【堆】好多好多基础知识
(zbl)
part1:基础知识
-
堆的定义:
它是一种数据结构,可以看作是一棵完全二叉树(没有写二叉树就来写堆小声bb)
一般我们用数组来存堆

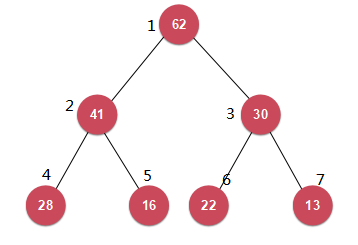 用数组存=>
用数组存=>
-
堆的性质:
一个长度为len的数组A,设它的结点个数为size,size<=len,辣么我们用A[i]储存二叉树中编号为i的结点值。树根为A[1],那么对于一个编号为i的结点,我们可以知道它的父结点(father(i))为i/2(请注意为整除),两个子结点分别为:左(left(i)):2i,右(right(i)):2i+1;
此外,堆具有一个完全二叉树不具备的性质:
大根堆:对于除根以外的每个结点i,A[father(i)]>=A[i];
小根堆:对于除根以外的每个结点i,A[father(i)]<=A[i];
-
操作一个堆:
- 向堆中加入一个元素(put):
以小根堆为例:(摘自ybt)
(1)在堆尾加入一个元素,并把这个结点置为当前结点;
(2)比较当前结点和它的父结点的大小
if(A[i]<A[father(i)])swap(A[i],A[father(i)])并把父结点置为当前结点;转(2)
if(A[i]>=A[father(i)]);转(3)
(3)结束;
手动码:
void put(int d){//小根堆 int now,next; heap[++heap_size]=d;//爸新加入的元素放到最后 now=heap_size;//记录新加入的值的位置 while(now>1){//保证没有比出堆取 next=now/2;//父结点 if(heap[now]>=heap[next])break;//如果满足小根堆的条件,直接弹出 swap(heap[now],heap[next]);//否则交换父结点与d now=next;//标记d现在的位置 } }
(据说algorithm里有函数,还没研究)
- 取出并删除一个元素(get)(取堆顶):
(1)取出堆的根结点的值;
(2)把堆的最后一个结点放到根的位置上,把根覆盖掉。堆长-1;
(3)把根结点置为当前父结点pa;
(4)如果pa无儿子(fa>len/2),则转(6),否则,把pa的两(或一)个儿子中最小的一个置为当前的子结点son;
(5)比较pa与son的值:
如果pa的值小于或等于son,则转(6);否则,交换这两个结点的值,把pa指向son,转(4);
(6)结束;
手动码:
void get(){ int now,next,res; res=heap[1]; heap[1]=heap[heap_size--]; now=1; while(now*2<=heap_size){ next=now*2; if(next<heap_size&&heap[next+1]<heap[next])next++; if(heap[now]<=heap[next])break; swap(heap[now],heap[next]); now=next; } return res; }
part2:一个例题
主要就是一些堆的基本操作,插入和删除元素,基本和上面一样qwq
直接代码奉上:
#include<iostream> #include<algorithm> #include<cstdio> #include<cstring> using namespace std; int n,a,b; int heap[1000010],heap_size; int get(){ int now,next,res; res=heap[1]; heap[1]=heap[heap_size--]; now=1; while(now*2<=heap_size){ next=now*2; if(next<heap_size&&heap[next+1]<heap[next])next++; if(heap[now]<=heap[next])break; swap(heap[now],heap[next]); now=next; } return res; } void put(int d){ int now,next; heap[++heap_size]=d; now=heap_size; while(now>1){ next=now/2; if(heap[now]>=heap[next])break; swap(heap[now],heap[next]); now=next; } } int main(){ scanf("%d",&n); for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ scanf("%d",&a); if(a==1){ scanf("%d",&b); put(b); continue; } if(a==2){ printf("%d\n",heap[1]); continue; } if(a==3){ get(); continue; } } return 0; }




