spring自定义标签
一、简介
- spring在解析标签时分为默认标签和自定义标签两种;默认标签如
bean标签,自定义标签如:aop、tx(关于事物的)、dubbo(rpc框架的)。在一些复杂的业务场景下,普通bean无法满足需求;spring提供了可扩展Schema的支持,只需要我们实现部分逻辑就可以为我们解析自定义标签;spring自定义标签用于配置较为复杂或者需要丰富的控制的时候。
二、使用
- 1、创建一个想要扩展的组件,其实就是创建一个bean(这里就用Dubbo简单模拟下,注意仅仅是模拟)
package com.zzq.provider.customtag.pojo;
public class Dubbo {
/*spring beanName*/
private String id;
/*消费方应用名,用于计算依赖关系,不是匹配条件,不要与提供方一样*/
private String name;
/*使用zookeeper注册中心暴露服务地址 */
private String address;
/*使用zookeeper注册中心暴露服务地址*/
private String protocol;
/*生成远程服务代理,可以像使用本地bean一样使用demoService*/
private String basePackage;
/*消费者调用超时设置为10秒*/
private String timeout;
/*端口*/
private String port;
public String getPort() {
return port;
}
public void setPort(String port) {
this.port = port;
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public String getProtocol() {
return protocol;
}
public void setProtocol(String protocol) {
this.protocol = protocol;
}
public String getBasePackage() {
return basePackage;
}
public void setBasePackage(String basePackage) {
this.basePackage = basePackage;
}
public String getTimeout() {
return timeout;
}
public void setTimeout(String timeout) {
this.timeout = timeout;
}
}
- 2、定义XSD文件描述组件内容(其实就是描述xml文件的) ,Spring-dubbo.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<schema xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
targetNamespace="http://www.lexueba.com/schema/dubbo"
xmlns:tns="http://www.lexueba.com/schema/dubbo"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
>
<element name="dubbo">
<complexType>
<attribute name="id" type="string"></attribute>
<attribute name="name" type="string"></attribute>
<attribute name="address" type="string"></attribute>
<attribute name="protocol" type="string"></attribute>
<attribute name="port" type="string"></attribute>
<attribute name="basePackage" type="string"></attribute>
<attribute name="timeout" type="string"></attribute>
</complexType>
</element>
</schema>
- 3、 实现BeanDefinitionParser接口或者继承AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser,用于解析XSD文件中的定义和组件的定义。如果您的业务需求比较复杂建议实现BeanDefinitionParser接口。
public class DubboBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
// element对应的类
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return Dubbo.class;
}
// 从element中解析并提取对应的元素
/*@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
String address = element.getAttribute("address");
String name = element.getAttribute("name");
String protocol = element.getAttribute("protocol");
String basePackage = element.getAttribute("basePackage");
String timeout = element.getAttribute("timeout");
String port = element.getAttribute("port");
if (StringUtils.hasText(id)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("id", id);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(address)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("address", address);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("name", name);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(protocol)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("protocol", protocol);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(basePackage)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("basePackage", basePackage);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(timeout)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("timeout", timeout);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(port)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("port", port);
}
System.out.println("id :" + id +" name : " +name +" address :" +address);
}*/
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
String id = element.getAttribute("id");
String address = element.getAttribute("address");
String name = element.getAttribute("name");
String protocol = element.getAttribute("protocol");
String basePackage = element.getAttribute("basePackage");
String timeout = element.getAttribute("timeout");
String port = element.getAttribute("port");
if (StringUtils.hasText(id)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("id", id);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(address)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("address", address);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(name)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("name", name);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(protocol)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("protocol", protocol);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(basePackage)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("basePackage", basePackage);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(timeout)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("timeout", timeout);
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(port)) {
builder.addPropertyValue("port", port);
}
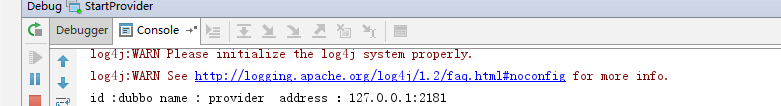
System.out.println("id :" + id +" name : " +name +" address :" +address);
}
}
- 4、创建handler,也就是遇到这个Schema要进入自定义标签的处理类调init方法,扩展自NamespaceHandlerSupport,目的是为了注册遇到这个自定义要进入哪个实现。
package com.zzq.provider.customtag.handler;
import com.zzq.provider.customtag.parser.DubboBeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;
public class DubboNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
@Override
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("dubbo",new DubboBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}
- 5、编写spring.handlers和spring.schemas文件,这个有点类似于SPI的形式
(1) spring.handlers
http\://www.lexueba.com/schema/dubbo=com.zzq.provider.customtag.handler.DubboNamespaceHandler
(2) spring.schemas
http\://www.lexueba.com/schema/dubbo.xsd=META-INF/Spring-dubbo.xsd
- 6、编写配置文件,注意xml的头要写正确,而且要对应, application-customtag.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!-- 自定义标签的测试 -->
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:myTagName="http://www.lexueba.com/schema/dubbo"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.lexueba.com/schema/dubbo http://www.lexueba.com/schema/dubbo.xsd">
<myTagName:dubbo id = "dubbo" name = "provider" address = "127.0.0.1:2181" protocol="zookeeper" basePackage="com.zzq.provider" port="8080" timeout="10000" />
</beans>
然后在启动时入口的配置文件导入即可:
<import resource="application-customtag.xml"></import>
-
7、完整的结构
-
8、运行结果
三、源码解析
- 定位到BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseCustomElement,这就是根据schema取对应的handler,也就是前面说的
DubboNamespaceHandler这种
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
// 获取对应命名空间
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
// 例如namespaceUri为http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop, 所以得到的是 AopNamespaceHandler
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}
public NamespaceHandler resolve(String namespaceUri) {
Map<String, Object> handlerMappings = getHandlerMappings();
// 根据命名空间找到对应信息
Object handlerOrClassName = handlerMappings.get(namespaceUri);
if (handlerOrClassName == null) {
return null;
}
else if (handlerOrClassName instanceof NamespaceHandler) {
return (NamespaceHandler) handlerOrClassName;
}
else {
String className = (String) handlerOrClassName;
try {
Class<?> handlerClass = ClassUtils.forName(className, this.classLoader);
if (!NamespaceHandler.class.isAssignableFrom(handlerClass)) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Class [" + className + "] for namespace [" + namespaceUri +
"] does not implement the [" + NamespaceHandler.class.getName() + "] interface");
}
NamespaceHandler namespaceHandler = (NamespaceHandler) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(handlerClass);
//初始化标签对应的处理类
namespaceHandler.init();
handlerMappings.put(namespaceUri, namespaceHandler);
return namespaceHandler;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new FatalBeanException("NamespaceHandler class [" + className + "] for namespace [" +
namespaceUri + "] not found", ex);
}
catch (LinkageError err) {
throw new FatalBeanException("Invalid NamespaceHandler class [" + className + "] for namespace [" +
namespaceUri + "]: problem with handler class file or dependent class", err);
}
}
}
private Map<String, Object> getHandlerMappings() {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
try {
//载入全部项目的META-INF/spring.handlers(aop项目beans项目等等)配置文件得到对应关系如http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop=org.springframework.aop.config.AopNamespaceHandler
Properties mappings =
PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties(this.handlerMappingsLocation, this.classLoader);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded NamespaceHandler mappings: " + mappings);
}
Map<String, Object> handlerMappings = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(mappings.size());
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(mappings, handlerMappings);
this.handlerMappings = handlerMappings;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable to load NamespaceHandler mappings from location [" + this.handlerMappingsLocation + "]", ex);
}
}
}
}
return this.handlerMappings;
}
- 此时已经取到了对应的handler,并且调用了其init方法。剩下的就是解析了。findParserForElement#parse ->findParserForElement
private BeanDefinitionParser findParserForElement(Element element, ParserContext parserContext) {
// 获取元素名称 <myTagName:dubbo> 中的dubbo 此时localName为dubbo
String localName = parserContext.getDelegate().getLocalName(element);
// 此时根据localName为dubbo找解析器 就是DubboBeanDefinitionParser
BeanDefinitionParser parser = this.parsers.get(localName);
if (parser == null) {
parserContext.getReaderContext().fatal(
"Cannot locate BeanDefinitionParser for element [" + localName + "]", element);
}
return parser;
}
- 然后再调用parse 方法,因为我是继承了AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser的,所以会进入AbstractBeanDefinitionParser#parse -> AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser#parseInternal
最后AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser#doParse子类实现或者重写其中任意一个方法做具体实现。
// 重写这个也行就看您需不需要parserContext对象了
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext parserContext, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
//此处调用具体的实现类
doParse(element, builder);
}






【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现