实验2 类和对象基础编程1
一、实验目的
加深对OOP中类、对象的理解,能够解释类的封装、类的接口 会使用C++语法规则正确定义、实现、测试类;会使用类创建对象,并基于对象编程 针对具体问题场景,练习运用面向对象思维进行设计,合理利用C++语言特性(访问权限控制, static, friend, const),在数据共享和保护之间达到平衡 会用多文件方式组织代码 加深对C++内存资源管理技术的理解,能够解释构造函数、析构函数的用途,分析它们何时会被调 用
二、实验内容
1. 实验任务1 验证性实验:简单类T的定义和测试。
这个简单任务覆盖以下内容:
类的定义(封装)
类的使用:对象的创建、访问
数据共享机制 在同一个对象的所有操作之间共享数据 —— 实现机制:封装
在同一个类的所有对象之间共享数据 —— 实现机制:类的static成员
在不同模块(类、函数)之间共享数据 —— 实现机制:友元
数据保护机制 const对象 const引用作为形参 const成员数据/函数
代码组织方式:多文件结构
test1
代码
t.h
类的声明、友元函数的声明
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <string> 4 5 // 类T: 声明 6 class T { 7 // 对象属性、方法 8 public: 9 T(int x = 0, int y = 0); // 普通构造函数 10 T(const T &t); // 复制构造函数 11 T(T &&t); // 移动构造函数 12 ~T(); // 析构函数 13 14 void adjust(int ratio); // 按系数成倍调整数据 15 void display() const; // 以(m1, m2)形式显示T类对象信息 16 17 private: 18 int m1, m2; 19 20 // 类属性、方法 21 public: 22 static int get_cnt(); // 显示当前T类对象总数 23 24 public: 25 static const std::string doc; // 类T的描述信息 26 static const int max_cnt; // 类T对象上限 27 28 private: 29 static int cnt; // 当前T类对象数目 30 31 // 类T友元函数声明 32 friend void func(); 33 }; 34 35 // 普通函数声明 36 void func();
t.cpp
类的实现、友元函数的实现
1 // 类T: 实现 2 // 普通函数实现 3 4 #include "t.h" 5 #include <iostream> 6 #include <string> 7 8 using std::cout; 9 using std::endl; 10 using std::string; 11 12 // static成员数据类外初始化 13 const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"}; 14 const int T::max_cnt = 999; 15 int T::cnt = 0; 16 17 18 // 对象方法 19 T::T(int x, int y): m1{x}, m2{y} { 20 ++cnt; 21 cout << "T constructor called.\n"; 22 } 23 24 T::T(const T &t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 25 ++cnt; 26 cout << "T copy constructor called.\n"; 27 } 28 29 T::T(T &&t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} { 30 ++cnt; 31 cout << "T move constructor called.\n"; 32 } 33 34 T::~T() { 35 --cnt; 36 cout << "T destructor called.\n"; 37 } 38 39 void T::adjust(int ratio) { 40 m1 *= ratio; 41 m2 *= ratio; 42 } 43 44 void T::display() const { 45 cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")" ; 46 } 47 48 // 类方法 49 int T::get_cnt() { 50 return cnt; 51 } 52 53 // 友元 54 void func() { 55 T t5(42); 56 t5.m2 = 2049; 57 cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); cout << endl; 58 }
main.cpp
测试模块、main函数
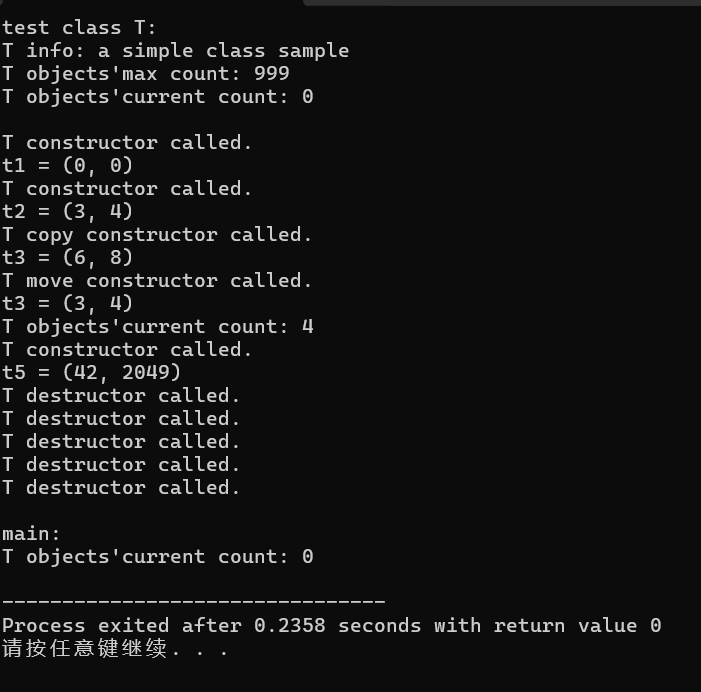
1 #include "t.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 7 void test(); 8 9 int main() { 10 test(); 11 cout << "\nmain: \n"; 12 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; 13 } 14 15 void test() { 16 cout << "test class T: \n"; 17 cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl; 18 cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl; 19 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl; 20 21 22 T t1; 23 cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl; 24 25 T t2(3, 4); 26 cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl; 27 28 T t3(t2); 29 t3.adjust(2); 30 cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl; 31 32 T t4(std::move(t2)); 33 cout << "t3 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl; 34 35 cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl; 36 37 func(); 38 }
运行结果:
Q&A
1.若去掉下图中line36中友元函数func()的声明,代码能否正常运行?若无法运行,报错信息是什么?原因?

结果:
编译无错误。
2.分析下列构造函数与析构函数的作用与调用时机

T(int x = 0,int y = 0);
普通构造函数,支撑0个参数传入(默认x,y均为0),1个参数传入(参数x为传入值,y为0),2个参数传入的情况(x,y均获得传入值)
当传入参数为int型的参数时,调用普通构造函数
T(const T &t);
复制构造函数,将T类型的对象t的值传给新构造的对象t2
当传入参数为T类型的一个已存在的对象时,调用复制构造函数
T(const T &&t)
移动构造函数,将T类型的,已经存在的对象t的参数,移动到新构造的对象t2的内存空间上
当传入参数为右值引用t,且编译器判断t的内存空间已经不需要使用时,调用移动构造函数
~T();
析构函数,当一个函数模块运行完,也就是当一个对象t的生命周期结束时,调用析构函数
3.分析将t.cpp中类属性的定义转移至t,h中,能否正常运行

运行结果:无报错,正常运行
2. 实验任务2 不使用C++标准库提供的复数模板类,设计并实现一个简化版的复数类Complex。
代码
complex.h
1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 4 //类的声明 5 class Complex{ 6 //对象的属性和方法 7 public: 8 Complex(double x = 0,double y = 0); 9 Complex(const Complex &c); 10 ~Complex(); 11 12 double get_real(); 13 double get_imag(); 14 Complex add(Complex c); 15 16 private: 17 double real; 18 double imag; 19 20 //类的属性和方法 21 22 public: 23 static const std::string doc; 24 25 26 //类Complex的友元函数 27 friend void output(Complex c); 28 friend double abs(Complex c); 29 friend Complex add(Complex c1,Complex c2); 30 friend bool is_equal(Complex c1,Complex c2); 31 friend bool is_not_equal(Complex c1,Complex c2); 32 }; 33 34 //普通函数声明 35 void output(Complex c); 36 double abs(Complex c); 37 Complex add(Complex c1,Complex c2); 38 bool is_equal(Complex c1,Complex c2); 39 bool is_not_equal(Complex c1,Complex c2);
complex.cpp
1 //类的实现,函数的实现 2 3 #include "tow_complex.h" 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <cmath> 7 8 using std::cout; 9 using std::endl; 10 using std::string; 11 12 //类的属性 方法 13 const string Complex::doc{"a simplified complex class"}; 14 15 //对象的属性 方法 16 Complex::Complex(double x,double y): real{x},imag{y} {} 17 18 Complex::Complex(const Complex &c): real{c.real}, imag{c.imag} {} 19 20 Complex::~Complex() {} 21 22 double Complex::get_real(){ 23 return real; 24 } 25 26 double Complex::get_imag(){ 27 return imag; 28 } 29 30 Complex Complex::add(Complex c){ 31 real +=c.real; 32 imag +=c.imag; 33 } 34 35 //友元函数的定义 36 37 void output(Complex c){ 38 double real = c.get_real(); 39 double imag = c.get_imag(); 40 if(imag>=0) 41 cout<<real<<" + "<<imag<<"i"<<endl; 42 else 43 cout<<real<<" - "<<abs(imag)<<"i"<<endl; 44 } 45 46 Complex add(Complex c1,Complex c2){ 47 Complex c3(c1.get_real()+c2.get_real(),c1.get_imag()+c2.get_imag()); 48 49 return c3; 50 } 51 52 bool is_equal(Complex c1,Complex c2){ 53 return (c1.real==c2.real)&&(c1.imag==c2.imag); 54 } 55 56 bool is_not_equal(Complex c1,Complex c2){ 57 return (c1.real!=c2.real)||(c2.imag!=c1.imag); 58 } 59 60 double abs(Complex c){ 61 double abs; 62 abs = sqrt(c.real*c.real+c.imag*c.imag); 63 return abs; 64 }
main.cpp
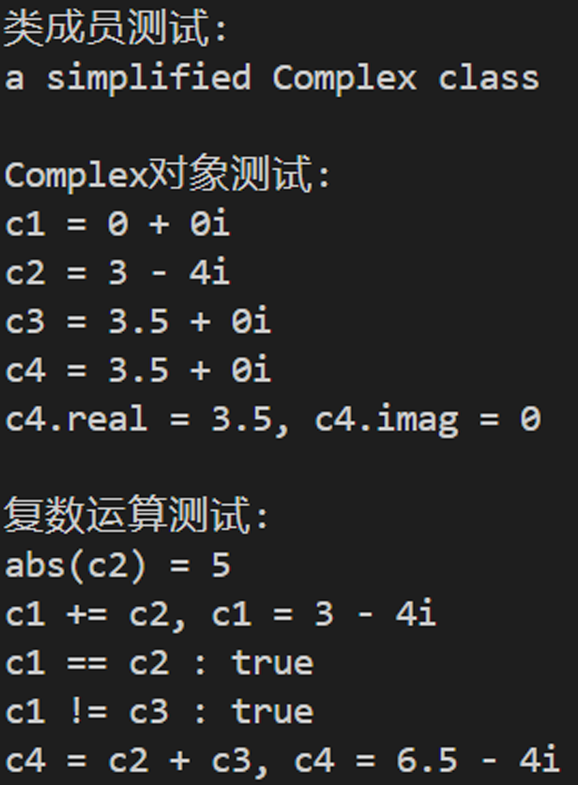
1 #include "tow_complex.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 using std::boolalpha; 7 8 void test() { 9 cout << "类成员测试: " << endl; 10 cout << Complex::doc << endl; 11 12 cout << endl; 13 14 cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl; 15 Complex c1; 16 Complex c2(3, -4); 17 const Complex c3(3.5); 18 Complex c4(c3); 19 20 cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 21 cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl; 22 cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl; 23 cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 24 cout << "c4.real = " << c4.get_real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.get_imag() << endl; 25 26 cout << endl; 27 28 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 29 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 30 c1.add(c2); 31 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl; 32 cout << boolalpha; 33 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; 34 cout << "c1 != c3 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c3) << endl; 35 c4 = add(c2, c3); 36 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl; 37 } 38 39 int main() { 40 test(); 41 }
运行结果:
3. 实验任务3 验证性实验
使用标准库模板类complex实现复数运算
代码:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <complex> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 using std::boolalpha; 7 using std::complex; 8 9 void test() { 10 cout << "标准库模板类comple测试: " << endl; 11 complex<double> c1; 12 complex<double> c2(3, -4); 13 const complex<double> c3(3.5); 14 complex<double> c4(c3); 15 16 cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl; 17 cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl; 18 cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl; 19 cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl; 20 cout << "c4.real = " << c4.real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.imag() << endl; 21 cout << endl; 22 23 cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl; 24 cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl; 25 c1 += c2; 26 cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl; 27 cout << boolalpha; 28 cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl; 29 cout << "c1 != c3 : " << (c1 != c3) << endl; 30 c4 = c2 + c3; 31 cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl; 32 } 33 34 int main() { 35 test(); 36 }
运行结果:

Q&A
1.标准库complex中提供的接口
(1)与test2相似的,提供了获取对象real与imag的接口与取模运算的接口abs()
但标准库中对该接口的命名更加简洁,即real() imag()
(2) 与test2最大的不同在于其判断两个Complex对象是否相等的接口设置
test2重新定义了两个普通函数作为类complex的友元函数,需要在类内声明友元关系,在类的外部声明与定义该普通函数
而complex标准库则重载了(==)与(!=)操作符,不需要定义额外的 is_equal 和 is_not_equal 函数,并且==与!=操作符也是我们判断两个对象是否相等时习惯使用的工具,符合我们的思维习惯,也更 好得体现了cpp面向对象的程序设计中,高度抽象类的特点而不关心计算机内部的实现过程的特点,使得程序的设计更加符合人们的思维方式。
4. 实验任务4 设计并实现一个分数类Fraction
代码:
Fraction.h
1 #pragma once 2 #include <string> 3 4 class Fraction{ 5 //对象的属性和方法 6 public: 7 Fraction(int x,int y = 1); 8 Fraction(Fraction &f); 9 ~Fraction(); 10 11 int get_up(Fraction f); 12 int get_down(Fraction f); 13 Fraction negative(); 14 15 private: 16 int up; 17 int down; 18 19 //类的属性和方法 20 public: 21 static const std::string doc; 22 23 //友元函数的声明 24 friend void output(Fraction f); 25 friend Fraction add(Fraction f1,Fraction f2); 26 friend Fraction sub(Fraction f1,Fraction f2); 27 friend Fraction mul(Fraction f1,Fraction f2); 28 friend Fraction div(Fraction f1,Fraction f2); 29 }; 30 31 //普通函数声明 32 void output(Fraction f); 33 Fraction add(Fraction f1,Fraction f2); 34 Fraction sub(Fraction f1,Fraction f2); 35 Fraction mul(Fraction f1,Fraction f2); 36 Fraction div(Fraction f1,Fraction f2);
Fraction.cpp
1 #include "Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <string> 4 5 using std::cout; 6 using std::endl; 7 using std::string; 8 9 //公倍数、公约数函数的声明 10 int max_yue(int x,int y); 11 int beishu(int x, int y); 12 13 //公倍数定义,返回值为xy的最大公倍数 14 int max_ynum(int a,int b){ 15 int r; 16 if(a>b){ 17 while(b){ 18 r = a%b; 19 a = b; 20 b = r; 21 } 22 return a; 23 }else if(a==b){ 24 return b 25 }else{ 26 while(a){ 27 r = b%a; 28 b = a; 29 a = r; 30 } 31 return b; 32 } 33 } 34 //公约数 ,返回值为xy的最小公倍数 35 int beishu(int x, int y){ 36 int yue = max_yue(x,y); 37 return x*y/yue; 38 } 39 40 41 42 //类的属性 43 std::string Fraction::doc="Fraction类 v 0.01版.\n目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加/减/乘/除运算."; 44 45 //对象的属性和方法 46 //构造函数,析构函数 47 Fraction(int x,int y = 1): up{x},down{y} {} 48 Fraction(Fraction &f) : real{f.up},down{f.down} {} 49 ~Fraction() {} 50 51 int get_up(Fraction f){ 52 return up/max_yue(abs(up),abs(down)); 53 } 54 55 int get_down(Fraction f){ 56 return down/max_yue(abs(up),abs(down)); 57 } 58 59 Fraction negative(){ 60 return Fraction (-up,down); 61 62 } 63 64 //普通函数的实现 65 66 //输出函数 67 void output(Fraction f){ 68 if(f.get_down()==0) 69 cout<< "分母为0!不符合分数要求!" <<endl; 70 if(f.get_down()==1) 71 cout << f.get_up() <<endl; 72 else if(f.get_up()==0) 73 cout <<"0"<<endl; 74 75 else if(f.get_up()>0&&f.get_down()>0) 76 cout << f.get_up()/max_yue(f.get_up(),f.get_down())<<"/" 77 <<f.get_down()/max_yue(f.get_up(),f.get_down())<<endl; 78 else 79 cout <<"-"<<f.get_up()/max_yue(f.get_up(),f.get_down())<<"/" 80 <<f.get_down()/max_yue(f.get_up(),f.get_down())<<endl; 81 } 82
Fraction add(Fraction f1, Fraction f2) {
return Fraction(f1.get_up() * f2.get_down() + f2.get_up() * f1.get_down(), f1.get_down() * f2.get_down());
}
Fraction sub( Fraction f1, Fraction f2) {
return Fraction(f1.gwt_up() * f2.get_down() - f2.get_up() * f1.get_down(), f1.get_down() * f2.get_down());
}
Fraction mul(Fraction f1, Fraction f2) {
return Fraction(f1.get_up() * f2.get_up(), f1.get_down() * f2.get_down());
}
Fraction div( Fraction f1, Fraction f2) {
return Fraction(f1.get_up() * f2.get_down(), f1.get_down() * f2.get_up());
}
main.cpp
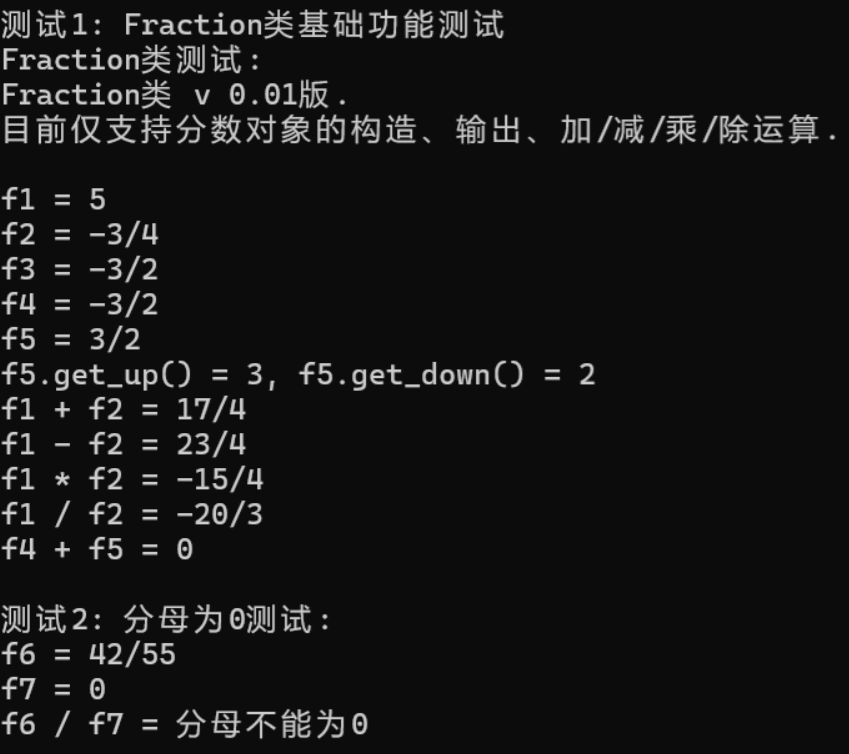
1 #include "Fraction.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::endl; 6 7 8 void test1() { 9 cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl; 10 cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl; 11 12 Fraction f1(5); 13 Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12); 14 Fraction f4(f3); 15 cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl; 16 cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl; 17 cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl; 18 cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl; 19 20 Fraction f5(f4.negative()); 21 cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl; 22 cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl; 23 24 cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 25 cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 26 cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 27 cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl; 28 cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl; 29 } 30 31 void test2() { 32 Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3); 33 cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl; 34 cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl; 35 cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl; 36 } 37 38 int main() { 39 cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n"; 40 test1(); 41 42 cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n"; 43 test2(); 44 }
运行结果:
总结:在设计友元函数时,一开始编写的程序将每一次的约分工作放在了加减乘除的函数定义中,使得代码看起来冗余且复杂,后来我将这部分工作放在了获取分数的分子分母的过程中,使得相同的工作只需要进行一次,提高了代码的简洁性和整洁性。
任务5:
代码
account.h
1 #ifndef __ACCOUNT_H__ 2 #define __ACCOUNT_H__ 3 class SavingsAccount { //储蓄账户类 4 private: 5 int id; //账号 6 double balance; //余额 7 double rate; //存款的年利率 8 int lastDate; //上次变更余额的时期 9 double accumulation; //余额按日累加之和 10 static double total; //所有账户的总金额 11 //记录一笔帐,date为日期,amount为金额,desc为说明 12 void record(int date, double amount); 13 //获得到指定日期为止的存款金额按日累积值 14 double accumulate(int date) const { 15 return accumulation + balance * (date - lastDate); 16 } 17 public: 18 //构造函数 19 SavingsAccount(int date, int id, double rate); 20 int getId() const { return id; } 21 double getBalance() const { return balance; } 22 double getRate() const { return rate; } 23 static double getTotal() { return total; } 24 void deposit(int date, double amount); //存入现金 25 void withdraw(int date, double amount); //取出现金 26 //结算利息,每年1月1日调用一次该函数 27 void settle(int date); 28 //显示账户信息 29 void show() const; 30 }; 31 #endif //__ACCOUNT_H__
account.cpp
1 #include "account.h" 2 #include <cmath> 3 #include <iostream> 4 using namespace std; 5 double SavingAccount::total = 0; 6 SavingAccount::SavingAccount(int date, int id, double rate) :id(id), balance(0), rate(rate), lastDate(date), accumulation(0) 7 { 8 cout << date << "\t#" << id << "is created" << endl; 9 } 10 void SavingAccount::record(int date, double amount) 11 { 12 accumulation = accumulate(date); 13 lastDate = date; 14 amount = floor(amount * 100 + 0.5) / 100; //保留小数点后两位 15 balance += amount; 16 total += amount; 17 cout << date << "\t#" << id << "\t"<<amount<<"\t"<<balance << endl; 18 } 19 void SavingAccount::deposit(int date, double amount) 20 { 21 record(date, amount); 22 } 23 void SavingAccount::withdraw(int date, double amount) 24 { 25 if (amount > getBalance()) 26 { 27 cout << "Error: not enough money" << endl; 28 } 29 else 30 { 31 record(date, -amount); 32 } 33 } 34 void SavingAccount::settle(int date) 35 { 36 double interest = accumulate(date) * rate / 365; 37 if (interest != 0) 38 { 39 record(date, interest); 40 } 41 accumulation = 0; 42 } 43 void SavingAccount::show() const 44 { 45 cout << "#" << id << "\tBalance: " << balance; 46 }
main.cpp
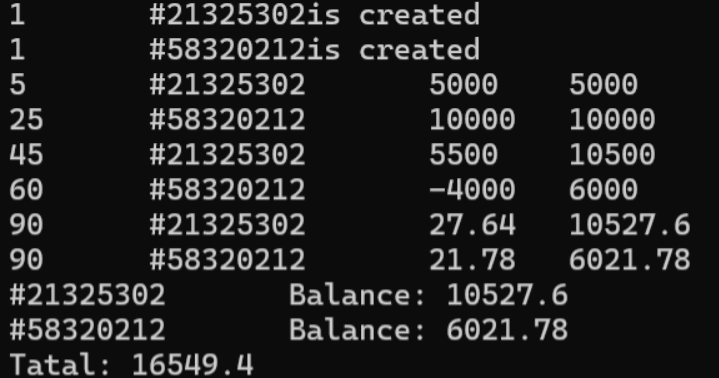
1 #include "account.h" 2 #include <iostream> 3 using namespace std; 4 int main() 5 { 6 SavingAccount sa0(1, 21325302, 0.015); 7 SavingAccount sa1(1, 58320212, 0.015); 8 sa0.deposit(5, 5000); 9 sa1.deposit(25, 10000); 10 sa0.deposit(45, 5500); 11 sa1.withdraw(60, 4000); 12 sa0.settle(90); 13 sa1.settle(90); 14 sa0.show(); cout << endl; 15 sa1.show(); cout << endl; 16 cout << "Tatal: " << SavingAccount::getTotal() << endl; 17 return 0; 18 }
运行结果: