BeanFactoryPostProcessor详解
一、简介
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口与 BeanPostProcessor接口类似,可以对bean的定义(配置元数据)进行处理;也就是spring ioc运行BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何其他的bean之前读取配置元数据,并有可能修改它;如果业务需要,可以配置多个BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类,通过"order"控制执行次序(要实现Ordered接口)。
二、使用
- spring-base.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.0.xsd"
>
<!-- spring ioc部分 start -->
<bean id ="myTestBean" class= "com.zzq.core.test.entity.MyTestBean" >
</bean>
<bean id ="customBeanFactoryPostProcessor" class= "com.zzq.core.test.processor.CustomBeanFactoryPostProcessor" ></bean>
<!-- spring ioc部分 end -->
</beans>
- CustomBeanFactoryPostProcessor.java
package com.zzq.core.test.processor;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.GenericBeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
/**
* 和BeanPostProcessor原理一致,Spring提供了对BeanFactory进行操作的处理器BeanFactoryProcessor,简单来说就是获取容器BeanFactory,这样就可以在真正初始化bean之前对bean做一些处理操作。
* 允许我们在工厂里所有的bean被加载进来后但是还没初始化前,对所有bean的属性进行修改也可以add属性值。
* **/
public class CustomBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor{
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("postProcessBeanFactory");
//获取BeanDefinition
/* TestService testService = (TestService) beanFactory.getBean("testServiceImpl");
//System.out.println("得到 testService ");
testService.doMessage(); */
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("myTestBean");
System.out.println("修改属性name值");
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("name", "liSi");
}
}
- MyTestBean.java
package com.zzq.core.test.entity;
public class MyTestBean {
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
- 运行的主函数BootStrap.java
package com.zzq.core.test;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import com.zzq.core.test.entity.MyTestBean;
public class BootStrap {
public static void main(String[] args) {
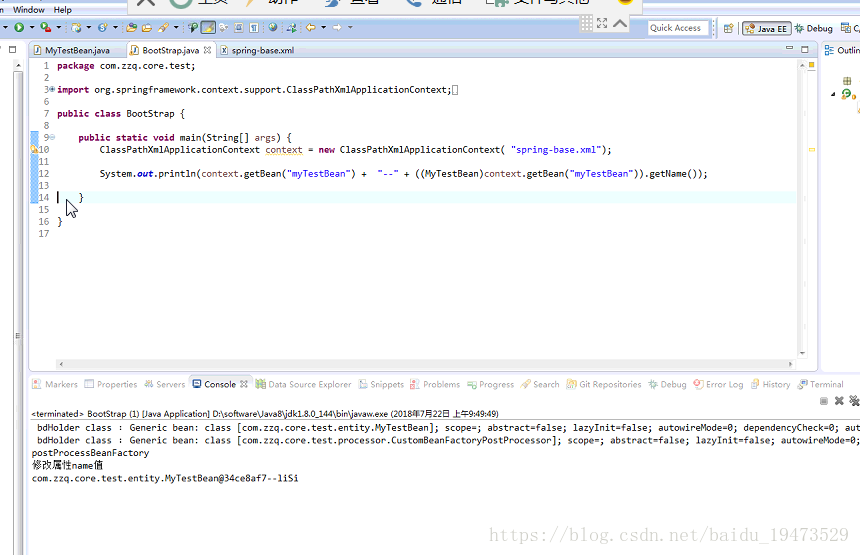
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext( "spring-base.xml");
System.out.println(context.getBean("myTestBean") + "--" + ((MyTestBean)context.getBean("myTestBean")).getName());
}
}
- 运行结果,对象的name属性已被更改。
三、查看源码
- 从ClassPathXmlApplicationContext开始到它父类AbstractApplicationContext的refresh方法。
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
//来个锁,不然 refresh() 还没结束,你又来个启动或销毁容器的操作,那不就乱套了嘛
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
...........................
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 【这里需要知道 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 这个知识点,Bean 如果实现了此接口,
// 那么在容器初始化以后,Spring 会负责调用里面的 postProcessBeanFactory 方法。】
// 这里是提供给子类的扩展点,到这里的时候,所有的 Bean 都加载、注册完成了,但是都还没有初始化
// 具体的子类可以在这步的时候根据吱声业务添加或修改一些特殊的 beanFactory属性
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 调用 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 各个实现类的 postProcessBeanFactory(factory) 方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
...........................
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
// 销毁已经初始化的 singleton 的 Beans,以免有些 bean 会一直占用资源
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
//取消刷新的标志
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
// 把异常往外抛
throw ex;
}
}
}
- 省略了部分代码,我们此次要关注的就是invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);方法。
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<String>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new LinkedList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryPostProcessors =
new LinkedList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>();
//getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()大部分情况下里面元素是空的,所以主要还是走下面beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType方法得到处理器
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryPostProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryPostProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryPostProcessors.add(registryPostProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
Map<String, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> beanMap =
beanFactory.getBeansOfType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryPostProcessorBeans =
new ArrayList<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor>(beanMap.values());
OrderComparator.sort(registryPostProcessorBeans);
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : registryPostProcessorBeans) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryPostProcessorBeans, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
processedBeans.addAll(beanMap.keySet());
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(getBeanFactoryPostProcessors(), beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
//根据BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口得到它的实现类
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
//将BeanFactoryPostProcessor处理器分成几种来执行 priorityOrderedPostProcessors orderedPostProcessorNames nonOrderedPostProcessorNames
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
OrderComparator.sort(priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
OrderComparator.sort(orderedPostProcessors);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
//最后,调用所有其他后处理器。
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<BeanFactoryPostProcessor>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
- 一般情况下不会走到for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()) {里面,getBeanFactoryPostProcessors()元素为空(如果一定要让它走这儿的话,可以自己继承ClassPathXmlApplicationContext,重写里面的postProcessBeanFactory方法,使用addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor)方法添加进去);它将BeanFactoryPostProcessor处理器分成几类来处理,反正最后都要到invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法的。
private void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
//调用实现类的postProcessBeanFactory方法
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}
到这儿基本结束了,另外文章代码或者我理解有误的地方,希望能批评指出。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号