc 1024000
* hard nproc 1024000
* soft nofile 1024000
* hard nofile 1024000
设置用户资源参数
vi /etc/security/limits.d/20-nproc.conf
# 设置es用户参数
es soft nproc 65536
添加启动用户,设置权限
useradd es #创建用户es groupadd es #创建组es usermod es -g es #将用户添加到组
题外话:
要是再Ubuntu下添加用户、组,则使用如下命令:
useradd -d "/home/es" -m -s "/bin/bash" es
该命令会创建用户和所属组
常用命令行选项:
- -d: 指定用户的主目录
-
-m: 如果存在不再创建,但是此目录并不属于新创建用户;如果主目录不存在,则强制创建; -m和-d一块使用。
-
-s: 指定用户登录时的shell版本
-
-M: 不创建主目录
mkdir -p /opt/es/{data,logs} # 创建数据和日志目录 # 修改文件所有者 chown -R es:es /opt/es/ chown -R es:es /opt/es/
修改Elasticsearch的配置文件
vi /opt/es/config/elasticsearch.yml # ======================== Elasticsearch Configuration ========================= # # NOTE: Elasticsearch comes with reasonable defaults for most settings. # Before you set out to tweak and tune the configuration, make sure you # understand what are you trying to accomplish and the consequences. # # The primary way of configuring a node is via this file. This template lists # the most important settings you may want to configure for a production cluster. # # Please consult the documentation for further information on configuration options: # https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/index.html # # ---------------------------------- Cluster ----------------------------------- # # Use a descriptive name for your cluster: # cluster.name: es-app # # ------------------------------------ Node ------------------------------------ # # Use a descriptive name for the node: # node.name: node-1 # # Add custom attributes to the node: # #node.attr.rack: r1 # # ----------------------------------- Paths ------------------------------------ # # Path to directory where to store the data (separate multiple locations by comma): # path.data: /opt/es/data # # Path to log files: # path.logs: /opt/es/logs # # ----------------------------------- Memory ----------------------------------- # # Lock the memory on startup: # #bootstrap.memory_lock: true # # Make sure that the heap size is set to about half the memory available # on the system and that the owner of the process is allowed to use this # limit. # # Elasticsearch performs poorly when the system is swapping the memory. # # ---------------------------------- Network ----------------------------------- # # Set the bind address to a specific IP (IPv4 or IPv6): # network.host: 192.168.244.129 # # Set a custom port for HTTP: # http.port: 9200 #
启动es
切换到es用户,到bin目录下启动es su - es cd /opt/es/bin ./elasticsearch 我这里没报错,直接在浏览器访问es 192.168.244.xx:9200
{ "name": "node-1", "cluster_name": "es-app", "cluster_uuid": "-oZN4SydQCWq1XaKH_e7qw", "version": { "number": "6.8.8", "build_flavor": "default", "build_type": "tar", "build_hash": "2f4c224", "build_date": "2020-03-18T23:22:18.622755Z", "build_snapshot": false, "lucene_version": "7.7.2", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version": "5.6.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version": "5.0.0" }, "tagline": "You Know, for Search" }
在版本7以后,启动可能会报如下错

解决办法,在配置文件中加入以下命令
xpack.ml.enabled: false
安装Kibana
将kibana-6.8.8-linux-x86_64上传至/usr/local/下,解压
tar -zxvf kibana-6.8.8-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
mv kibana-6.8.8-linux-x86_64 kibana
编辑kibana配置
vi /usr/local/kibana/config/kibana.yml # Kibana is served by a back end server. This setting specifies the port to use. #server.port: 5601 # Specifies the address to which the Kibana server will bind. IP addresses and host names are both valid values. # The default is 'localhost', which usually means remote machines will not be able to connect. # To allow connections from remote users, set this parameter to a non-loopback address. server.host: "192.168.244.129" # Enables you to specify a path to mount Kibana at if you are running behind a proxy. # Use the `server.rewriteBasePath` setting to tell Kibana if it should remove the basePath # from requests it receives, and to prevent a deprecation warning at startup. # This setting cannot end in a slash. #server.basePath: "" # Specifies whether Kibana should rewrite requests that are prefixed with # `server.basePath` or require that they are rewritten by your reverse proxy. # This setting was effectively always `false` before Kibana 6.3 and will # default to `true` starting in Kibana 7.0. #server.rewriteBasePath: false # The maximum payload size in bytes for incoming server requests. #server.maxPayloadBytes: 1048576 # The Kibana server's name. This is used for display purposes. #server.name: "your-hostname" # The URLs of the Elasticsearch instances to use for all your queries. elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://192.168.244.129:9200"] # When this setting's value is true Kibana uses the hostname specified in the server.host # setting. When the value of this setting is false, Kibana uses the hostname of the host # that connects to this Kibana instance. #elasticsearch.preserveHost: true # Kibana uses an index in Elasticsearch to store saved searches, visualizations and # dashboards. Kibana creates a new index if the index doesn't already exist. #kibana.index: ".kibana" # The default application to load.
启动kibana
cd /usr/local/kibana/bin/ ./kibana
浏览器地访问
http://192.168.244.xx:5601
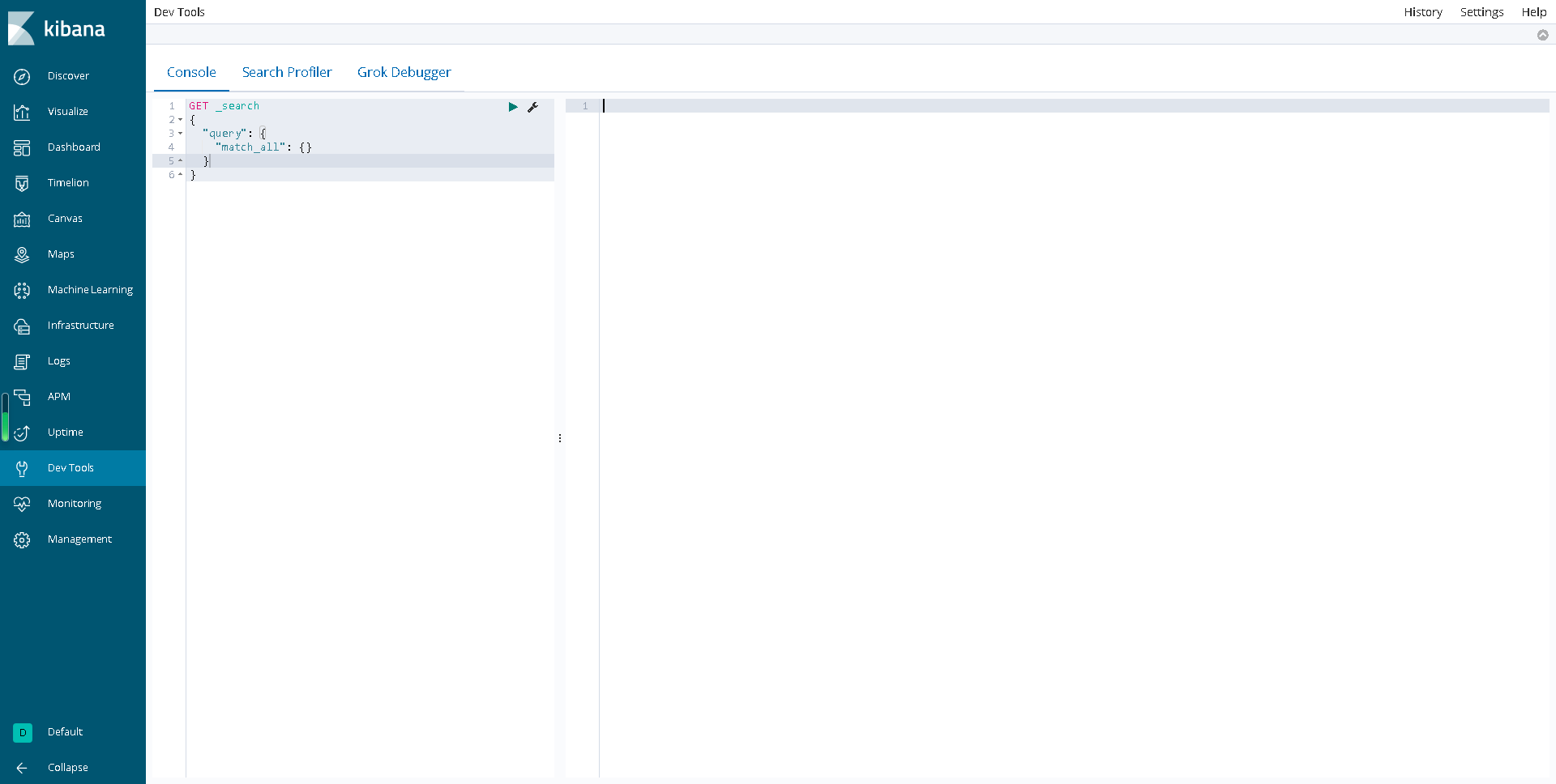
看到如下界面即成功
设置es开机自启动
创建es 的系统启动服务文件,进入到 cd /etc/init.d 目录; cd /etc/init.d 【进入到目录】 vi elasticsearch 【创建es系统启动服务文件】 编写启动脚本; #!/bin/bash #chkconfig: 345 63 37 #description: elasticsearch #processname: elasticsearch export ES_HOME=/opt/es/ case $1 in start) su - es<<! cd $ES_HOME ./bin/elasticsearch -d -p pid exit ! echo "elasticsearch is started" ;; stop) pid=`cat $ES_HOME/pid` kill -9 $pid echo "elasticsearch is stopped" ;; restart) pid=`cat $ES_HOME/pid` kill -9 $pid echo "elasticsearch is stopped" sleep 1 su es<<! cd $ES_HOME ./bin/elasticsearch -d -p pid exit ! echo "elasticsearch is started" ;; *) echo "start|stop|restart" ;; esac exit 0 保存退出 修改文件权限; 复制代码 chmod 777 elasticsearch 添加和删除服务并设置启动方式; 复制代码 chkconfig --add elasticsearch #【添加系统服务】 chkconfig --del elasticsearch #【删除系统服务】
若是在国产操作系统UOS或者Ubuntu上设置服务,可以使用
systemctl enable elasticsearch #【添加服务】
systemctl disable elasticsearch #【删除服务】 关闭和启动服务; 复制代码 service elasticsearch start #【启动】 service elasticsearch stop #【停止】 systemctl start elasticsearch systemctl stop elasticsearch service elasticsearch restart #【重启】 设置服务是否开机启动; 复制代码 chkconfig elasticsearch on #【开启】 chkconfig elasticsearch off #【关闭】 ________________________________________ 验证是否已启动命令: 复制代码 ps -ef | grep elasticsearch #【查看是否有es的进程】 结束进程命令用kill -9 进程ID;
设置kibana开机自启动
cd /etc/init.d touch kibana chmod +x kibana vi kibana并输入以下内容: #!/bin/bash # chkconfig: 2345 98 02 # description: kibana KIBANA_HOME=/usr/local/kibana case $1 in start) $KIBANA_HOME/bin/kibana &;; *) echo "kibana is start";; esac
如若是在Ubuntu上配置开机自启动,则可以仿照下面的方式
#!/bin/bash ### BEGIN INIT INFO # Provides: kibana # Required-Start: # Required-Stop: # Default-Start: 2 3 4 5 # Default-Stop: 0 1 6 # Short-Description: start and stop kibana # Description: kibana ### END INIT INFO KB_HOME=/opt/software/kibana case $1 in start)$KB_HOME/bin/kibana --allow-root &;; *) echo "kibana is start";; esac
kibana和elasticsearch都是不能在root用户下启动的,所以在脚本加个参数“--allow-root”



