python中常用模块2
time模块即1与时间有关的模块
可以分为三类:
1.时间戳 从1970-1-1 0:0:0开始计算时间
time.time()
2.结构化时间
time.localtime() 返回的是一个元祖 是指当地的时间
time.localtime()也可以获取单个值 例如:time.localtime().tm_year
time.gmtime() 指时间统一时间
3.格式化的字符串时间
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p")
time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d %X %p")
三种格式之间也可相互转化
和时间相关的常用模块还有datetime模块,datetime模块可以分成两个部分1.和日期相关2.和时间相关
datetime模块
datetime.datetime.now() 获取当前的详细时间,也可以获取时间的部分
例如:datetime.datetime.now().hour
亦可以替换时间的某一部分
例如:x=datetime.datetime.now()
x1=x.replace(year=2020)
print(x)
这样就可以把年份换掉了
datetime.timedelta() 时间差对象不常用
pickle模块
pickle是一个用来序列化的模块,序列化即将内存中的数据结构转化为一种中间格式存储到硬盘中,永久存储.说道序列化就要提到反序列化,即把硬盘上存储的中间格式数据还原到内存中使用.
pickle.dump()和pickle.dumps()都是序列化.区别在与pickle.dump对write进行了封装
pickle.load()和pickle.loads()都是反序列化.区别是pickle.load对read进行了封装.
shelve模块
也是用于序列化的,和pickle的不同在于不需要关心文件模式,直接把它当成字典看待,也可以直接对数据进行修改,而不用覆盖原有的数据.
json模块
json是java script object notation的缩写对于python来说json就是一种通用的数据格式
js 中的数据类型 python数据类型 的对应关系
{} 字典
[] list
string "" str
int/float int/float
true/false True/False
null None
json的常用功能
json.dump()和json.dumps()
json.load()和json.loads()
xml模块
xml指可扩展的标记语言
xml.etree.ElementTree.parse() 解析文件
rootTree = tree.getroot() 获取根便签
for item in rootTree.iter() 获取全文内所有标签
item.tag() 获取标签名
item.attrib() 获取标签的属性
item.text() 获取文本的内容
rootTree.find() 获取单个属性
rootTree.remove() 删除标签
添加标签
x=xml.etree.ElementTree.Element()
rootTree.append(x)
tree.write() 写入文件
configparser模块
用于解析配置文件的模块,配置文件只有两种内容:section和option
configparser.ConfigParser() 创建一个解释器
config.read() 读取并解析文件
config.sections() 获取所有分区
config.options() 获取所有选项
config.get(sections,options) 获取某个值,返回的是字符串类型的值
config.has_option() 是否存在某个选项
config.add_section() 添加分区
config.set()
config.remove_option() 删除选项
config.set() 可以用于修改
config.write() 写入文件
logging模块
1. 日志的级别
loging.debug 调试信息 10
logging.info 常规信息 20
logging.warning 警告信息 30
logging.error 错误信息 40
logging.critical 严重错误 50
默认情况下 级别是30 logging warning 日志的输入位置是控制台
2.自定义日志的配置
logging.basicConfig(
filename="a.log",
filemode="at",
level=10,
format="%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(funcName)s %(lineno)s %(message)s",
datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %X %p"
)
日志模块的四个核心角色
1.logger 2.filter 3.handler 4. formatter
1.生成一个日志
logger=logging.getLogger('logger')
.设置日志级别
logger.setLever(logging.DEBUG)
2.日志处理器
logging.FileHandler()
3.格式化处理器
logging.Formatter("%(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(funcName)s %(lineno)s %(message)s",datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %X %p")
4.将以上三步进行连接
logger文件的继承
以字典生成logger
logging.StreamHandler() 输出到控制台
logging.FileHandler() 输出到文件
hashlib模块
hash是一种算法,将 一的个任意长的数据得到固定长度特征码.
重要用于密码验证
m=hashlib.md5("aaa".encode("utf-8"))
加盐
m.update("abcdefplkjoujhh".encode("utf-8"))
print(m.hexdigest)
re模块
主要正则表达式相关即 一堆带有特殊意义的符号组成式子
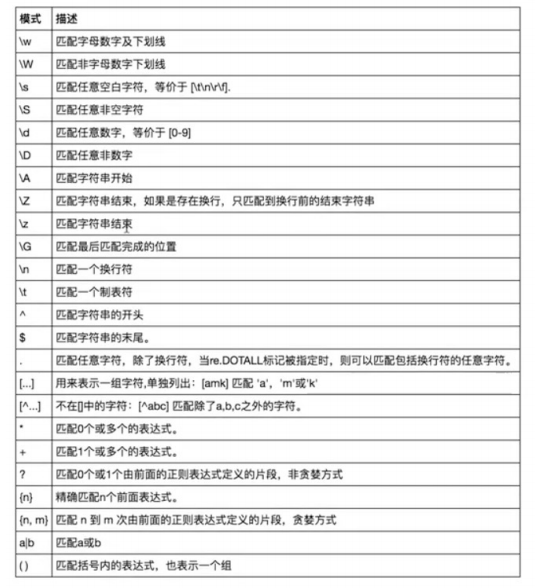
re.findall() 找出所有
re.match 从字符串开始处匹配,只找一个
re.search() 从全文范围匹配,只取一个
re.split() 切分
re.sub() 替换
当要匹配的内容包含\时
\\\\
subprocess模块
res=subprocess.Popen(cmd,shell=True,stdout=subprocess.PIPE,stderr=subprocess.PIPE)
stdout 输出管道
stdin 输入管道
stderr 错误管道
res.stdout.read()
subprocess 主要用于执行系统指令 (启动子进程) 与os.system的不同在于
subprocess 可以与这个子进程进行数据交换





