(4)理解 neutron ml2---port创建流程代码解析
port是neutron的核心资源之一,port的主要目的是承载Mac地址和ip地址。
有了Mac和ip地址虚拟机才能够实现彼此之间的通信。当然port不一定是
仅仅给虚拟机使用,也可能将port绑定在路由器上。一个port一定是属于一个
networks的,但是一个port有可能属于多个subnets,属于多个subnets意味着
一个网卡可以有多个ip地址,在创建虚拟机绑定网络的时候可以指定挂载的网卡
和对应的fixed_ip。
网卡创建的代码依然是放在了plugin.py这个文件里
/neutron/plugins/ml2/plugin.py
@utils.transaction_guard @db_api.retry_if_session_inactive() def create_port(self, context, port): result, mech_context = self._create_port_db(context, port) # notify any plugin that is interested in port create events kwargs = {'context': context, 'port': result} registry.notify(resources.PORT, events.AFTER_CREATE, self, **kwargs) try: self.mechanism_manager.create_port_postcommit(mech_context) except ml2_exc.MechanismDriverError: with excutils.save_and_reraise_exception(): LOG.error(_LE("mechanism_manager.create_port_postcommit " "failed, deleting port '%s'"), result['id']) self.delete_port(context, result['id'], l3_port_check=False) self.notify_security_groups_member_updated(context, result) try: bound_context = self._bind_port_if_needed(mech_context) except os_db_exception.DBDeadlock: # bind port can deadlock in normal operation so we just cleanup # the port and let the API retry with excutils.save_and_reraise_exception(): LOG.debug("_bind_port_if_needed deadlock, deleting port %s", result['id']) self.delete_port(context, result['id']) except ml2_exc.MechanismDriverError: with excutils.save_and_reraise_exception(): LOG.error(_LE("_bind_port_if_needed " "failed, deleting port '%s'"), result['id']) self.delete_port(context, result['id'], l3_port_check=False) return bound_context.current
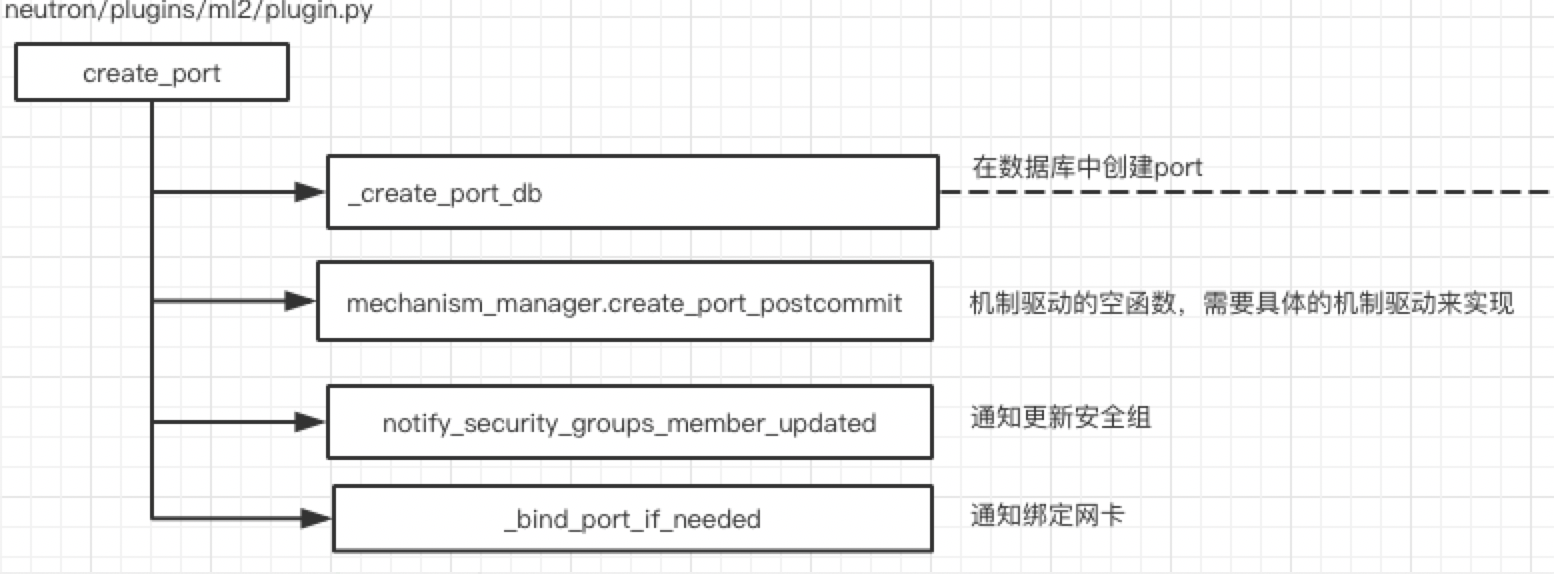
其中最重要的是上面四个步骤,最最重要的是_create_port_db这个函数。
def _create_port_db(self, context, port): attrs = port[attributes.PORT] if not attrs.get('status'): attrs['status'] = const.PORT_STATUS_DOWN session = context.session with session.begin(subtransactions=True): dhcp_opts = attrs.get(edo_ext.EXTRADHCPOPTS, []) port_db = self.create_port_db(context, port) result = self._make_port_dict(port_db, process_extensions=False) self.extension_manager.process_create_port(context, attrs, result) self._portsec_ext_port_create_processing(context, result, port) # sgids must be got after portsec checked with security group sgids = self._get_security_groups_on_port(context, port) self._process_port_create_security_group(context, result, sgids) network = self.get_network(context, result['network_id']) binding = db.add_port_binding(session, result['id']) mech_context = driver_context.PortContext(self, context, result, network, binding, None) self._process_port_binding(mech_context, attrs) result[addr_pair.ADDRESS_PAIRS] = ( self._process_create_allowed_address_pairs( context, result, attrs.get(addr_pair.ADDRESS_PAIRS))) self._process_port_create_extra_dhcp_opts(context, result, dhcp_opts) self.mechanism_manager.create_port_precommit(mech_context) self._setup_dhcp_agent_provisioning_component(context, result) self._apply_dict_extend_functions('ports', result, port_db) return result, mech_context
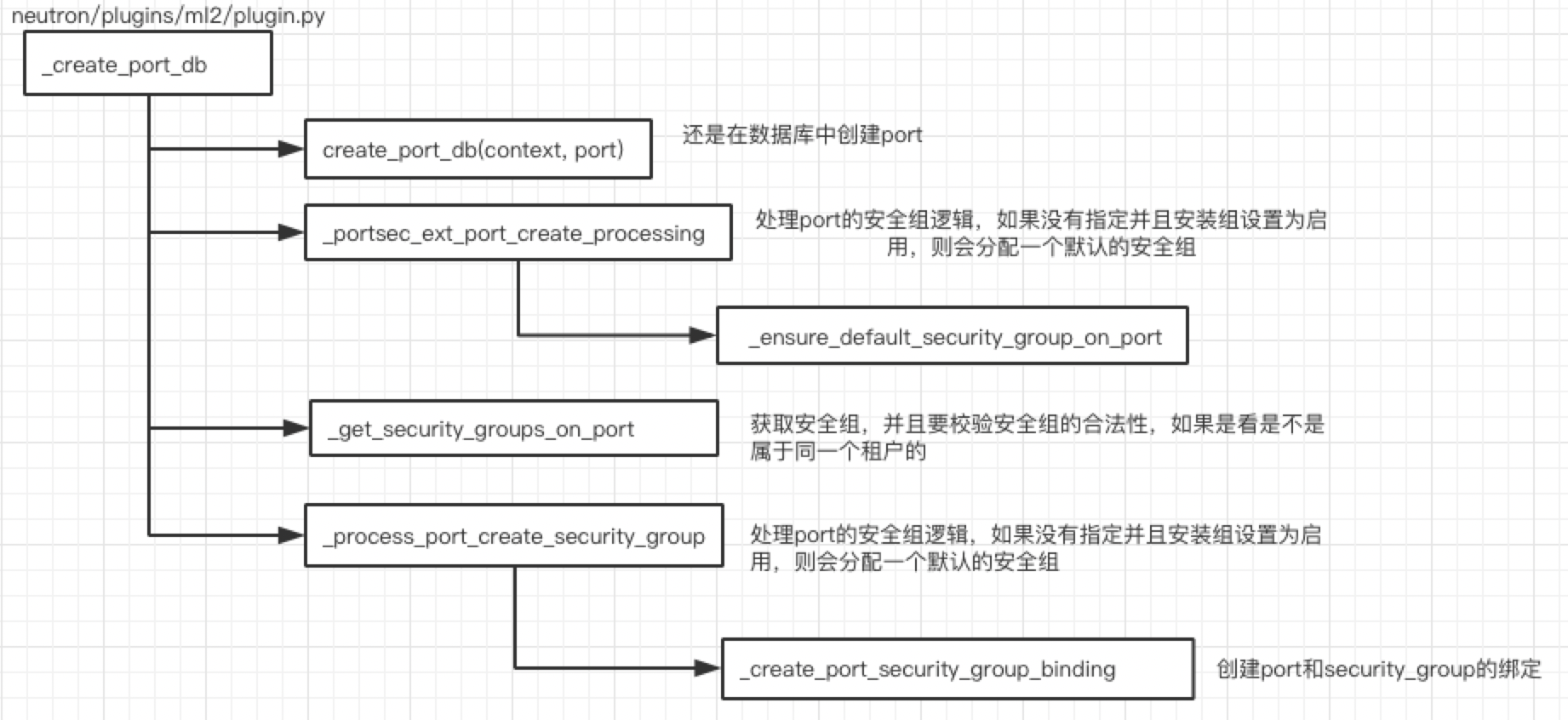
如上图所示_create_port_db做了很多和安全组以及port_binding相关的工作:主要是将port,security_group, port_binding等相关数据存入数据库,从中可以总结出ml2关于数据库
操作的逻辑,涉及数据存储到数据库的工作都会放在_create_xxx_db(xxx代表subnet, port, network等)函数内部进行操作。比如这里的创建_create_port_db。
db.add_port_binding(session, result['id'])
这句话处理port_binding相关的入库工作。具体代码如下所示:
def add_port_binding(session, port_id): with session.begin(subtransactions=True): record = models.PortBinding( port_id=port_id, vif_type=portbindings.VIF_TYPE_UNBOUND) session.add(record) return record
create_port_db则处理的是port本身的入库逻辑。port的创建有一个比较重要的逻辑就是分配ip地址,ip地址和mac地址是port这个资源模型所要承载的最终要的两个数据。
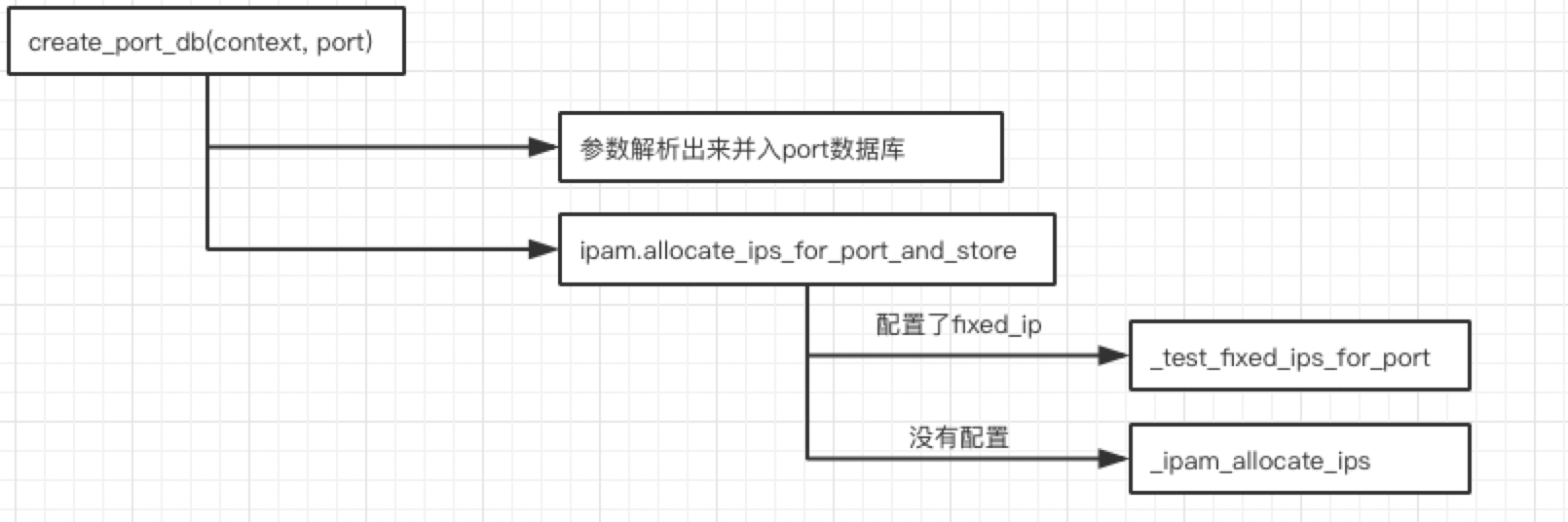
下面看一下分配ip地址的代码:
def allocate_ips_for_port_and_store(self, context, port, port_id): # Make a copy of port dict to prevent changing # incoming dict by adding 'id' to it. # Deepcopy doesn't work correctly in this case, because copy of # ATTR_NOT_SPECIFIED object happens. Address of copied object doesn't # match original object, so 'is' check fails port_copy = {'port': port['port'].copy()} port_copy['port']['id'] = port_id network_id = port_copy['port']['network_id'] ips = [] try: ips = self._allocate_ips_for_port(context, port_copy) for ip in ips: ip_address = ip['ip_address'] subnet_id = ip['subnet_id'] IpamPluggableBackend._store_ip_allocation( context, ip_address, network_id, subnet_id, port_id) return ips except Exception: with excutils.save_and_reraise_exception(): if ips: ipam_driver = driver.Pool.get_instance(None, context) if not ipam_driver.needs_rollback(): return LOG.debug("An exception occurred during port creation. " "Reverting IP allocation") self._safe_rollback(self._ipam_deallocate_ips, context, ipam_driver, port_copy['port'], ips, revert_on_fail=False)

