2、java语言基础
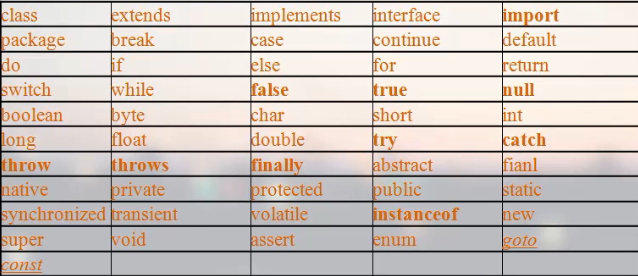
1、关键字
被Java语言赋予特定含义的单词被称为关键字
关键字都是小写的
在Java开发工具中,针对关键字有特殊颜色的标记
2、标识符
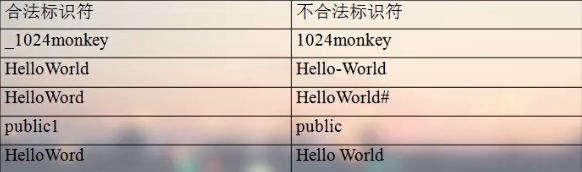
Java标识符命名规则
·标识符是由,数字,字母,下划线和美元符号构成,其他符号不可以
·必须以字母、下划线和美元符号开头,不能以数字开头
关键字不能作为标识符
标识符区分大小写,理论上没有长度限制
3、字面值
什么是字面值?
·字面值就是可以直接看到是多少的数据
字面值的分类
·字符串,用双引号括起来的内容,例如:"monkey"
·整数,所有整数,例如:1024
·小数,所有小数,例如:3.14
·字符,用单引号括起来的内容,里面只能放单个数字,单个字母或单个符号,例如:‘a'
·布尔,只有true和false
public class Literal_value{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("HeiHei!"); System.out.println(2048); System.out.println(0.11); System.out.println('A'); System.out.println(false); } }
4、变量
什么是变量?
·在程序执行的过程中,在某个范围内其值可以发生改变的量
Java中如何定义变量(以下两种均可)
1.数据类型变量名=变量值;
2.数据类型变量名;
变量名=变量值;
为什么定义变量?
变量其实就是内存中的一块空间,这块空间有“类型”,“名字”,“值”。可以用来不断的存放同一类型的常量,并可以重复使用。
public class variable{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a=10; System.out.println(a); a=20; System.out.println(a); //int a =20; error 同一个域中 不能对变量再次重新声明 int b,c,d=15; //error 只给d赋值了 b和c没有赋值 System.out.println(d); } }
5、java数据类型
整数型
·byte占一个字节-128到127(字节型)
·short 占两个字节-215~215-1-32768~32767(短整型)
·int占四个字节-231~231-1-2147483648~2147483648(整型)
·long 占八个字节-2063-263-1(长整型)
public class data_type{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; long b = 1000; //程序将2147483648看做是int类型,因为2147483648已经超出了int类型的取值范围,所以会报错 //正确的方法是在long类型赋值的时候,需要在后面加上‘L’ //程序会默认的把整型的字面值当做int类型 long ab = 2147483648L; int c = 999; //从容量大的向容量小的类型转换时,需要强制类型转换 //这么做可能会损失精度,所以不建议使用 int d = (int)c; //需要注意,给byte类型赋值时,需要注意取值范围 //byte d=128;error byte e=127; } }
浮点型
·float 占四个字节-3.403E38~3.403E38单精度
·double占八个字节-1.798E308~1.798E308双精度
public class floats{ public static void main(String[] args){ double d = 3.14; float f = 1.2F; //因为默认为double类型,因超过double限制,所以需要加F float f1 = (float)d; //强制转换为float型 float f2 = (float)5.1; //强制转换为float型 } }
字符型
·char占两个字节0~65535
public class chars{ public static void main(String[] args){ char c1 = 'a'; char c2 = '小'; //char c3 = 'ab'; error 'ab'这个叫做字符串 char c4 = 97; char c5 = 65; char c6 = 48; System.out.println(c4); // ASCII码中97代表a System.out.println(c5); // ASCII码中97代表A System.out.println(c6); // ASCII码中97代表0 char a1 = '\''; // 转义字符 \ char a2 = '\t'; // 制表符 char a3 = '\n'; // 换行付 char a4 = 'a'; char a5 = 'b'; char a6 = 'c'; System.out.println(a1); System.out.println(a2); System.out.println(a4); System.out.println(a3); System.out.println(a5); System.out.println(a6); } }
布尔型
·boolean
public class bool{ public static void main(String[] args){ boolean flag = true; if (flag){ System.out.println("True"); }else{ System.out.println("Flase"); } } }
6、基础数据类型的一些问题和总结
关于基本数据类型转换规则:
1、8种基本数据类型除boolean类型之外都可以相互转换。
2、小容量向大容量转换叫做自动类型转换:
byte<short(char)<int<long<float<double
3、byte,short,char做混合运算的时候,各自都先转换成int在做运算
4、大容量向小容量转换是强制类型转换,需要加强制转换符。编译虽然通过,运行期可能损失精度。谨慎使用。
5、如果整数没有超出byte,ahort,char的取值范围,可以直接将这个整数赋值给byte,short,char
6、多种数据类型做混合运算,先转换成容量最大的那种再做运算
public class data_byte{ public static void main(String[] args){ byte a1 = 4; byte a2 = 6; //byte a3 = a1 + a2; error 不兼容类型 ,程序在运行时,会将b1和b2转换成int类型,然后再做加法运算 byte a3 = (byte)(a1 + a2); System.out.println(a3); // 10 byte a4 = 10; short a5 = 20; int a6 = a4 + a5; System.out.println(a6); //30 char a7= 'a'; // ASCII中a为97 int a8 = 100; int a9 = a7 + a8; //197 System.out.println(a9); } }
7、算术运算符

自增或自减运算符放在变量的前后有什么区别?
单独使用:没有区别
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; ++a; // a = a + 1 System.out.println(a); // 11 int b = 6; b++; // b = b + 1 System.out.print(b); // 7 System.out.print('\n'); int c = 8; --c; System.out.println(c); // 7 int d = 11; d--; System.out.println(d); // 10 } }
参与运算时:
如果放在变量的前面,则先进行自增或自减,然后再参与运算
如果放在变量的后面,则先参与运算,然后再进行自增或自减
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 6; int a1 = ++a; a = a +1 = 7,a1 = a = 7 System.out.println("a1 = " + a1); //7 System.out.println("a = " + a); //7 int b = 9; int b1 = b++; b1 = b =9, b = b +1 =10 System.out.println("b1 = " + b1); // 9 System.out.println("b = " + b); //10 int c = 10; int c1 = ++c; // c = 11,c1=c=11 int c2 = c++; // c2 = c = 11,c = c +1 == 12 System.out.println("c1 = " + c1); // 11 System.out.println("c2 = " + c2); // 11 System.out.println("c = " + c); // 12 int d = 10; int d1 = d++; // d1 = d =10, d = d + 1 =11 int d2 = ++d; // d = d + 1 = 12, d2 = d =12 System.out.println("d1 = " + d1); // 10 System.out.println("d2 = " + d2); // 12 System.out.println("d = " + d); // 12 } }
小练习
练习1:请问下面程序打印结果是什么?

public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; int b = 10; int c = 10; a = b++; c = --a; b = ++a; a = c--; System.out.println("a = " + a); //9 System.out.println("b = " + b); //10 System.out.println("c = " + c); //8 } }
练习2:请问下面程序打印结果是什么?
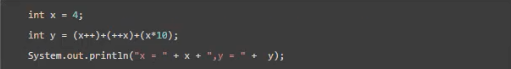
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ int x = 4; int y = (x++)+(++x)+(x*10); System.out.println("x = " + x); // 6 System.out.println("y = " + y); // 70 } }
练习3:下面程序有没有问题?

public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ byte b = 10; // b = b +1 ; error 原因:由int转为byte属于从大向小转换,应添加强制转换符 b = (byte)(b + 1); System.out.println("b = " + b); // 11 } }
练习1:请问下面程序打印结果是什么?

public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ int i = 10; i = i++; System.out.println("i = " + i); // 10 } }
8、赋值运算符
+=把左边和右边做加法,然后赋值给左边
-=把左边和右边做减法,然后赋值给左边
*=把左边和右边做乘法,然后赋值给左边
/=把左边和右边做除法,然后赋值给左边
%=把左边和右边做取余,然后赋值给左边
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a =10; a += 10; System.out.println(a); // 20 a -= 5; System.out.println(a); // 15 a *= 3; System.out.println(a); // 45 a /= 15; System.out.println(a); // 3 a %= 2; System.out.println(a); // 1 byte b =10; //b = b + 10; error 报错 b += 10; //说明扩展运算符在进行运算时,不会改变其类型,但会损失精度 } }
9、关系运算符
==判断是否相等(基本数据类型)
!= 不等于
< 大于
>=大于等于
< 小于
<=小于等于
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; int b = 15; System.out.println(a>b); // false System.out.println(a==b); // false System.out.println(a<b); // true System.out.println(a>=b); // flase System.out.println(a<=b); // true System.out.println(a!=b); // true } }
10、布尔运算符
& 逻辑与两边都是true,结果是true
| 逻辑或一边是true,结果就是true
! 逻辑非取反!true->false
^ 逻辑异或两边只要是不一致就是true
&&短路与用法和:一样。
|| 短路或用法和|一样
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println(5>3 & 3<5); //true System.out.println(7<9 | 7>9); //true System.out.println(!true); //false System.out.println(4>2 ^ 2>4); //true int a = 10; int b = 10; System.out.println(a>b && a++>b);//如果前面是false的话,后面表达式不会执行,如果前面是true的话,后面表达式会执行 System.out.println(a); //10 int c =10; int d =10; System.out.println(c==d || c++>=d);//如果前面是true的话,后面表达式不会执行,如果前面是false的话,后面表达式会执行 System.out.println(c); //10 } }
11、字符串链接运算符
1.如果两边都是数值型,则进行加法运算
2.如果两边任意一边是字符串型,则进行字符串连接运算
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println("数值为:" + 3.14); // 数值为:3,。14 int a = 10; int b = 20; System.out.println("a + b = " + (a+b)); // a + b =30 System.out.println(a + "+" + b + "=" + (a+b)); // 10 + 20 = 30 } }
12、三元运算符
boolean装达式?表达式1:表达式2;
如果boolean表达式的值是true,则返回表达式1,如果是falae,则返回表达式2
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; int b = 11; int c = (a>b) ? a : b; System.out.println(c); } }
小练习:
用java代码查找出下面三个数中的最大值,并打印出来!

public class lianxi{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 30; int d = (a>b) ? a : b; int max = (d>c) ? d : c; System.out.println(max); } }
13、位运算符
& 位与
| 位或
^ 位异或
~ 取反
>> 向右移
>>>无符号右移
<< 向左移
public class math{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println(6 & 3); //2 先把数字转化为二进制在进行比较 System.out.println(6 | 3); //7 System.out.println(6 ^ 3); //5 System.out.println(~6); //7 System.out.println(12>>1); //6 向右移n位,就除以2的n次方 System.out.println(12>>2); //3 System.out.println(12>>3); //1 System.out.println(12<<1); //24 向左移n位,就乘以2的n次方 System.out.println(12<<2); //48 System.out.println(12<<3); //96 // ^的特点:一个数据对另一个数据位异或2次,则这个数据本身不变 System.out.println(2^3^2); //2 } }
小练习:
1、请实现两个整数变量的交换(不使用第三方变量)
方法一:
public class lianxi{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a =20; int b =30; a = a+b; // a = 50 ,b = 30 b = a-b; // b = 50 - 30 ,a = 50; a = a-b; // a = 50,b = 20 ,a = 30; System.out.println("a=" + a); //a = 30 System.out.println("b=" + b); //b = 20 } }
方法二:
public class lianxi{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a =20; int b =30; a = a ^ b; b = a ^ b; a = a ^ b; System.out.println("a = " + a); // a = 30 System.out.println("b = " + b); // b = 20 } }
2、最有效率的算出2*8的结果
public class lianxi{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println(2<<3); // 16 } }
14、if、else if、else 判断语句
public class if_else{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 40; if(a>=90){ System.out.println("你很优秀哦!"); }else if(a>=80 & a<=89){ System.out.println("你也很优秀"); }else if(a>=70 & a<=89){ System.out.println("你很一般"); }else if(a>=60 & a<=69){ System.out.println("还行,你及格了"); }else{ System.out.println("加油!你的潜力很大!"); } } }
15、Switch语句
1、程序遇到break之后就停止了,break可以不写,如果不写的话,会发生case穿透
2、defau1t也可以没有
3、switch后面可以放byte,short,char,int类型的,只要可以自动转换为int类的都可以。jdk7之后可以放String类型
public class switchs{ public static void main(String[] args){ int a = 1; switch(a){ case 1: System.out.println("one"); break; case 2: System.out.println("二"); break; case 3: System.out.println("三"); break; default: System.out.println("四五六七八"); break; } } }
16、for循环语句
1、执行初始化的表达式,并且在整个循环里面只执行
2、将初始化的表达式的值在条件表达式里面进行判断
如果结果是true,则程序继续执行
如果结果是falae,则循环执行结束:
3、java语句
4、执行循环之后的表达式
5、程序再回到第二步继续执行
public class For{ public static void main(String[] args){ for(int i = 0; i < 10;i++){ System.out.println("HelloWorld!"); } } }
小练习:
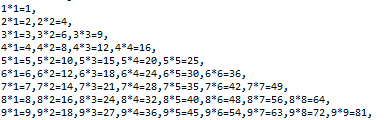
1、在屏幕中打印九九乘法表
public class For{ public static void main(String[] args){ for (int i=1;i<10;i++ ){ for(int j=1;j<=i;j++){ System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + (i*j) + ","); } System.out.print('\n'); } } }
2、计算1-100所有的奇数求和
public class For{ public static void main(String[] args){ int j = 0; for(int i = 1; i < 100;i += 2){ j= j + i; } System.out.println(j); } }
17、while循环
当写while语句时,千万别写出死循环!
public class While{ public static void main(String[] args){ int i =10; while(i>0){ System.out.println("HelloWorld!"); i--; } } }
18、do while语句
public class do_while{ public static void main(String[] args){ int i =10; do{ System.out.println(i); i--; }while(i>0); } }
19、函数方法
1、方法的结构:
public class sumInt{ public static void main(String[] args){ sumInt(3,4); int Sum = sumsInt(4,5); System.out.println(Sum); } // 无返回值类型,用void public static void sumInt(int a,int b){ int sum = a + b; System.out.println(sum); } // 有返回值类型 public static int sumsInt(int a,int b){ int sum = a + b; return sum; } }
2、方法的调用
class diaoyong{ public static void main(String[] args){ A2(10,10); diaoyong.A2(20,20); B.B1(30,30); } public static void A2(int a,int b){ int sum = a + b; System.out.println(sum); } } class B{ public static void B1(int a,int b){ int sum = a + b; System.out.println(sum); } }
注意:不要出现方法的互相调用,这样会导致一个错误StackOverFlowError
class diaoyong{ public static void main(String[] args){ B.B1(); } } class B{ public static void B1(){ B2(); } public static void B2(){ B1(); } }
3、ruturn的使用
return后面不能有语句,否则会出现缺少返回语句的错误!
class Return{ public static void main(String[] args){ int sum = sumInt(3,4); System.out.println(sum); } public static int sumInt(int a,int b){ int sum = a + b; return sum; System.out.println("出错误了吧!"); } }
20、方法重载
方法重载的条件:
1、需要在同一个类里面;
2、方法名相同;
3、参数列表不同(参数类型、个数、顺序)
class chongzai{ public static void main(String[] args){ } //参数个数不同,m1方法构成重载 public static void m1(){} public static void m1(int i){} //参数类型不同,m2构成重载 public static void m2(int i){} public static void m2(long i){} //参数的顺序不同,m3方法可以构成重载,但是在开发中,不这样使用 public static void m3(int i,long j){} public static void m3(long j,int i){} //下面的几种方法均不可以,程序会报错 /* // 方法重名 public static void m4(){} public static void m4(){} //重载跟返回值类型没有关系 public static void m5(){} public static int m5(){ return 1; } //重载跟修饰符列表没有关系 public static void m6(){} public void m6(){} */ }
21、递归
1、使用递归方式计算1至n的和
递归就是方法自己调用自己,要有一个结束条件,否则或出现StackOverflowError
class chongzai{ public static void main(String[] args){ System.out.println(sum(100)); } public static int sum(int n){ if(n==1){ return 1; }else{ return n + sum(n-1); } } }

