socketpair通信
1、线程间通信(参考安卓源码InputTransport.cpp)
#include <pthread.h> #include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */ #include <sys/socket.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> static const size_t SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE = 32 * 1024; void *pthread_1(void *arg) { int fd = *((int *)arg); char buf[512]; int len; int cnt = 0; while (1) { len = sprintf(buf, "hello, main pthread, cnt = %d", cnt++); write(fd, buf, len); len = read(fd, buf, 500); buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); sleep(5); } return NULL; } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int sockets[2]; pthread_t thread_id; if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0, sockets)) { printf("socketpair error\n"); return -1; } int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE;
/* 创建4个buff, sockets[0]的发送buff和接收buff; sockets[1]的发送buff和接收buff*/ setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize)); setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize)); setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize)); setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize)); int res = pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, pthread_1, (void *)(&sockets[1])); if (res) { printf("pthread_create error\n"); return -1; } int fd = sockets[0]; char buf[512]; int len; int cnt = 0; while (1) { len = sprintf(buf, "hello, pthread1, cnt = %d", cnt++); write(fd, buf, len); //将buf中的内容通过fd句柄发送到snd buff len = read(fd, buf, 500); //通过读fd中的rcv buff, 将内容读到buf中,然后打印出来 buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); sleep(5); } return 0; }
打印信息:
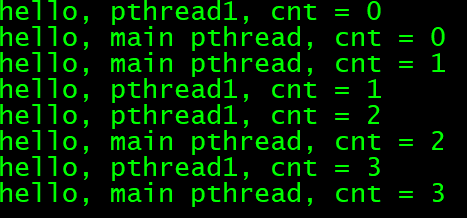
再打开一个终端查看进程:ps -A 查看socketpair的pid为6065
cd /proc/6065
ls task
2、父子进程间通信
需要注意的是fd == 0是子进程,fd > 0 是父进程
#include <unistd.h> #include <sys/types.h> /* See NOTES */ #include <sys/socket.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <unistd.h> static const size_t SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE = 32 * 1024; int main(int argc, char **argv) { int sockets[2]; if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0, sockets)) { printf("socketpair error\n"); return -1; } int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE; setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize)); setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize)); setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize)); setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize)); pid_t fd = fork();if (fd == 0) { /* 子进程 */ int fd = sockets[1]; char buf[512]; int len; int cnt = 0; while (1) { len = sprintf(buf, "hello, father pid, cnt = %d", cnt++); write(fd, buf, len); len = read(fd, buf, 500); buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); sleep(5); } } if (fd > 0) { /* 父进程 */ int fd = sockets[0]; char buf[512]; int len; int cnt = 0; while (1) { len = sprintf(buf, "hello, child pid, cnt = %d", cnt++); write(fd, buf, len); len = read(fd, buf, 500); buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); sleep(5); } } return 0; }
运行结果:

查看进程:ps -A 有2个名为fork的进程

3、使用binder传递文件句柄,实现进程间通信
4、看得出来socketpair实现了进程或线程间的双全工通信
而管道一般是半全工通信,要双全工就得创建2个管道
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> int main(int argc, char **argv) { int fd[2]; //fd[0]是读,fd[1]是写 int fd2[2]; int res = pipe(fd); if (res) { printf("create pipe error\n"); return -1; } res = pipe(fd2); if (res) { printf("create pipe2 error\n"); return -1; } pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid > 0) { char buf[512]; int len; while (1) { len = sprintf(buf, "hello my child!"); buf[len] = '\0'; write(fd[1], buf, len); len = read(fd2[0], buf, 512); buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); sleep(3); } } else if (pid == 0) {char buf[512]; int len; while (1) { len = read(fd[0], buf, 512); buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); len = sprintf(buf, "hello my father!"); buf[len] = '\0'; write(fd2[1], buf, len); sleep(3); } } return 0; }
同样pipe也可以用于线程间通信:
#include <unistd.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <pthread.h> struct pipe_rw { int fd_r; int fd_w; }; void *thread_handle(void *arg) { struct pipe_rw *pPipeRw = (struct pipe_rw *)arg; char buf[512]; int len; while (1) { len = read(pPipeRw->fd_r, buf, 512); buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); len = sprintf(buf, "hello my father"); buf[len] = '\0'; write(pPipeRw->fd_w, buf, len); sleep(3); } } int main(int argc, char **argv) { int fd[2]; //fd[0]是读,fd[1]是写 int fd2[2]; int res = pipe(fd); if (res) { printf("create pipe error\n"); return -1; } res = pipe(fd2); if (res) { printf("create pipe2 error\n"); return -1; } pthread_t thread; struct pipe_rw pipe_arg; pipe_arg.fd_r = fd[0]; pipe_arg.fd_w = fd2[1]; pthread_create(&thread, NULL, thread_handle, &pipe_arg); char buf[512]; int len; while (1) { len = sprintf(buf, "hello my child"); buf[len] = '\0'; write(fd[1], buf, len); len = read(fd2[0], buf, 512); buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); sleep(3); } return 0; }
命名管道:
write:
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #define PATH "./myfifo" int main(int argc, char **argv) { int res = mkfifo(PATH, 0666|S_IFIFO); //在当前目录下创建一个名为myfifo的管道 if (res) { printf("create named pipe error\n"); return -1; } int fd = open(PATH, O_WRONLY); //命名管道是可以直接open的 if (fd < 0) { printf("open %s error\n", PATH); return -1; } char buf[512]; int len; len = sprintf(buf, "hello world"); while (1) { write(fd, buf, len); sleep(3); } close(fd); return 0; }
read:
#include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <stdio.h> #define PATH "./myfifo" int main(int argc, char **argv) { int fd = open(PATH, O_RDONLY); if (fd < 0) { printf("open %s error\n", PATH); return -1; } char buf[512]; int len; while (1) { len = read(fd, buf, 512); buf[len] = '\0'; printf("%s\n", buf); } close(fd); return 0; }



