Spring MVC(Boot) Servlet 3.0异步处理,DeferredResult和Callable
简介
- 自
Servlet 3.0支持异步处理,有什么妙用呢? - 以
Tomcat为例,我们可以使用更少的Tomcat线程处理更多的任务。当有一个请求到达时,我们用另一个用户线程去处理任务,使Tomcat容器线程得以空闲,可以去为其他请求服务。 Spring几乎作为Java EE开发的必备框架,在这块也是有支持的。- 我们看下官方文档:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/5.2.19.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/web.html#mvc-ann-async
- 为避免链接失效,我再截个图,文档内容如下图所示。


- 上面文档也说了,2种方式,
DeferredResult和Callable,下面我就来实践下。
使用
DeferredResult
- 用法就是返回DeferredResult,自己
开一个线程,有结果的时候,再调用DeferredResult的setResult方法,这里用的是CompletableFuture开启异步任务,不是直接开线程。 - 代码如下所示。
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/asyncAndMerge")
public class AsyncAndMergeController {
...省略...
/*** 异步,不阻塞Tomcat的线程 ,提升Tomcat吞吐量***/
@RequestMapping("/async")
public DeferredResult<String> async() {
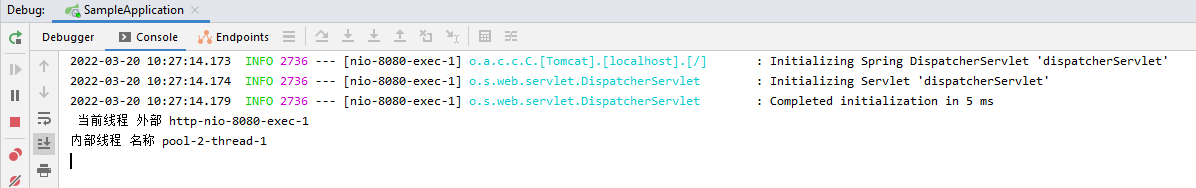
System.out.println(" 当前线程 外部 " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
DeferredResult<String> result = new DeferredResult<>();
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(testService::testDeferredResult,executorService)
.whenCompleteAsync((res, throwable) -> result.setResult(res));
return result;
}
...省略...
}
@Service
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
...省略...
@Override
public String testDeferredResult() {
System.out.println("内部线程 名称 "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "testDeferredResult";
}
...省略...
}
- 执行结果
Callable
- 用法就是返回
Callable,在call方法写业务逻辑。 - 代码如下所示。
...省略...
/*** 异步,不阻塞Tomcat的线程 ,提升Tomcat吞吐量***/
@RequestMapping("/async2")
public Callable<String> async2() {
System.out.println(" 当前线程 外部 " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
Callable<String> callable = new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
System.out.println(" 当前线程 内部 " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
return "success";
}
};
return callable;
}
...省略...
- 注意还需要配置
TaskExecutor。否则有以下提示。
An Executor is required to handle java.util.concurrent.Callable return values.
Please, configure a TaskExecutor in the MVC config under “async support”.
The SimpleAsyncTaskExecutor currently in use is not suitable under load.
- 增加如下代码
package com.springboot.sample.conf;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.task.AsyncTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.core.task.TaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.scheduling.annotation.EnableAsync;
import org.springframework.scheduling.concurrent.ThreadPoolTaskExecutor;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.async.TimeoutCallableProcessingInterceptor;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.AsyncSupportConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
// 试了 implements WebMvcConfigurer 也行
@Configuration
//@EnableAsync 这里不用开启异步也行
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
@Override
public void configureAsyncSupport(final AsyncSupportConfigurer configurer) {
configurer.setDefaultTimeout(60 * 1000L);
configurer.registerCallableInterceptors(timeoutInterceptor());
configurer.setTaskExecutor(asyncTaskExecutor());
}
@Bean
public TimeoutCallableProcessingInterceptor timeoutInterceptor() {
return new TimeoutCallableProcessingInterceptor();
}
@Bean
public AsyncTaskExecutor asyncTaskExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
//核心线程数:线程池创建时候初始化的线程数
//最大线程数:线程池最大的线程数,只有在缓冲队列满了之后才会申请超过核心线程数的线程
//缓冲队列:用来缓冲执行任务的队列
//允许线程的空闲时间60秒:当超过了核心线程出之外的线程在空闲时间到达之后会被销毁
//线程池名的前缀:设置好了之后可以方便我们定位处理任务所在的线程池
//线程池对拒绝任务的处理策略:这里采用了CallerRunsPolicy策略,当线程池没有处理能力的时候,该策略会直接在 execute 方法的调用线程中运行被拒绝的任务;如果执行程序已关闭,则会丢弃该任务
executor.setCorePoolSize(5);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(10);
executor.setQueueCapacity(200);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("taskExecutor-");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
}
- 执行结果如下图所示。

小结和代码
-
DeferredResult和Callable都是为了能腾出Tomcat线程,让它为能承接更多的请求,提示服务器的吞吐量。DeferredResult相较于Callable是需要调用setResult方法手动设置返回的。 -
例子代码地址:https://gitee.com/apple_1030907690/spring-boot-kubernetes/tree/v1.0.5/





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· Manus重磅发布:全球首款通用AI代理技术深度解析与实战指南
· 被坑几百块钱后,我竟然真的恢复了删除的微信聊天记录!
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 园子的第一款AI主题卫衣上架——"HELLO! HOW CAN I ASSIST YOU TODAY
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix