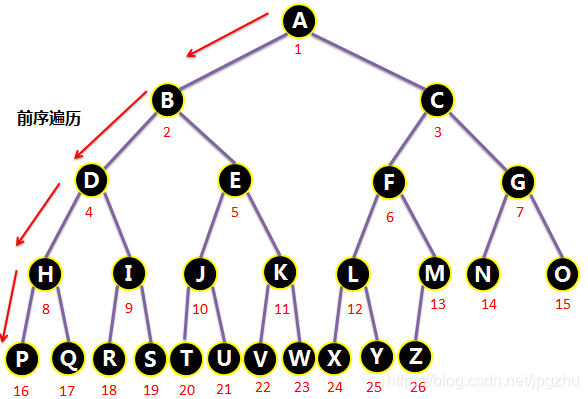
自己动手作图深入理解二叉树、满二叉树及完全二叉树
一、背景
二叉树是数据结构中的重点,也是难点。二叉树是一种非线性结构,比数组、栈、队列等线性结构相比复杂度更高,想要做到心中有“树”,需要自己动手画图、观察、思考,才能领会其真谛。该文将会结合图形,深入理解二叉树、满二叉树及完全二叉树的概念。
二、基本概念
2.1 结点
- 结点是组成二叉树的最小单元。
-- 用图形表示

-- 用代码表示
// 结点
class Node<E> {
E e;
Node left, right;
Node(E e) {
this.e= e;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
2.2 二叉树
- 每个结点的度(结点拥有的子树数目)不超过2的树叫做二叉树
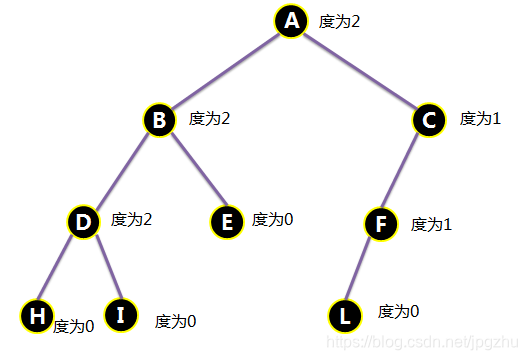
2.2.1 二叉树的深度
- 结点的最大层次数称为树的深度或高度
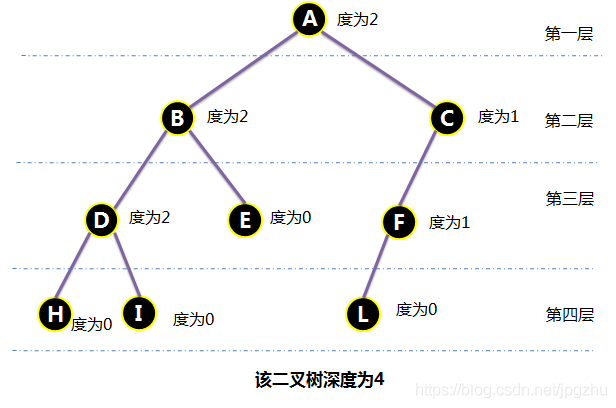
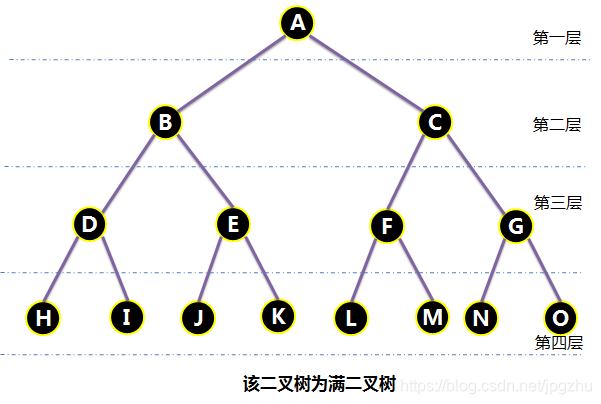
2.3 满二叉树
- 指深度为k且有2k-1个结点的二叉树,即所有分支结点都存在左子树和右子树,并且所有叶子都在同一层上。
- 下图中深度为4,24-1=15个结点,且所有叶子都在第四层上。
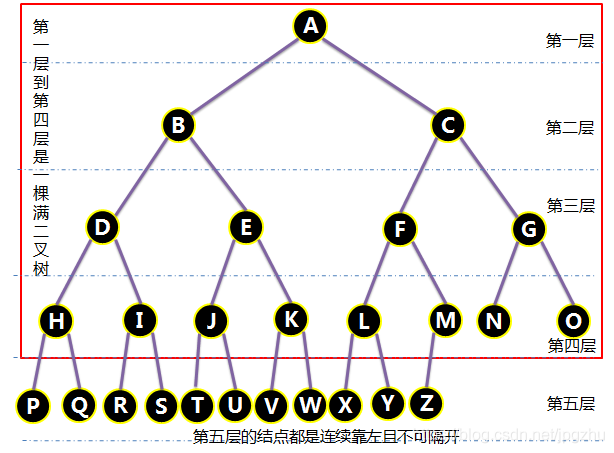
2.4 完全二叉树
- 一颗深度为k的二叉树,k层的结点都是连续靠左并不可隔开的,并且1~k-1层的结点也组成了一棵满二叉树,这样的二叉树,我们称为完全二叉树。
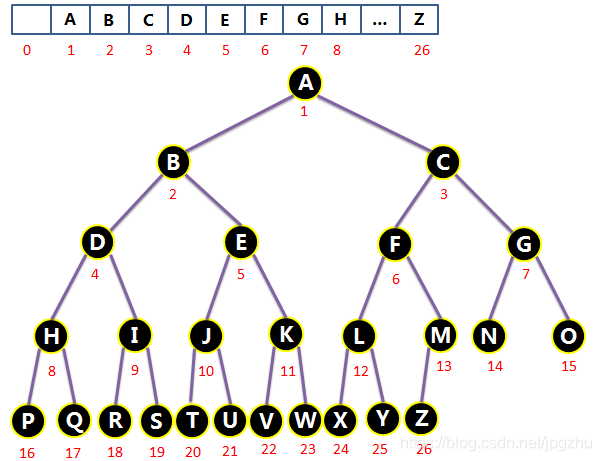
2.4.1 完全二叉树的线性存储
- 出于简便起见,完全二叉树通常采用数组进行线性存储
/**
* 完全二叉树的线性存储
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-24
*/
public class FullBinaryTree {
private Object[] arr;
private int size;
FullBinaryTree(int capacity) {
this.arr = new Object[capacity + 1];
this.size = 0;
}
public int getSize() {
return this.size;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.size == 0;
}
public void add(Object e, int index) {
assert index <= this.arr.length;
this.arr[index] = e;
this.size++;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "FullBinaryTree{" +
"arr=" + Arrays.toString(arr) +
", size=" + size +
'}';
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
FullBinaryTree fullBinaryTree = new FullBinaryTree(26);
// 从下标1开始存入26个字母
for (Character c = 'A'; c <= 'Z'; c++) {
fullBinaryTree.add(c, c - 'A' + 1);
}
System.out.println( fullBinaryTree.toString());
}
}

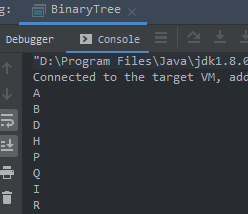
2.4.2 完全二叉树的创建与遍历
/**
* 完全二叉树的创建与遍历
*
* @author zhuhuix
* @date 2020-06-24
*/
public class BinaryTree {
// 结点
private Node root;
// 结点数
private int size;
// 存放结点
private ArrayList<Node> list;
public BinaryTree() {
this.root = null;
this.size = 0;
this.list = new ArrayList<>();
}
public void createTree(Object[] array){
for(int i=0;i<array.length;i++){
Node node =new Node(array[i]);
list.add(node);
if (this.root==null){
this.root = node;
}
}
if(list.size()>0){
for(int i=0;i<array.length/2;i++){
if(2*i+1<list.size()) {
list.get(i).left=list.get(2 * i + 1);
}
if(2*i+2<list.size()) {
list.get(i).right=list.get(2 * i + 2);
}
}
}
}
// 前序遍历
public void preOrder(Node root){
if(root == null){
return ;
}
else{
System.out.println(root.getData());
}
preOrder(root.left);
preOrder(root.right);
}
public Node getRoot() {
return root;
}
// 私有内部类-树结点
private class Node {
Object data;
Node left, right;
Node(Object data) {
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
Object getData() {
return data;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinaryTree binaryTree = new BinaryTree();
Character[] array ={'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L',
'M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z'};
binaryTree.createTree(array);
binaryTree.preOrder(binaryTree.getRoot());
}
}