spring读取配置文件原理解析
目录
简介
- 在项目中,我们一般都会用配置文件(properties文件)更优雅的实现基础配置信息;在java中我们一般会用内置的工具包
java.util.Properties去读取properties配置文件;往往有一些问题是,我们要自己写代码去读取配置文件,还有就是如何管理已经读取过的配置,这种配置文件的数据一般不会频繁改变,不可能我需要一次就读一下文件吧!那就太不优雅了,而且自己去写读取文件的代码也麻烦。 - 而
Spring刚好能解决这样的痛点,Spring有一个类PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer,这个类是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类。其主要的原理在是。Spring容器初始化的时候,会读取 xml 或者 annotation 对 Bean 进行初始化。Bean初始化的时候会对配置的${xxxx}进行替换,根据我们Properties文件中配置的进行替换。从而实现表达式的替换操作 。 - 如果不了解
BeanFactoryPostProcessor的,可以参考BeanFactoryPostProcessor详解
使用
我这里有2中方式,二选一(可能不止)
- 1、xml方式配置
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer(我源码演示使用的是第1种)
...... 省略 ............
<!-- 加载配置文件 -->
<bean class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer">
<property name="locations">
<list>
<value>classpath:prop-jdbc.properties</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 一般需要把配置文件合并形成 一个 ,否则在AbstractBeanFactory#resolveEmbeddedValue里面for循环时会有可能遍历某个StringValueResolver找不到想要的配置而报错 , 还有个办法设置忽略ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders修改为true -->
<property name="ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders" value="true"></property>
</bean>
...... 省略 ............
- 2、java config (看了源码之后想到
直接创建PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer对象);
package com.zzq.core.configuration;
import java.io.File;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.FileSystemResource;
@Configuration
public class ConfigurationTest {
//PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 一般需要把配置文件合并形成 一个 ,否则在AbstractBeanFactory#resolveEmbeddedValue里面for循环时会有可能遍历某个StringValueResolver可能找不到想要的配置而报错 , 还有个办法设置忽略ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders修改为true
@Bean
public PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer propertyPlaceholder(){
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer configurer = new PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer();
File file = new File("D:/eclipse_workspace/CeShi2/test_web/src/main/resources/zookeeper.properties");
//File jdbc = new File("D:/eclipse_workspace/CeShi2/test_web/src/main/resources/prop-jdbc.properties");
org.springframework.core.io.Resource [] locations = {new FileSystemResource(file)
/*,new FileSystemResource(jdbc)*/};
//location.add(new FileSystemResource(file));
configurer.setLocations(locations);
configurer.setIgnoreUnresolvablePlaceholders(true);
return configurer;
}
}
要注意此处
Resource接口的实现类有很多,我用的绝对路径FileSystemResource;还可以使用classPath路径,使用ClassPathResource实现类;还有些其他的可以实现可以自己参考下源码Resource的其他实现。
来看下prop-jdbc.properties的内容

获取值可以使用@Value注解,在controller使用
@Value("${druid.url}")
private String druidUrl;
最后测试一波,能够成功获取到值

源码分析
基本信息
- 先来看看
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer的继承关系

解析配置文件
PropertyResourceConfigurer是BeanFactoryPostProcessor的实现类,在项目启动时会调用到AbstractApplicationContext#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,里面最终就是for循环调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类的postProcessBeanFactory方法;这段逻辑可以参考BeanFactoryPostProcessor详解。

- 当调用到
PropertyResourceConfigurer#postProcessBeanFactory
//BeanFactoryPostProcessor的后处理
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
try {
//合并配置文件的属性值
Properties mergedProps = mergeProperties();
// Convert the merged properties, if necessary.
//如有必要, 转换合并的属性
convertProperties(mergedProps);
// Let the subclass process the properties.
//让子类处理属性
processProperties(beanFactory, mergedProps);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
- 进入
mergeProperties方法
protected Properties mergeProperties() throws IOException {
Properties result = new Properties();
if (this.localOverride) {
// Load properties from file upfront, to let local properties override.
loadProperties(result);
}
if (this.localProperties != null) {
for (Properties localProp : this.localProperties) {
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(localProp, result);
}
}
if (!this.localOverride) {
// Load properties from file afterwards, to let those properties override.
// 从文件加载属性
loadProperties(result);
}
return result;
}
-
loadPropertiesprotected void loadProperties(Properties props) throws IOException { if (this.locations != null) { for (Resource location : this.locations) { if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Loading properties file from " + location); } try { //查找配置文件的属性 并且都合并到props PropertiesLoaderUtils.fillProperties( props, new EncodedResource(location, this.fileEncoding), this.propertiesPersister); } catch (IOException ex) { if (this.ignoreResourceNotFound) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Could not load properties from " + location + ": " + ex.getMessage()); } } else { throw ex; } } } } }
- 验证我们上面的知识:此时我们知道
locations是Resource数组,并且实现类是ClassPathResource
- 验证我们上面的知识:此时我们知道
-
来到
PropertiesLoaderUtils#fillProperties这个方法就在读取配置文件了,并把值设置到props里static void fillProperties(Properties props, EncodedResource resource, PropertiesPersister persister) throws IOException { InputStream stream = null; Reader reader = null; try { //得到文件名称 String filename = resource.getResource().getFilename(); //判断不为空 并且后缀是.xml if (filename != null && filename.endsWith(XML_FILE_EXTENSION)) { stream = resource.getInputStream(); persister.loadFromXml(props, stream); } else if (resource.requiresReader()) { // 需要 Reader reader = resource.getReader(); persister.load(props, reader); } else { // 普通的properties文件读取 stream = resource.getInputStream(); persister.load(props, stream); } } finally { if (stream != null) { stream.close(); } if (reader != null) { reader.close(); } } }
- 看到这个方法我觉得以后非要自己读取配置文件可以调用
PropertiesLoaderUtils#fillProperties(前提是引入了相关spring jar包),具体操作可以参考从spring、spring boot中找到解析properties、xml、yml、yaml文件的方法
- 看到这个方法我觉得以后非要自己读取配置文件可以调用
-
convertProperties转换属性没啥好说的,没有覆盖方法,就是返回原值。可以看看最后的convertProperty方法
protected String convertPropertyValue(String originalValue) {
return originalValue;
}
-
重点是之类覆盖的方法
processProperties,来到子类PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer#processPropertiesprotected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, Properties props) throws BeansException { // 创建字符串解析器 StringValueResolver valueResolver = new PlaceholderResolvingStringValueResolver(props); // 处理属性 - 重点 doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver); } -
doProcessProperties处理配置属性protected void doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess, StringValueResolver valueResolver) { BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor(valueResolver); String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames(); for (String curName : beanNames) { // Check that we're not parsing our own bean definition, // to avoid failing on unresolvable placeholders in properties file locations. //检查我们没有解析自己的bean定义, //以避免在属性文件位置的不可解析占位符上失败。 if (!(curName.equals(this.beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this.beanFactory))) { BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName); try { visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage(), ex); } } } // New in Spring 2.5: resolve placeholders in alias target names and aliases as well. //Spring2.5中的新特性:解析别名目标名称和别名中的占位符。 beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver); // New in Spring 3.0: resolve placeholders in embedded values such as annotation attributes. // Spring3.0中的新特性:解析嵌入值(如注释属性)中的占位符。 放到 embeddedValueResolvers属性里面 便于注解获取字符串的值 重点 beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver); } -
AbstractBeanFactory#addEmbeddedValueResolver
public void addEmbeddedValueResolver(StringValueResolver valueResolver) {
Assert.notNull(valueResolver, "StringValueResolver must not be null");
// 把解析器添加进去
this.embeddedValueResolvers.add(valueResolver);
}
设置值
- 我们首先定位到创建bean的代码
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#doCreateBean;给属性赋值,以上面的TestControllerdruidUrl属性为例
protected Object doCreateBean(final String beanName, final RootBeanDefinition mbd, final Object[] args) {
.................省略代码.....................
// 这一步也是非常关键的,这一步负责属性装配,因为前面的实例只是实例化了,并没有设值,这里就是设值
populateBean(beanName, mbd, instanceWrapper);
.................省略代码.....................
}
- 再来看看
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, BeanWrapper bw) {
// bean 实例的所有属性都在这里了
PropertyValues pvs = mbd.getPropertyValues();
if (bw == null) {
if (!pvs.isEmpty()) {
throw new BeanCreationException(
mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName, "Cannot apply property values to null instance");
}
else {
// Skip property population phase for null instance.
return;
}
}
// Give any InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors the opportunity to modify the
// state of the bean before properties are set. This can be used, for example,
// to support styles of field injection.
// 到这步的时候,bean 实例化完成(通过工厂方法或构造方法),但是还没开始属性设值,
// InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor 的实现类可以在这里对 bean 进行状态修改,
// 我也没找到有实际的使用,所以我们暂且忽略这块吧
boolean continueWithPropertyPopulation = true;
if (!mbd.isSynthetic() && hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors()) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 如果返回 false,代表不需要进行后续的属性设值,也不需要再经过其他的 BeanPostProcessor 的处理
if (!ibp.postProcessAfterInstantiation(bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName)) {
continueWithPropertyPopulation = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
if (!continueWithPropertyPopulation) {
return;
}
//目前看到的上面autowireByName和autowireByType的属性注入是定义bean(xml定义和代码定义)的时候才会进,下面postProcessPropertyValues是用来处理注解的注入 还有@Bean注解可以设置
//mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode()一般为0 都不进 , 在源码BeanDefinitionParserDelegate#parseBeanDefinitionAttributes方法发现xml方式可以设置autowireMode属性值,java config方式目前不知
//byName 比如可以这样设置 <bean id ="myTestBean" class= "com.zzq.core.test.entity.MyTestBean" autowire="byName">
//在mybatis 源码 ClassPathMapperScanner.class#processBeanDefinitions发现这段代码直接设置mapper为byType if !explicitFactoryUsed definition.setAutowireMode(AbstractBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE);
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME ||
mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
MutablePropertyValues newPvs = new MutablePropertyValues(pvs);
// Add property values based on autowire by name if applicable.
// 通过名字找到所有属性值,如果是 bean 依赖,先初始化依赖的 bean。记录依赖关系
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME) {
autowireByName(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
// Add property values based on autowire by type if applicable.
// 通过类型装配。复杂一些
if (mbd.getResolvedAutowireMode() == RootBeanDefinition.AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE) {
autowireByType(beanName, mbd, bw, newPvs);
}
pvs = newPvs;
}
//InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor接口的主要作用在于目标对象的实例化过程中需要处理的事情,包括实例化对象的前后过程以及实例的属性设置
boolean hasInstAwareBpps = hasInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessors();
boolean needsDepCheck = (mbd.getDependencyCheck() != RootBeanDefinition.DEPENDENCY_CHECK_NONE);
if (hasInstAwareBpps || needsDepCheck) {
//筛选属性
PropertyDescriptor[] filteredPds = filterPropertyDescriptorsForDependencyCheck(bw, mbd.allowCaching);
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
// 此处重点
// 这里有个非常有用的 BeanPostProcessor 进到这里: AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// 对采用 @Autowired、@Value 注解的依赖进行设值,这里的内容也是非常丰富的,不过本文不会展开说了,感兴趣的读者请自行研究
//@Resource注解一般使用这个后处理器org.springframework.context.annotation.CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// @Autowired注解是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor @Resource注解是CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
if (needsDepCheck) {
checkDependencies(beanName, mbd, filteredPds, pvs);
}
}
// 设置 bean 实例的属性值,不过pvs空元素的时候并不会进
applyPropertyValues(beanName, mbd, bw, pvs);
}
- 使用
@Value注解依赖进行设值的后处理器是AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor,先来debug看看执行完AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues的效果。
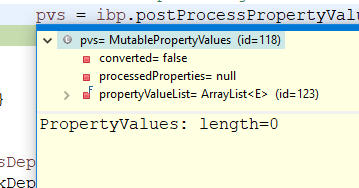

- 此处的
pvs是空元素,所以后面执行到applyPropertyValues会直接return。 - 可以看到在执行完
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues后TestController的druidUrl属性值已经被设置进去了,我们具体看看内部的实现。
- 此处的
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
// 查找需要依赖注入的元数据属性
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
// 注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findAutowiringMetadata此处是从缓存里找数据,injectionMetadataCache的元素是在AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#applyMergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessors初始化的。buildAutowiringMetadata方法就是封装一个metadata对象,供下面注入使用。
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(Class<?> clazz) {
LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement>();
for (Field field : targetClass.getDeclaredFields()) {
Annotation ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
continue;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
}
for (Method method : targetClass.getDeclaredMethods()) {
Annotation ann = null;
Method bridgedMethod = BridgeMethodResolver.findBridgedMethod(method);
if (BridgeMethodResolver.isVisibilityBridgeMethodPair(method, bridgedMethod)) {
ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(bridgedMethod);
}
if (ann != null && method.equals(ClassUtils.getMostSpecificMethod(method, clazz))) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(method.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation is not supported on static methods: " + method);
}
continue;
}
if (method.getParameterTypes().length == 0) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation should be used on methods with actual parameters: " + method);
}
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
PropertyDescriptor pd = BeanUtils.findPropertyForMethod(bridgedMethod, clazz);
currElements.add(new AutowiredMethodElement(method, required, pd));
}
}
elements.addAll(0, currElements);
targetClass = targetClass.getSuperclass();
}
while (targetClass != null && targetClass != Object.class);
return new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements);
}

-
原理很简单就是找到满足条件的加入到
list里,最后构建出一个InjectionMetadata对象返回 -
现在已经获取到要注入那些属性了,现在来看看注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);public void inject(Object target, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable { Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate = (this.checkedElements != null ? this.checkedElements : this.injectedElements); if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) { boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled(); for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) { if (debug) { logger.debug("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element); } element.inject(target, beanName, pvs); } } }
element包装的就是要注入的属性,当然element也可能是方法,因为我看到有两个实现类;

-
现在这儿就看
AutowiredFieldElement#injectprotected void inject(Object bean, String beanName, PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable { Field field = (Field) this.member; try { Object value; if (this.cached) { value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue); } else { DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required); Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<String>(1); TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter(); //这个beanName 是当前类文件的beanName value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter); synchronized (this) { if (!this.cached) { if (value != null || this.required) { this.cachedFieldValue = desc; //保存依赖关系 registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames); if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) { String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next(); if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName)) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(autowiredBeanName, field.getType())) { this.cachedFieldValue = new RuntimeBeanReference(autowiredBeanName); } } } } else { this.cachedFieldValue = null; } this.cached = true; } } } if (value != null) { ReflectionUtils.makeAccessible(field); //通过反射对字段注入 field.set(bean, value); } } catch (Throwable ex) { throw new BeanCreationException("Could not autowire field: " + field, ex); } } -
下一步就是获取属性值,定位到
DefaultListableBeanFactory#resolveDependencypublic Object resolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, String beanName, Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException { descriptor.initParameterNameDiscovery(getParameterNameDiscoverer()); if (descriptor.getDependencyType().equals(ObjectFactory.class)) { return new DependencyObjectFactory(descriptor, beanName); } else if (descriptor.getDependencyType().equals(javaxInjectProviderClass)) { return new DependencyProviderFactory().createDependencyProvider(descriptor, beanName); } else { // 一般都是走这里 return doResolveDependency(descriptor, descriptor.getDependencyType(), beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter); } }protected Object doResolveDependency(DependencyDescriptor descriptor, Class<?> type, String beanName, Set<String> autowiredBeanNames, TypeConverter typeConverter) throws BeansException { //得到注解上的值 一般是获取value属性的值 Object value = getAutowireCandidateResolver().getSuggestedValue(descriptor); if (value != null) { if (value instanceof String) { // 表达式注解获取值 一般是获取配置里的值 重点 String strVal = resolveEmbeddedValue((String) value); BeanDefinition bd = (beanName != null && containsBean(beanName) ? getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName) : null); value = evaluateBeanDefinitionString(strVal, bd); } TypeConverter converter = (typeConverter != null ? typeConverter : getTypeConverter()); return (descriptor.getField() != null ? converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getField()) : converter.convertIfNecessary(value, type, descriptor.getMethodParameter())); } ..........省略下面获取属性值用不到的代码................ } }- 还记得之前创建的的创建
字符串解析器吗?这里就会用到它了resolveEmbeddedValue
public String resolveEmbeddedValue(String value) { String result = value; for (StringValueResolver resolver : this.embeddedValueResolvers) { if (result == null) { return null; } result = resolver.resolveStringValue(result); } return result; }
public String resolveStringValue(String strVal) throws BeansException { String value = this.helper.replacePlaceholders(strVal, this.resolver); return (value.equals(nullValue) ? null : value); }public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) { Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null"); return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet<String>()); }//解析出表达式的值 protected String parseStringValue( String strVal, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) { StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(strVal); // placeholderPrefix 占位符前缀 int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix); while (startIndex != -1) { //找到占位符结束位置的下标 int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex); if (endIndex != -1) { //得到真实的key值 String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex); String originalPlaceholder = placeholder; if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException( "Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions"); } // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key. //递归调用,分析占位符键中包含的占位符。 placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); // Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key... //获取解析键的值 String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder); if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) { int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator); if (separatorIndex != -1) { String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex); String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length()); propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder); if (propVal == null) { propVal = defaultValue; } } } if (propVal != null) { // Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the // previously resolved placeholder value. propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders); //替换占位符 result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal); if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'"); } startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length()); } else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) { //忽略不可解析的占位符 ,占位符的解析支持多个StringValueResolver , 因为某个StringValueResolver可能找不到想要的配置,其他的StringValueResolver能找到,可以设置这个值为true 避免抛出异常 // Proceed with unprocessed value. // 这里的startIndex肯定是为-1的 startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length()); } else { // PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer 一般需要把配置文件合并形成 一个 ,否则在AbstractBeanFactory#resolveEmbeddedValue里面for循环时会有可能遍历某个StringValueResolver找不到想要的配置而报错 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" + placeholder + "'" + " in string value \"" + strVal + "\""); } visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder); } else { startIndex = -1; } } return result.toString(); } - 还记得之前创建的的创建
-
最后会调用到此处
PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer#resolvePlaceholder//得到配置文件的值 protected String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholder, Properties props, int systemPropertiesMode) { String propVal = null; if (systemPropertiesMode == SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_OVERRIDE) { propVal = resolveSystemProperty(placeholder); } if (propVal == null) { //会进入这里 propVal = resolvePlaceholder(placeholder, props); } if (propVal == null && systemPropertiesMode == SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_MODE_FALLBACK) { propVal = resolveSystemProperty(placeholder); } return propVal; }protected String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholder, Properties props) { return props.getProperty(placeholder); } -
得到了属性值,最后就是对属性设值



-
本篇文章比较长,读完确实需要比较大的耐心;最后本人水平有限,如果文章有误的地方,希望批评指正,感谢您的观看。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 25岁的心里话
· 按钮权限的设计及实现