多线程与高并发六-容器
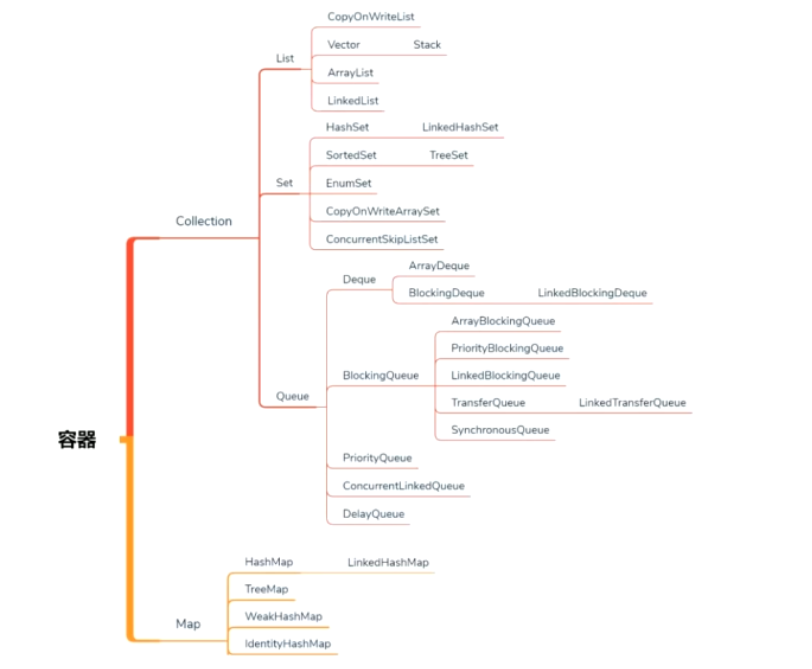
容器图
一、MAP
1、不需要同步的情况
HashMap
TreeMap
LinkedHashMap
2、并发不高的情况
Hashtable
Collections.synchronizedMap();
3、高并发的情况
ConcurrentHashMap (分成16段,然后给各段加锁,多线程访问小分段,所以效率高些)
ConcurrentHashSet
ConcurrentSkipListMap 跳表,已排序,可以用来快速查找
二、LIST
1、不需要同步的情况
ArrayList
LinkedList
2、并发的情况
Vector
Collections.synchronizedList( )
CopyOnWriteList
写时复制容器 copy on write 写的时候,复制一份新的供读
多线程环境下,写时效率低,读时效率高
适合写少读多的环境
三、QUEUE
1、不需要同步的情况
LinkedList
PriorityQueue
2、高并发的情况
-
高性能队列:CocurrentLinkedQueue / concurrentArrayQueue
-
阻塞队列:BlockingQueue
BlockingQueue可以作为多个线程之间的数据共享通道。
BlockingQueue的特点是什么?
BlockingQueue的优势在于,增加了更多API,比如put,take
或者阻塞,或者指定时间等待
实现生产者-消费者模型,也是多线程里面最重要的一个模型,也是MQ的基础——MQ的本质,就是一个大型的生产者、消费者模型
LinkedBlockingQueue:基于链表实现,适合做无界队列或者边界值非常的大队列,阻塞使用await实现的,底层应该是park
ArrayBlockingQueue(int capacity):基于数组实现,适合做有界队列
//满了不会报异常,但是不会加进去
public boolean offer(E e) {
...
}
//如果满了,就会等待,程序阻塞
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
...
}
//满了报异常
public boolean add(E e) {
if (offer(e))
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}
//如果空了,就会等待,程序阻塞
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
...
}
//如果队列为空,直接返回null
public E poll() {
...
}
put() 和 take() 方法是体现 Blocking 的关键。
-
执行定时任务:DelayQueue
DelayQueue可以实现在时间上的排序
需要实现compareTo方法
需要指定等待时间
用来按时间进行任务调度
public class DelayQueue<E extends Delayed> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E> {
}
示例:
static BlockingQueue<MyTask> tasks = new DelayQueue<>();
static class MyTask implements Delayed {
long runningTime;
MyTask(long rt) {
this.runningTime = rt;
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
if(this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) < o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
return -1;
else if(this.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS) > o.getDelay(TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
@Override
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return unit.convert(runningTime - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "" + runningTime;
}
}
MyTask t1 = new MyTask(now + 5000);
tasks.put(t1);
DelayQueue是阻塞无界队列,实现了BlockingQueue。默认排了序,每个元素需要等一段时间才能被取出来,每个元素自己会记录时间,等待时间最短的排在前面,最先取出来。
- 转发消息:TransferQueue
TransferQueue是一个接口,实现类为:LinkedTransferQueue
// 生产者有数据时首先看有没有消费者,有的话,直接给消费者,不放进队列了
// 没有消费者的话 就阻塞在这里,后面的代码执行不了了
public void transfer(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (xfer(e, true, SYNC, 0) != null) {
Thread.interrupted(); // failure possible only due to interrupt
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
使用时需先启动消费者,后启动生产者。可以用于实时消息处理。
- SynchronusQueue: 一种特殊TransferQueue,容量为0
//阻塞等待消费者消费 用的是transfer
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) throw new NullPointerException();
if (transferer.transfer(e, false, 0) == null) {
Thread.interrupted();
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
//如果容量不为0,报错
public boolean add(E e) {
if (offer(e))
return true;
else
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}
本文来自博客园,作者:gary2048,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zhoum/p/15130505.html


