微服务迁移记(六):集成jwt保护微服务接口安全
JWT=json web token,是一种跨语言的身份校验机制,通信双方之间以Json对象的形式安全的传递信息,对数据进行加密传输,保证信息传递过程中的身份可信。
微服务各模块或不同应用程序、终端之间的RPC调用,也应该保障数据传递的安全和可靠,避免身份伪造、传递数据被拦截获取和篡改等信息安全。
我们对前面的微服务API实现层进行如下改造:
第一步:调用接口前,先进行接口用户登录,获取令牌(TOKEN)。
这个用户登录和后台的用户登录不同,是我们分配给每个需要调用API的终端的用户信息。所以我们要再创建一张表,用来保存API权限,为了便于后期扩展,我们还可以增加一些字段如调用阈值,可以再加一个子表,保存这个用户具备哪些接口的调用权限以及阈值等。(说明:下面的代码示例并未取数据库,只是实现业务逻辑)
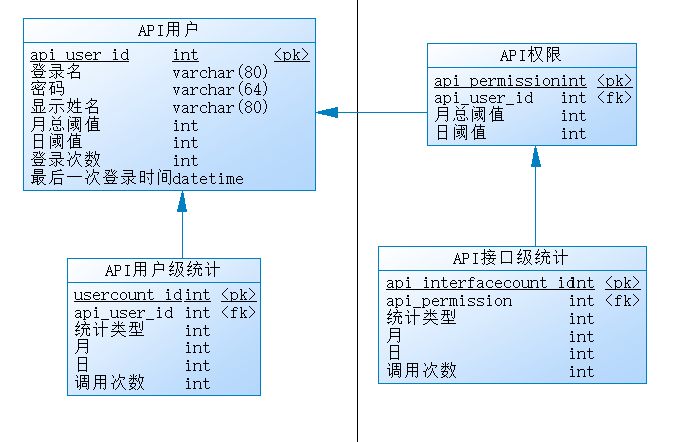
1. JwtUtil类,主要用来做token生成和校验。客户端应该与服务端超时时间保持一致或小于服务端超时时间。
/** * @program: zyproject * @description: jwt公共类 * @author: zhouyu(zhouyu629 # qq.com) * @create: 2020-03-04 **/ public class JwtUtil { static final long EXPTIME = 3600_000_000L; //超时时间 static final String SECRET = "Abc@1234"; //示例代码,默认密钥 /** * 生成token * @param user_name * @return */ public static String generatorToken(String user_name){ HashMap<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("user_name",user_name); String jwt = Jwts.builder() .setClaims(map) .setExpiration(new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()+EXPTIME)) .signWith(SignatureAlgorithm.HS512,SECRET) .compact(); return "Bearer "+ jwt; } /** * token校验 * @param token */ public static void validateToken(String token){ try{ Map<String,Object> body = Jwts.parser() .setSigningKey(SECRET) .parseClaimsJws(token.replace("Bearer ","")) .getBody(); }catch (Exception e){ throw new IllegalStateException("Invalid Token."+e.getMessage()); } } }
2. 过滤器:JwtAuthenticationFilter
该过滤器的主要作用是对受保护的接口进行签名校验,如果客户端没有携带token或token不正确,则返回统一报错信息。
isProtectedUrl:验证当前请求是否需要保护
isExceedUrl:例外URL,如登录、统一报错接口,不需要进行token认证
BusinessException:这个是自定义的异常信息,后面有单独章节说明如何做控制器、过滤器的统一出错处理。
/** * @program: zyproject * @description: 接口认证过滤器 * @author: zhouyu(zhouyu629 # qq.com) * @create: 2020-03-04 **/ public class JwtAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter { private final static AntPathMatcher pathMatcher = new AntPathMatcher(); @Override protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest httpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse httpServletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws ServletException, IOException { try { if(isProtectedUrl(httpServletRequest) && !isExceedUrl(httpServletRequest)){ String token = httpServletRequest.getHeader("Authorization"); JwtUtil.validateToken(token); } }catch (Exception e){ //httpServletResponse.sendError(CodeEnum.UNAUTHORIZED.getCode(),e.getMessage()); throw new BusinessException(CodeEnum.UNAUTHORIZED); } filterChain.doFilter(httpServletRequest,httpServletResponse); } private boolean isProtectedUrl(HttpServletRequest request){ return pathMatcher.match("/api/**",request.getServletPath()); } private boolean isExceedUrl(HttpServletRequest request){ return pathMatcher.match("/init/**",request.getServletPath()); }
3. 我们在ApiInitController里,做用户登录和统一报错返回。
/** * @program: zyproject * @description: API初始化相关 * @author: zhouyu(zhouyu629 # qq.com) * @create: 2020-03-04 **/ @RestController @RequestMapping("/init") public class ApiInitService implements IApiInitService { //控制器统一出错信息 @RequestMapping("/api-error") public ResponseData apierror(HttpServletRequest request){ Exception e = (Exception)request.getAttribute("filter.error"); try{ //应该对Exception做更细致的划分 BusinessException be = (BusinessException)e; return ResponseData.out(be.getCodeEnum(),null); }catch (Exception ex) { return ResponseData.out(CodeEnum.FAIL,e.getMessage()); } } //用户登录,测试阶段写死admin登录 @GetMapping("/login") @Override public ResponseData login(String user_name) { if("admin".equals(user_name)){ String jwt = JwtUtil.generatorToken(user_name); return ResponseData.out(CodeEnum.SUCCESS,jwt); }else { return ResponseData.out(CodeEnum.AUTHORIZEDUSERNAMEORPASSWORDINVALID, null); } } }
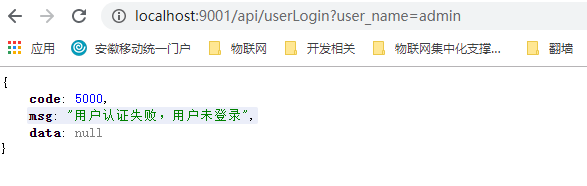
通过以上操作,如果直接访问接口,则会提示未登录,如:
用postman进行登录后,再调用api测试
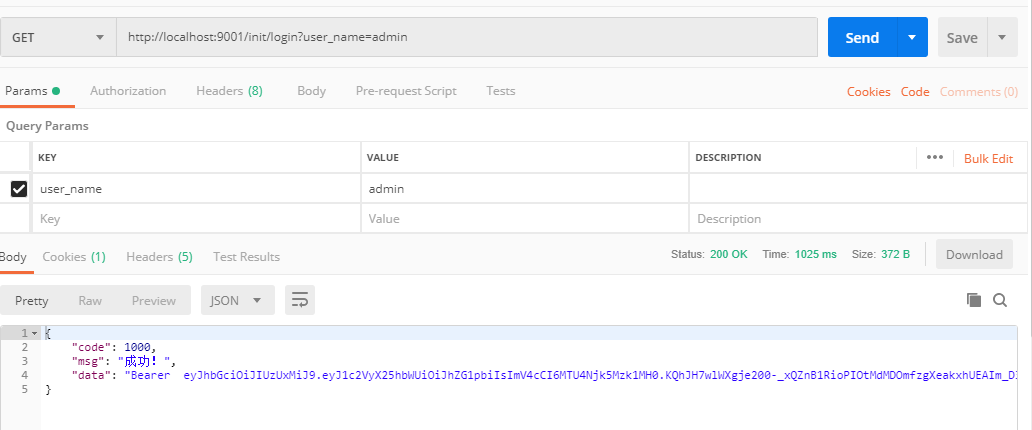
拿分配的token,再去访问api相关接口,返回成功:

第二步:访问具体API,Header中需要携带JWT信息,对令牌(TOKEN)的合法性进行校验
接下来,改造WEB层访问,首次请求,拿到token缓存起来,以后每次调用,缓存不过期,就直接使用,过期后就重新拿。
1. 增加一个拦截器,为所有的FeiClient添加头信息,携带token。
/** * @program: zyproject * @description: Feign拦截器,用于在所有请求上加上header,适用于jwt token认证 * @author: zhouyu(zhouyu629 # qq.com) * @create: 2020-03-04 **/ public class FeignInterceptor implements RequestInterceptor { private final String key = "Authorization"; private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass()); @Autowired private ApiInitService apiInitService; @Override public void apply(RequestTemplate requestTemplate) { HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest(); logger.info("当前路径:"+ request.getServletPath()); if(request.getServletPath().indexOf("init") < 0) { //后期把token放到redies里保存起来 if (!requestTemplate.headers().containsKey(key)) { //拿token String token = this.apiInitService.getToken(); requestTemplate.header(key, token); } } } }
2. FeignClient接口改造
为了不让spring创建相同context的bean,为FeiClient注解增加ContextId
/** * @program: zyproject * @description: 系统登录方法 * @author: zhouyu(zhouyu629 # qq.com) * @create: 2020-03-04 **/ @FeignClient(name = "zyproject-api-service-system",contextId = "apiinit",configuration = {}) public interface ApiInitFeign extends IApiInitService { }
需要保护的接口,使用拦截器
/** * @program: zyproject * @description: RPC调用系统管理相关接口服务 * @author: zhouyu(zhouyu629 @ qq.com) * @create: 2020-02-11 **/ @FeignClient(name ="zyproject-api-service-system",contextId = "system",configuration = {FeignInterceptor.class}) public interface SystemFeign extends ISystemService { }
到此,API接口保护完成,客户端测试通过。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· .NET周刊【3月第1期 2025-03-02】
· [AI/GPT/综述] AI Agent的设计模式综述