c语言和matlab语言实现牛顿迭代法解非线性方程和非线性方程组
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<stdlib.h> 3 #include<math.h> 4 #include<float.h> 5 #include<time.h> 6 7 #define PI 3.14159265358979323846 /* pi */ 8 #define ε 1.0e-12 9 int main() 10 { 11 double x0 = PI;//取的初始值 12 double x1 = 0.0;//有x0算出的x1,初始值先给定0 13 double fx = 0.0;//f(x) 14 double fxp = 0.0;//f(x)的导数 15 double faix = 0.0;//计算结果,牛顿迭代格式 faix =x-(fx/fxp) 16 int i = 0;//迭代计算次数 17 while (fabs((x0 - x1) / x1) > ε)//判断两次迭代变量之间相对误差与精度比较 18 { 19 x1 = x0;//用x1存放上次的x0 20 fx = sin(x0) - x0 / 2; 21 fxp = cos(x0) - 0.5; 22 faix = x0 - fx / fxp; 23 x0 = faix;//将迭代后的结果赋给上次代入值变量,供下一次代入使用 24 i++;//计算次数 25 printf("第%d次迭代,迭代结果为:,%+.12e \n", i, x1); 26 } 27 }
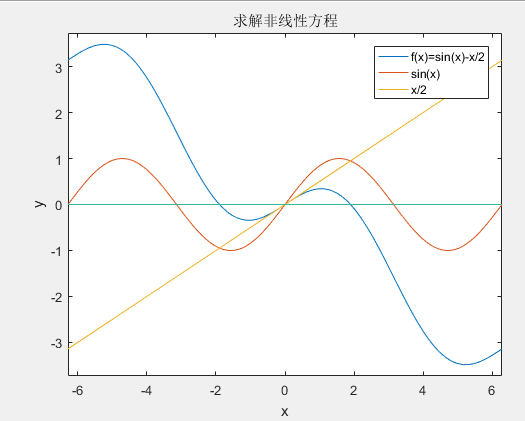
题目:计算sinx=x/2的根。
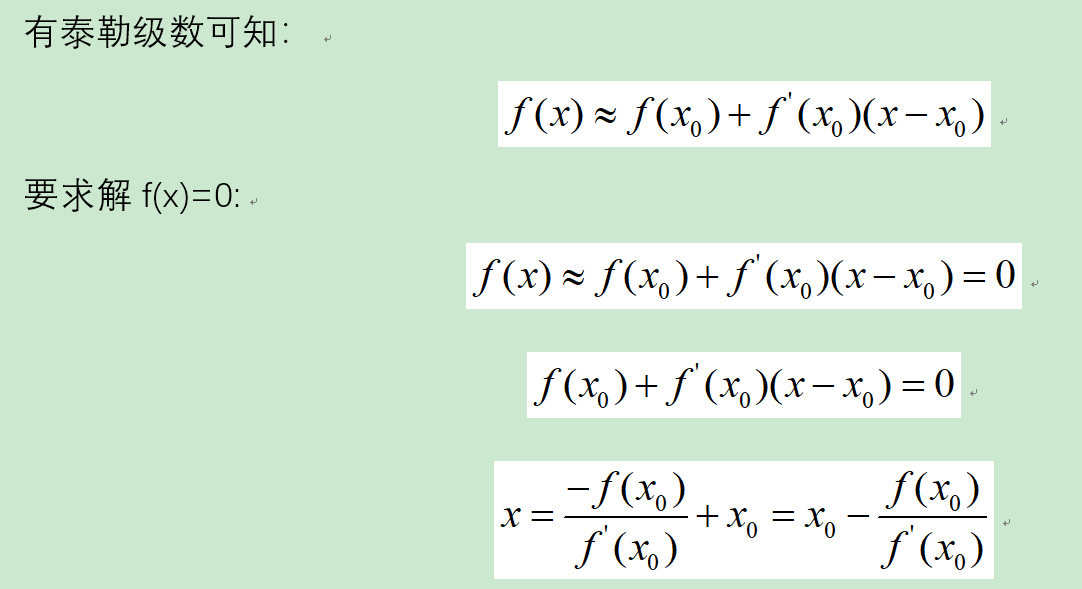
分析:newton法在大范围的收敛定理:
函数f(x)在区间[a,b]上存在二阶连续导数,且满足4个条件:
1. f(a)*f(b)<0
2. 当x属于[a,b]时,函数的导数值不等于零。
3. 当x属于[a,b]时,函数的二阶导数值保号。
4. a-f(a)/f'(a)<=b,且b-f(b)/f'(b)<=a

计算结果:

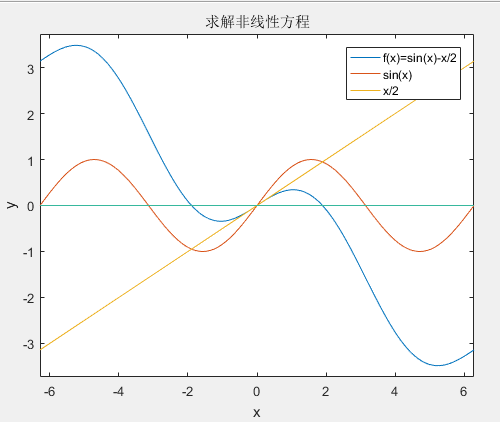
matlab求解非线性方程:
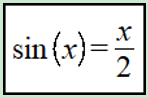 ,x=[pi/2,pi] 。
,x=[pi/2,pi] 。
1 clc; 2 clear all; 3 close all; 4 %% 绘图 5 ezplot('sin(x)-x/2') 6 hold on; 7 ezplot('sin(x)') 8 hold on; 9 ezplot('x/2') 10 hold on; 11 ezplot('y=0*x') 12 legend('f(x)=sin(x)-x/2','sin(x)','x/2') 13 title('求解非线性方程') 14 %% 牛顿迭代法 15 fx=@(x)sin(x)-x/2.0;%定义 f(x)=sin(x)-x/2 匿名函数 16 DfxDx=@(x) cos(x)-1/2.0;% 定义f'(x) 17 epsilonT=1e-12;%收敛判断标准:相对误差 18 x0=pi;%给初值 19 n=0;%迭代次数 20 while 1 21 x1=x0-fx(x0)/DfxDx(x0); 22 epsilon=abs((x1-x0)/x1); 23 x0=x1; 24 n=n+1; 25 disp(['第' num2str(n) '次迭代,x=', num2str(x1,15)]); 26 if epsilon<epsilonT 27 break;%跳出while循环 28 end 29 end 30 disp('end')
第1次迭代,x=2.0943951023932
第2次迭代,x=1.91322295498104
第3次迭代,x=1.89567175194481
第4次迭代,x=1.89549428525543
第5次迭代,x=1.89549426703398
第6次迭代,x=1.89549426703398
end
mathematica求解:
Clear["Global`*"]
f = Sin[#] - #/2 &;(*f[x_]:=Sin[x]-x/2;*)
newton[f_, x0_] :=
With[{fp = f'}, FixedPoint[# - f[#]/fp[#] &, x0, 6]];
NumberForm[newton[f, Pi] // N, 20]

Clear["Global`*"] newtonMethod[func_, funcp_, init_, dx_ : 0.0001, tol_ : 10.^-6] := Module[{x = init + dx, x0 = init}, While[Abs[(x - x0)/x] > tol, {x0, x} = {x, x0 - func[x0]/funcp[x0]}; Print[NumberForm[x // N, {20, 19}]]]; x] func = Sin[#] - #/2 &; NumberForm[newtonMethod[func, func', Pi, 10.^-3, 10.^-12] // N, 20]

Clear["Global`*"] newtonMethod[func_, funcp_, init_, dx_ : 0.0001, tol_ : 10.^-6] := Module[{x = init + dx, x0 = init, n = 0}, While[Abs[(x - x0)/x] > tol && n < 6,(*当误差大于容许误差或者迭代超过6次,就停止*) {x0, x} = {x, x0 - func[x0]/funcp[x0]};(*牛顿迭代法*) n = n + 1;(*计数*) Print["第" , n , "次计算:", NumberForm[x // N, {20, 19}]]];(*打印*) x(*函数返回值*) ]; func = Sin[#] - #/2 &; NumberForm[newtonMethod[func, func', Pi, 10.^-3, 10.^-12] // N, 20]

1stopt解非线性方程:
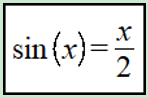 ,x=[pi/2,pi] 。
,x=[pi/2,pi] 。
1 NewCodeBlock"求解非线性方程"; 2 // 3 AlgorithmOption =[1,0,1.00E-30,1000,20,30,50,20,0,0.15,1]; 4 Parameter x=[pi/2,pi]; 5 Function sin(x)=x/2;
求解非线性方程
====== 结果 ======
迭代数: 21
计算用时(时:分:秒:微秒): 00:00:00:119
计算结束原因: 达到收敛判断标准
优化算法: 通用全局优化算法(UGO1)
函数表达式 sin(x)-(x/2) = 0
目标函数值(最小): 0
x: 1.89549426703398
====== 计算结束 ======
准牛顿方法解非线性方程:sin(x)=x/2,x=[pi/2,pi]
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/101077902

1 %% qusi-newton 准牛顿(割线法,不用求导数,用割线斜率代替切线) 2 clc; 3 clear all; 4 close all; 5 f=@(x)sin(x)-x/2.0;%定义 f(x)=sin(x)-x/2 匿名函数 6 epsilonT=1e-12;%收敛判断标准:相对误差 7 x0=pi/2;%给初值 8 x1=pi/2+0.1; 9 n=0;%迭代次数 10 while 1 11 % x2=x0-f(x0)*(x1-x0)/(f(x1)-f(x0)); 12 x2=x1-f(x1)*(x1-x0)/(f(x1)-f(x0));%等同于上句,都行 13 epsilon=abs((x1-x0)/x1); 14 x0=x1; 15 x1=x2; 16 n=n+1; 17 disp(['第' num2str(n) '次迭代,x=', num2str(x1,15)]); 18 if epsilon<epsilonT 19 break;%跳出while循环 20 end 21 end 22 disp('qusi-newton end')
第1次迭代,x=1.96101103612234
第2次迭代,x=1.88595391153747
第3次迭代,x=1.89514618938836
第4次迭代,x=1.89549620158427
第5次迭代,x=1.89549426664428
第6次迭代,x=1.89549426703398
第7次迭代,x=1.89549426703398
第8次迭代,x=1.89549426703398
qusi-newton end
非线性多元方程组用牛顿法求解:
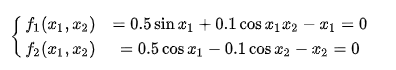

1 % https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/146371408 2 % https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/63103354 知乎代码 3 clc; 4 clear all; 5 close all; 6 x0=[1 2]; 7 eps=1e-12; 8 [allx,ally,r,n]=mulNewton(fun,x0,eps); 9 10 disp(['迭代' num2str(n) '次,' 'x1=' num2str(eval(r(1)),100) ',x2=' num2str(eval(r(2)),100) ])% 0.19808577588668504464406945200284 11 % disp(r) 12 disp('newton end') 13 %% 子函数区域 14 function [allx,ally,r,n]=mulNewton(F,x0,eps) 15 if nargin==2 16 eps=1.0e-4; 17 end 18 x0 = transpose(x0); 19 Fx = subs(F,transpose(symvar(F)),x0);%将初始点代入方程组 20 var = transpose(symvar(F)); 21 dF = jacobian(F,var);%求雅克比矩阵 22 dFx = subs(dF,transpose(symvar(F)),x0);%将当前解带入雅克比矩阵 23 r=x0-inv(dFx)*Fx';%迭代 24 n=1; 25 tol=1; 26 N=100; 27 symx=length(x0); 28 ally=zeros(symx,N); 29 allx=zeros(symx,N); 30 31 while tol>eps 32 x0=r; 33 Fx = subs(F,transpose(symvar(F)),x0); 34 dFx = subs(dF,transpose(symvar(F)),x0); 35 r=vpa(x0-inv(dFx)*Fx'); 36 tol=norm(r-x0) 37 if(n>N) 38 disp('迭代步数太多,可能不收敛!'); 39 break; 40 end 41 allx(:,n)=x0; 42 ally(:,n)=Fx; 43 n=n+1; 44 end 45 end 46 47 48 function f = fun(x) 49 k=2; 50 for i=1:k 51 x(i)=sym (['x',num2str(i)]); 52 end 53 54 f(1)=0.5*sin(x(1))+0.1*cos(x(1)*x(2))-x(1); 55 f(2)=0.5*cos(x(1))-0.1*cos(x(2))-x(2); 56 end

1stopt求解非线性方程组:
1 NewCodeBlock"求解非线性方程组"; 2 //https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/63103354 3 //https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/146371408 4 AlgorithmOption =[1,0,1.00E-30,1000,20,30,50,20,0,0.15,1]; 5 Parameter x(2); 6 Function 0.5*sin(x1)+0.1*cos(x1*x2)-x1=0; 7 0.5*cos(x1)-0.1*cos(x2)-x2=0;
求解非线性方程组
====== 结果 ======
迭代数: 21
计算用时(时:分:秒:微秒): 00:00:00:429
计算结束原因: 达到收敛判断标准
优化算法: 通用全局优化算法(UGO1)
函数表达式 1: 0.5*sin(x1)+0.1*cos(x1*x2)-x1-0 = 0
2: 0.5*cos(x1)-0.1*cos(x2)-x2-0 = 0
目标函数值(最小): 0
x1: 0.198085775886685
x2: 0.398040303134032====== 计算结束 ======
多元线性方程组求解:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/128577559
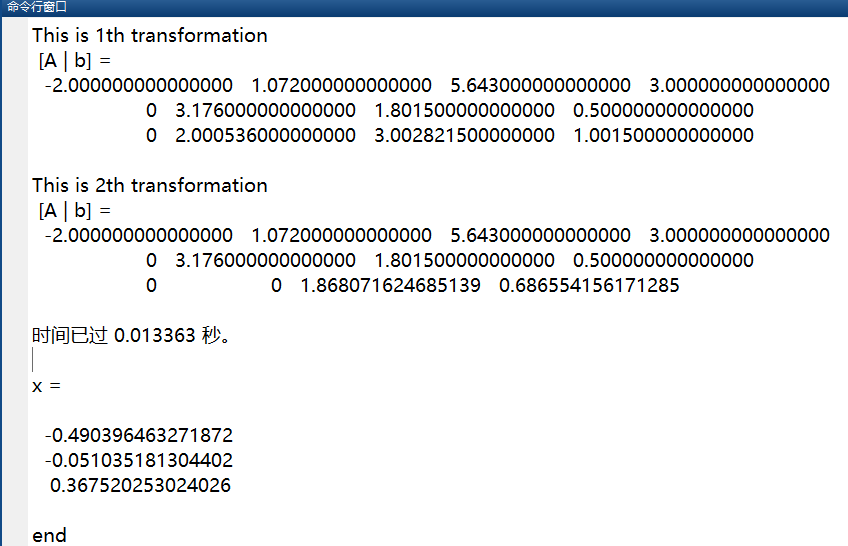
高斯列主元消去法:

1 % 高斯列主元消去法 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/128577559 2 % 先选择每列元素绝对值最大值放通过行变换放在主对角线上,之后将矩阵A化为上三角矩阵,然后回代求解线性方程组Ax=b。 3 clc; 4 clear all; 5 close all; 6 % A=[2 8 2; 7 % 1 6 -1; 8 % 2 1 2];%https://wenku.baidu.com/view/99bf58cf050876323112120c.html 9 % b=[14 13 5]'; 10 A=[0.001 2 3; 11 -1 3.712 4.623; 12 -2 1.072 5.643];%https://wenku.baidu.com/view/99bf58cf050876323112120c.html 13 b=[1 14 2 15 3 ]; 16 x = gaussPivotScale(A, b) 17 disp('end'); 18 19 function x = gaussPivotScale(A, b) 20 21 %GAUSSPIVOTSCALE It uses Gauss elimination with partial pivoting 22 % and row scaling to solve the linear system Ax = b. 23 % A : It is the n-by-n coefficient matrix. 24 % b : It is the n-by-1 result vector. 25 % x : It is the n-by-1 solution vector. 26 27 tic 28 format long 29 30 % judge wether there is a solution or not from the linear system 31 r_A = rank(A); 32 r_Ab = rank([A, b]); 33 34 if r_A ~= r_Ab 35 disp('This linear system is no solution'); 36 end 37 38 % Elimination 39 40 [row, ~] = size(A); 41 C = [A, b]; 42 43 for k = 1 : row-1 44 45 % style of table 46 fprintf('This is%2dth transformation \n [A | b] = \n', k); 47 48 M = max(abs(C(k:end, k:end-1)), [], 2); % find maximum in kth row,A所有行每行元素绝对值最大值 49 a = abs(C(k:end, k)); % each value is absoluted value in kth column,所有行第k列绝对值 50 [~, id] = max(a ./ M); % find row with maximum 51 52 if id > k 53 C([k, id], :) = C([id, k], :); % pivot rows 54 end 55 56 mult = C(k+1:row, k) / C(k, k); % construct multipliers 57 58 % creat mesh, and improve speed 59 [C_k, mult] = meshgrid(C(k, :), mult); 60 C(k+1:row, :) = C(k+1:row, :) - C_k .* mult; 61 62 disp(C) 63 end 64 65 % Back Substitution 66 [row, ~] = size(C); 67 68 for k = row : -1 : 1 69 C(k, :) = C(k, :) ./ C(k, k); 70 C(1:k-1, row+1) = C(1:k-1, row+1) - C(1:k-1, k) * C(k, row+1); 71 end 72 73 x = C(:, end); 74 75 toc 76 77 end