spring boot 单元测试使用new MockMvc和@RunWith+@AutoConfigureMockMvc注解的区别
在单元测试中用以上两种都能实现,但是@RunWith注解还可以实现代码中的依赖注入(前者不能)
单测代码如下
Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rest")
public class ArticleRestController {
@Resource
ArticleRestService articleRestService;
/**
* 增加一篇文章
*
* @param article
* @return
*/
// @RequestMapping(value = "/article", method = RequestMethod.POST, produces = "application/json")
@PostMapping("/article")
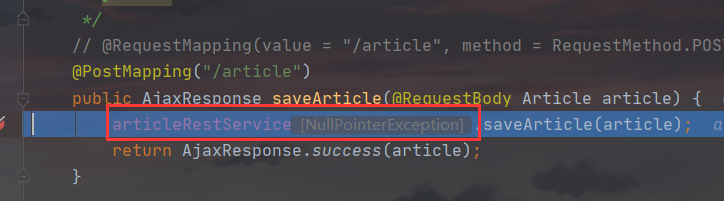
public AjaxResponse saveArticle(@RequestBody Article article) {
articleRestService.saveArticle(article);
return AjaxResponse.success(article);
}
}
自定义MockMvc做法,会报出空指针异常
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
public class ArticleRestControllerTest {
//mock对象
private MockMvc mockMvc;
//mock对象初始化
@BeforeEach
public void setUp() {
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(new ArticleRestController()).build();
}
//测试方法
@Test
public void saveArticle() throws Exception {
String article = "{\n" +
" \"id\": 1,\n" +
" \"author\": \"zimug\",\n" +
" \"title\": \"手摸手教你开发spring boot\",\n" +
" \"content\": \"c\",\n" +
" \"reader\":[{\"name\":\"zimug\",\"age\":18},{\"name\":\"kobe\",\"age\":37}]\n" +
"}";
MvcResult result = mockMvc.perform(
MockMvcRequestBuilders.request(HttpMethod.POST, "/rest/article")
.contentType("application/json").content(article))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.data.author").value("zimug"))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.data.reader[0].age").value(18))
.andDo(print())
.andReturn();
log.info(result.getResponse().getContentAsString());
}
}
使用@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)注解
@Slf4j
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc //相当于new MockMvc
@SpringBootTest
public class ArticleRestControllerTest2 {
//mock对象
@Resource
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Resource
ArticleRestService articleRestService;
//测试方法
@Test
public void saveArticle() throws Exception {
String article = "{\n" +
" \"id\": 1,\n" +
" \"author\": \"zimug\",\n" +
" \"title\": \"手摸手教你开发spring boot\",\n" +
" \"content\": \"c\",\n" +
" \"reader\":[{\"name\":\"zimug\",\"age\":18},{\"name\":\"kobe\",\"age\":37}]\n" +
"}";
MvcResult result = mockMvc.perform(
MockMvcRequestBuilders.request(HttpMethod.POST, "/rest/article")
.contentType("application/json").content(article))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.data.author").value("zimug"))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.data.reader[0].age").value(18))
.andDo(print())
.andReturn();
log.info(result.getResponse().getContentAsString());
}
}
不会报出异常
解析
- RunWith方法为我们构造了一个的Servlet容器运行运行环境,并在此环境下测试。然而为什么要构建servlet容器?因为使用了依赖注入,注入了MockMvc对象,而在上一个例子里面是我们自己new的。
- 而@AutoConfigureMockMvc注解,该注解表示 MockMvc由spring容器构建,你只负责注入之后用就可以了。这种写法是为了让测试在Spring容器环境下执行。
- Spring的容器环境是什么呢?比如常见的 Service、Dao 都是Spring容器里的bean,装载到容器里面都可以使用@Resource和@Autowired来注入引用。
- 简单的说:如果你单元测试代码使用了依赖注入就加上@RunWith,如果你不是手动new MockMvc对象就加上@AutoConfigureMockMvc
感谢您的阅读,如果您觉得阅读本文对您有帮助,请点一下“推荐”按钮。本文欢迎各位转载,但是转载文章之后必须在文章页面中给出作者和原文连接。
分类:
Java




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器