Elasticsearch(2) 数据搜索
本文介绍如何在Elasticsearch中对数据进行搜索。
1、简述
在Elasticsearch中的搜索中,有两类搜索:
- queries
- aggregations
区别在于:query可以进行全文搜索,而aggregation可以进行统计及分析。当然可以结合query及aggregation一起使用,比如先对文档进行搜索,然后进行aggregation。
GET blogs/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "community"
}
},
"aggregations": {
"top_authors": {
"terms": {
"field": "author"
}
}
}
}
在上面搜索中,先搜索title含有community的文档,然后再对数据进行aggregation。
2、搜索所有文档
使用如下命令搜索所有文档:
GET /_search
此时没指定任何index,因此搜索该cluster下的所有的index。默认返回个数是10个,除非设定size:
GET /_search?size=20
上面命令也等同于:
GET /_all/_search
可以对多个index进行搜索:
POST /index1,index2,index3/_search
也可以这么写,表明针对所有以index开头的索引进行搜索,但排除index3索引。
POST /index*,-index3/_search
如果想对特定的index进行搜索,可以这样:
GET twitter/_search
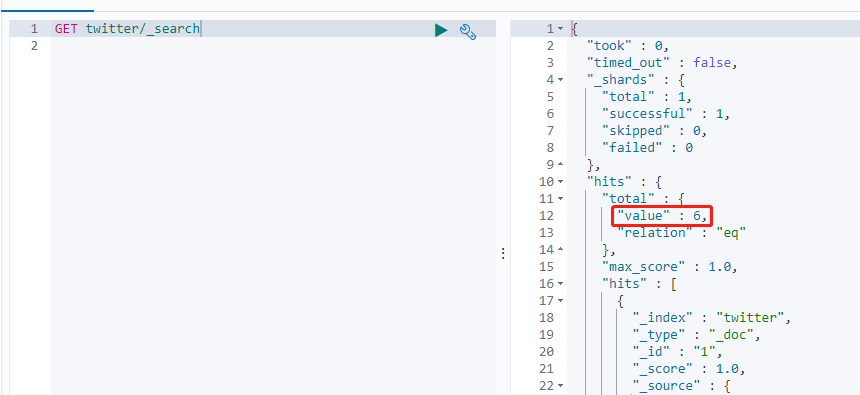
上图中,可以看到twiter索引里有7个文档。再hits数组里可以看到所有的结果。同时也可以看到_score 的项,表示我们搜索结果的相关度。这个分数值越高表明搜索匹配的相关度越高。再默认没有sort的情况下,所有搜索的结果读书安装分数由大到小来进行排列的。
在默认情况下,可以得到10个结果,当然可以通过设置size参数来得到想要的个数。同时也可以配合from来进行分页。
GET twitter/_search?size=2&from=2
并且只显示两个文档。通过这种方法可以对文档进行分页显示。
上面查询类似DSL查询的如下语句:
GET twitter/_search
{
"size": 2,
"from": 2,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
可以通过filter_path来控制输出的较少的字段,比如:
GET twitter/_search?filter_path=hits.total
3、_source filtering
通过_source来定义想要返回的字段:
GET twitter/_search
{
"_source": ["user", "city"],
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}
也可以使用这种方式
GET twitter/_search
{
"_source": {
"includes": ["user", "city"]
},
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}
可以设置_source为false,这样不返回任何_source信息:
GET twitter/_search
{
"_source": false,
"query": {
"match": {
"user": "张三"
}
}
}
也可以接收通配符形式的控制:
GET twitter/_search
{
"_source": {
"includes": [
"user*",
"location*"
],
"excludes": [
"*.lat"
]
},
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
如果我们把 _source 设置为[],则显示所有的字段:
GET twitter/_search
{
"_source": [],
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}
4、script fields
有事,我们想要的field可能在_source里根本没有,则可以使用script field来生成这些field。允许为每个匹配返回script evaluation(基于不用的字段):
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"script_fields": {
"years_to_100": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "100-doc['age'].value"
}
},
"year_of_birth":{
"script": "2019 - doc['age'].value"
}
}
}
注意,使用script的方法来生成查询结果对于大量的文档来说,可能会占用大量资源。doc在这里指定是doc value。否则的话,我们需要使用ctx._source来做一些搜索动作。所以可以把上面命令修改为:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"script_fields": {
"years_to_100": {
"script": {
"lang": "painless",
"source": "100-params._source['age']"
}
},
"year_of_birth":{
"script": "2019 - params._source['age']"
}
}
}
因为age是long数据类型。它是由doc value的,所以我们通过doc['age']来访问,而且这些访问是比较快的。
5、count api
使用_count来查询索引里有多少文档:
GET twitter/_count
可以根据满足条件来查询文档数量(比如,可以查询到city为北京的所有文档的数量):
GET twitter/_count
{
"query": {
"match": {
"city": "北京"
}
}
}
6、settings
通过接口获取一个index的settings:
GET twitter/_settings

从图中可以看到twitter索引中有多少个shards及多少个reblicas。我们也可以通过如下的接口来设置:
PUT twitter
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}
一旦把number_of_shards定下来了,就不可以修改了。除非把index删除,并重新index它。因为每个文档存储到哪一个shard是和number_of_shards这个数值有关的。一旦这个数值发生改变,那么之后寻找哪个文档所在的shard就会不准确。
7、mapping
查询当前index的mapping
GET twitter/_mapping
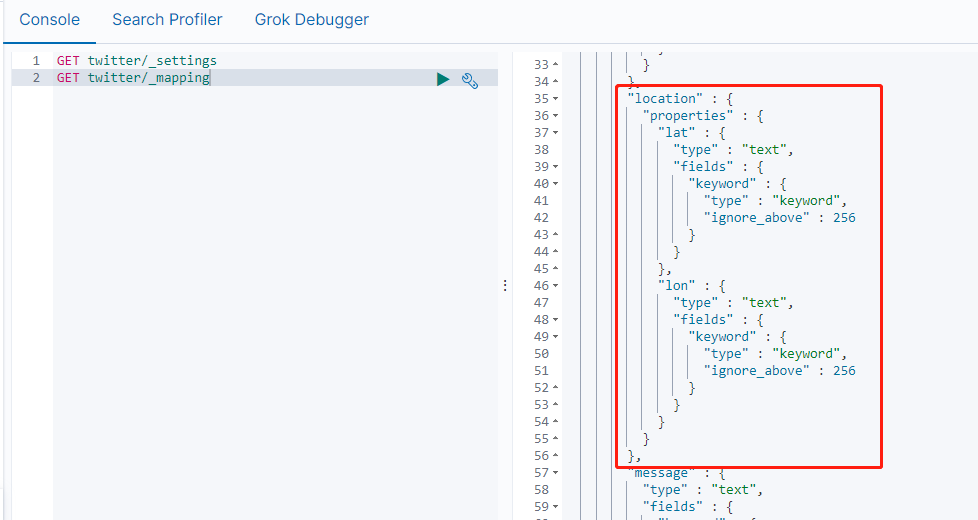
从上图的显示中可以看出来location里的经纬度是一个multi-field类型。这显然不是我们所需的。正确的类型应该是:geo_point。因此需要修正我们的mapping。
注意:
我们不能为已经建立好的index动态修改mapping。这是因为一旦修改,那么之前建立的索引就变成不能搜索了。一种办法是reindex从而重新建立我们的索引。如果之前的mapping加入新的字段,那么欧盟可以不用重新建立索引。
为了能能够正确地创建我们的mapping,我们必须先把之前的twitter索引删除掉,并同时使用settings来创建这个index。具体的步骤如下:
DELETE twitter
PUT twitter
{
"settings": {
"number_of_shards": 1,
"number_of_replicas": 1
}
}
PUT twitter/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"address": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"age": {
"type": "long"
},
"city": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"country": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"location": {
"type": "geo_point"
},
"message": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"province": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"uid": {
"type": "long"
},
"user": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
}
重新查看mapping,此时可以看到已经创建好了新的mapping,并更正了location类型:
GET twitter/_mapping
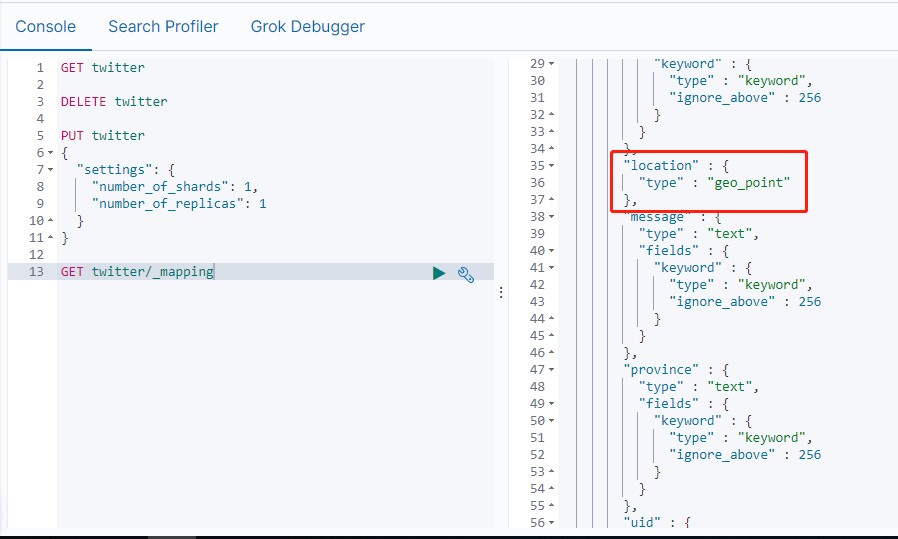
再次运行之前的bulk接口,并把所需要的数据导入到twitter索引中。
POST _bulk
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 1} }
{"user":"双榆树-张三","message":"今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去","uid":2,"age":20,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市海淀区","location":{"lat":"39.970718","lon":"116.325747"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 2 }}
{"user":"东城区-老刘","message":"出发,下一站云南!","uid":3,"age":30,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市东城区台基厂三条3号","location":{"lat":"39.904313","lon":"116.412754"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 3} }
{"user":"东城区-李四","message":"happy birthday!","uid":4,"age":30,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市东城区","location":{"lat":"39.893801","lon":"116.408986"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 4} }
{"user":"朝阳区-老贾","message":"123,gogogo","uid":5,"age":35,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市朝阳区建国门","location":{"lat":"39.718256","lon":"116.367910"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 5} }
{"user":"朝阳区-老王","message":"Happy BirthDay My Friend!","uid":6,"age":50,"city":"北京","province":"北京","country":"中国","address":"中国北京市朝阳区国贸","location":{"lat":"39.918256","lon":"116.467910"}}
{ "index" : { "_index" : "twitter", "_id": 6} }
{"user":"虹桥-老吴","message":"好友来了都今天我生日,好友来了,什么 birthday happy 就成!","uid":7,"age":90,"city":"上海","province":"上海","country":"中国","address":"中国上海市闵行区","location":{"lat":"31.175927","lon":"121.383328"}}
至此,我们已经完整地建立了我们所需要的索引。在下面,我们开始使用DSL(Domain Specific language)来进行查询。
8、查询数据
1)match query
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"city": "北京"
}
}
}
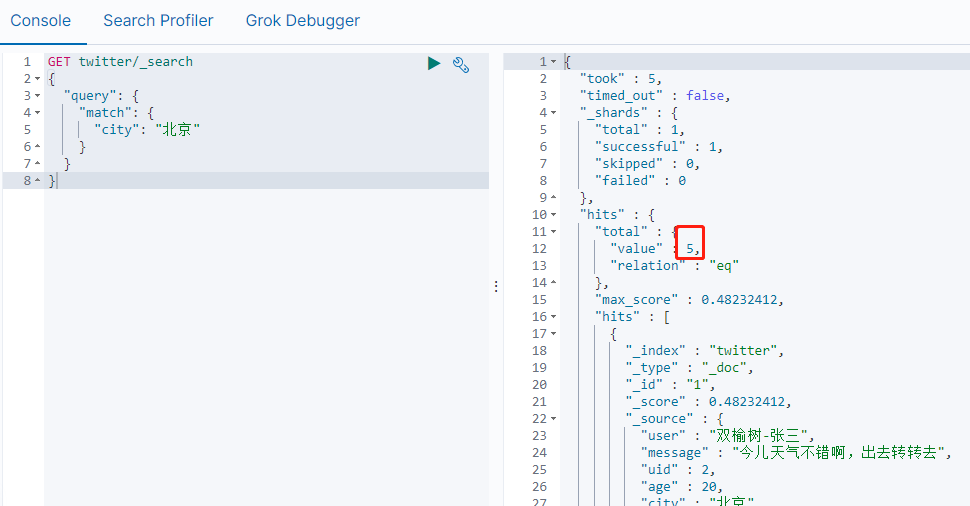
从上述查询结果来看,可以看到有5个用户来自北京。而且查询出来的结果是按照关联(relavance)来进行排序的。
也可以使用script query来完成:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"script": {
"script": {
"source": "doc['city.keyword'].contains(params.name)",
"lang": "painless",
"params": {
"name": "北京"
}
}
}
}
}
script query 和match query查询结果是一样的。但是不建议使用script query方法(比较低效)。假如文档是几百万或者PB级的数据量,那么上面的运算可能被执行无数次,那么可能需要巨大的计算量。在这种情况下,我们需要考虑ingest的时候做计算。
上述的搜索也可以这么实现:
GET twitter/_search?q=city:"北京"
显示如下:
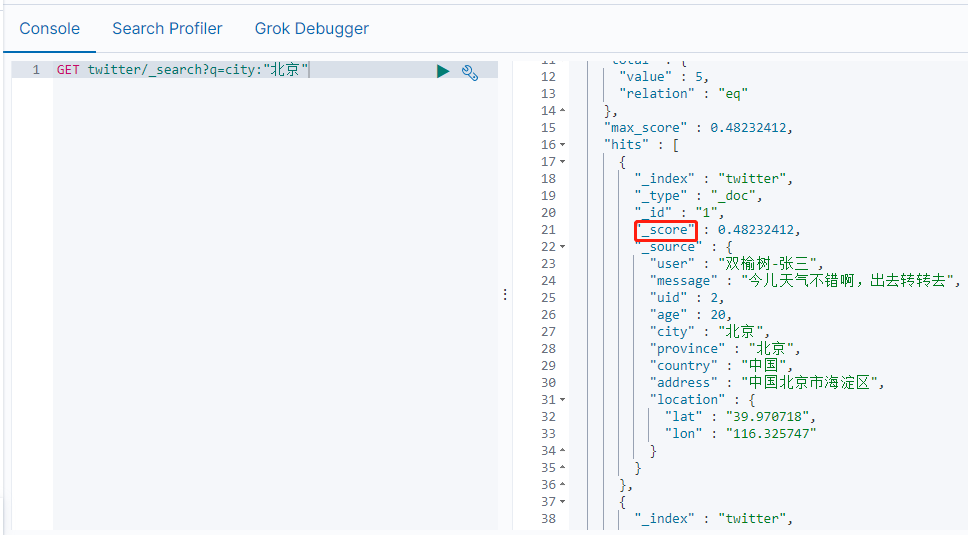
_score项说明:表示与搜索结果相关度。分值越高,表明搜索匹配的相关度越高。在默认没有sort的情况下,所有的搜索的结果都是按照分数由大到小来进行排列的。
如果不要score,我们可以选择filter来完成。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"city.keyword": "北京"
}
}
}
}
}
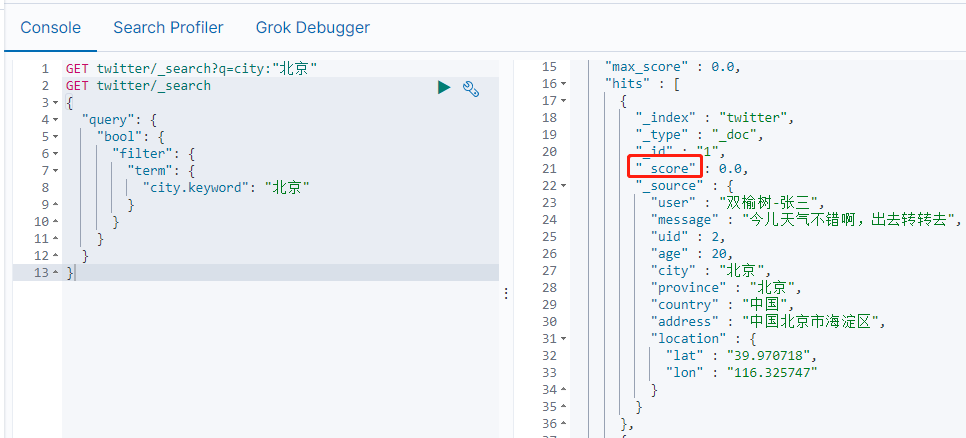
从返回的结果来看,_score项为0.对于这种搜索,只要yes或no。我们并不关心她们的相关性。city.keyword表示在mapping中是一个multi-field项。它既是text也是keyword类型。对于一个keyword类型的项来说,这个项里面保存所有字符都被当作一个字符串。它们在建立文档时,不需要进行index。keyword字段用于精确搜索,aggregation和排序(sorting)。所以在filter中,使用term来完成查询。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"constant_score": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"city.keyword": {
"value": "北京"
}
}
}
}
}
}
使用match query时,默认的操作是or。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"user": {
"query": "朝阳区-老贾",
"operator": "or"
}
}
}
}
等同于
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"user": "朝阳区-老贾"
}
}
}
因为默认操作是or,上面的查询的结果是任何匹配:"朝"、"阳"、"区"、"老"和"贾"这5个字中的任何一个将被显示。具体数据显示如下(注意,score相关性的大小)。
{
"took" : 1,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 5,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 4.4209847,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 4.4209847,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老贾",
"message" : "123,gogogo",
"uid" : 5,
"age" : 35,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区建国门",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.718256",
"lon" : "116.367910"
}
}
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 2.9019678,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老王",
"message" : "Happy BirthDay My Friend!",
"uid" : 6,
"age" : 50,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.918256",
"lon" : "116.467910"
}
}
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.8713734,
"_source" : {
"user" : "东城区-老刘",
"message" : "出发,下一站云南!",
"uid" : 3,
"age" : 30,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市东城区台基厂三条3号",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.904313",
"lon" : "116.412754"
}
}
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "6",
"_score" : 0.4753614,
"_source" : {
"user" : "虹桥-老吴",
"message" : "好友来了都今天我生日,好友来了,什么 birthday happy 就成!",
"uid" : 7,
"age" : 90,
"city" : "上海",
"province" : "上海",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国上海市闵行区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "31.175927",
"lon" : "121.383328"
}
}
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.4356867,
"_source" : {
"user" : "东城区-李四",
"message" : "happy birthday!",
"uid" : 4,
"age" : 30,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市东城区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.893801",
"lon" : "116.408986"
}
}
}
]
}
}
可以设置minimum_should_match来设置至少匹配的term。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"user": {
"query": "朝阳区-老贾",
"operator": "or",
"minimum_should_match": 3
}
}
}
}
上面显示,我们至少要匹配"朝"、"阳"、"区"、"老"和"贾"这5个字中的3个字才可以。显示结果如下:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 4.4209847,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 4.4209847,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老贾",
"message" : "123,gogogo",
"uid" : 5,
"age" : 35,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区建国门",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.718256",
"lon" : "116.367910"
}
}
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 2.9019678,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老王",
"message" : "Happy BirthDay My Friend!",
"uid" : 6,
"age" : 50,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.918256",
"lon" : "116.467910"
}
}
}
]
}
}
也可以修改为and操作。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"user": {
"query": "朝阳区-老贾",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}
显示结果:
{
"took" : 15,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 4.4209847,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 4.4209847,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老贾",
"message" : "123,gogogo",
"uid" : 5,
"age" : 35,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区建国门",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.718256",
"lon" : "116.367910"
}
}
}
]
}
}
在这种情况下,需要索引匹配5个字才可以。显然我们可以通过使用and来提高搜索的精度。
2)Ids query
可以通过id来查询。比如:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": ["1", "2"]
}
}
}
上述查询将返回id为1、2的文档。
3)multi_match
上面的搜索之中,我们特别指明一个专有的field来进行搜索,但是在很多情况下,我们并不知道哪一个是field含有这个关键字。在这种情况下,我们可以使用multi_match来进行搜索:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "朝阳",
"fields": [
"user",
"address^3",
"message"
],
"type": "best_fields"
}
}
}
上述代码中,multi_search的type为best_fields,也就是说它搜索了3个字段。最终分数_score是按照得分最高那个字段分数为准。代码中可以同时对fields:user,address,message进行搜索,但是我们对address含有"朝阳"的文档的分数进行3倍加权。返回结果:
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 6.1777167,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老王",
"message" : "Happy BirthDay My Friend!",
"uid" : 6,
"age" : 50,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.918256",
"lon" : "116.467910"
}
}
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 5.9349246,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老贾",
"message" : "123,gogogo",
"uid" : 5,
"age" : 35,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区建国门",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.718256",
"lon" : "116.367910"
}
}
}
]
4)Prefix query
返回提供的字段中包含特定前缀的文档。如返回user字段中包含"朝"开头的文档:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"user": {
"value": "朝"
}
}
}
}
5) Term query
term query 会在给定字段中进行精确的字词匹配。因此,您需要提供准确的术语以及获取正确的结果。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"user.keyword": {
"value": "朝阳区-老贾"
}
}
}
}
在这里,使用 user.keyword 来对“朝阳区-老贾”进行精确匹配查询相应的文档。
6)Terms query
对多个 terms 进行查询,可以使用如下的方式。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"user.keyword": [
"双榆树-张三",
"东城区-老刘"
]
}
}
}
7)Term_set query
查询在提供的字段中包含最少数目的精确术语的文档。除可以定义返回文档所需的匹配术语数之外,terms_set 查询与术语查询相同。
PUT /job-candidates
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"name": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"programming_languages": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"required_matches": {
"type": "long"
}
}
}
}
PUT /job-candidates/_doc/1?refresh
{
"name": "Jane Smith",
"programming_languages": [ "c++", "java" ],
"required_matches": 2
}
PUT /job-candidates/_doc/2?refresh
{
"name": "Jason Response",
"programming_languages": [ "java", "php" ],
"required_matches": 2
}
GET /job-candidates/_search
{
"query": {
"terms_set": {
"programming_languages": {
"terms": [ "c++", "java", "php" ],
"minimum_should_match_field": "required_matches"
}
}
}
}
在上面,我们为job-candidates索引创建了两文档。此时需要找出在programming_languages中同时包含c++、java以及php中至少两个term的文档。此时上述代码使用了一个在文档中定义的字段required_matches来定义最少满足要求的term个数。当如果没有一个专有的字段来定义这个字段的话,另外一种方式是使用mininum_should_match_script来定义:
GET /job-candidates/_search
{
"query": {
"terms_set": {
"programming_languages": {
"terms": [ "c++", "java", "php" ],
"minimum_should_match_script": {
"source": "2"
}
}
}
}
}
上面标示要至少同时满足2个及以上的term。上面搜索结果为:
{
"took" : 30,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 2,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.1005894,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "job-candidates",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.1005894,
"_source" : {
"name" : "Jane Smith",
"programming_languages" : [
"c++",
"java"
],
"required_matches" : 2
}
},
{
"_index" : "job-candidates",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 1.1005894,
"_source" : {
"name" : "Jason Response",
"programming_languages" : [
"java",
"php"
],
"required_matches" : 2
}
}
]
}
}
也就是说之前的两个文档都同时满足条件。如果使用如下方式来进行搜索:
GET /job-candidates/_search
{
"query": {
"terms_set": {
"programming_languages": {
"terms": [ "c++", "java", "nodejs" ],
"minimum_should_match_script": {
"source": "2"
}
}
}
}
}
我们将看到只有一个文档是满足条件的。
9、复合查询(compound query)
格式如下:
POST _search
{
"query": {
"bool" : {
"must" : {
"term" : { "user" : "kimchy" }
},
"filter": {
"term" : { "tag" : "tech" }
},
"must_not" : {
"range" : {
"age" : { "gte" : 10, "lte" : 20 }
}
},
"should" : [
{ "term" : { "tag" : "wow" } },
{ "term" : { "tag" : "elasticsearch" } }
],
"minimum_should_match" : 1,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
}
从上面代码中可以看出,它是由 bool 下面的 must, must_not, should 及 filter 共同来组成的。
用例:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"city": "北京"
}
},
{
"match": {
"age": "30"
}
}
]
}
}
}
这个查询要求是必须是北京城市的,并且年龄刚好是30岁的。
如果想知道为什么的出来这样的结果,我们可以在搜索的指令中加如"explained":"true"。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"city": "北京"
}
},
{
"match": {
"age": "30"
}
}
]
}
},
"explain": true
}
这样在显示结果中可以看到一些解释:
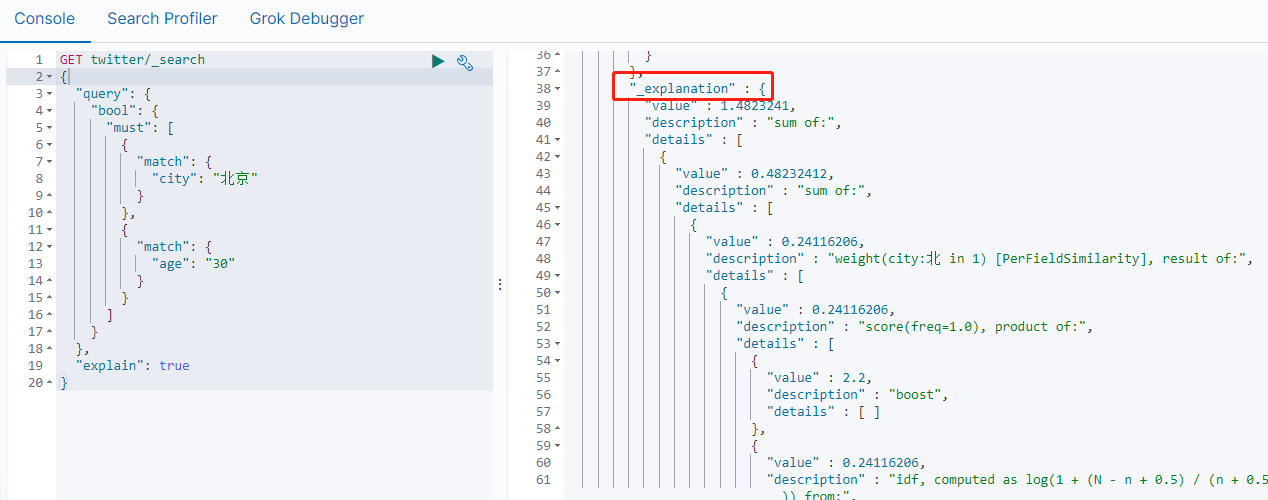
同样如果需要排除某些条件,我们可以使用must_not。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"match": {
"city": "北京"
}
}
]
}
}
}
这个代码表示我们想寻找不在北京的所有文档。所以显示的文档只有一个,即来自上海的文档。
should表述"或"的意思,也就是有就更好,没有就算了。比如:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"age": "30"
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match_phrase": {
"message": "Happy birthday"
}
}
]
}
}
}
搜索意思是age必须是30岁,如果文档中含有"Happy birthday",则相关性会更高,那么搜索得到的结果会排在前面。
在上面的结果中,我们可以看到:同样是年龄30岁的两个文档,第一个文档由于含有 “Happy birthday” 这个字符串在 message 里,所以它的结果是排在前面的,相关性更高。我们可以从它的 _score 中可以看出来。第二个文档里 age 是30,但是它的 message 里没有 “Happy birthday” 字样,但是它的结果还是有显示,只是得分比较低一些。
在使用上面的复合查询时,bool 请求通常是 must,must_not, should 及 filter 的一个或其中的几个一起组合形成的。我们必须注意的是:
查询类型对 hits 及 _score 的影响
| Clause | 影响 #hits | 影响 _score |
| must | Yes | Yes |
| must_not | Yes | No |
| should | No* | Yes |
| filter | Yes | No |
如上面的表格所示,should 只有在特殊的情况下才会影响 hits。在正常的情况下它不会影响搜索文档的个数。那么在哪些情况下会影响搜索的结果呢?这种情况就是针对只有 should 的搜索情况,也就是如果你在 bool query 里,不含有 must, must_not 及 filter 的情况下,一个或更多的 should 必须有一个匹配才会有结果,比如:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"should": [
{
"match": {
"city": "北京"
}
},
{
"match": {
"city": "武汉"
}
}
]
}
}
}
10、位置查询
Elasticsearch最厉害的是位置查询。这在很多关系数据库里并没有。例如:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"address": "北京"
}
}
]
}
},
"post_filter": {
"geo_distance": {
"distance": "3km",
"location": {
"lat": 39.920086,
"lon": 116.454182
}
}
}
}
上述代码表示,查找地址来有北京,并且在以位置(116.454182, 39.920086)为中心的3公里以内的所有文档。
查询结果:
{
"took" : 4,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.48232412,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 0.48232412,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老王",
"message" : "Happy BirthDay My Friend!",
"uid" : 6,
"age" : 50,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.918256",
"lon" : "116.467910"
}
}
}
]
}
}
下面,我们找出5公里以内的所有位置信息,并按照远近大小进行排序:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"address": "北京"
}
}
]
}
},
"post_filter": {
"geo_distance": {
"distance": "5km",
"location": {
"lat": 39.920086,
"lon": 116.454182
}
}
},
"sort": [
{
"_geo_distance": {
"location": "39.920086,116.454182",
"order": "asc",
"unit": "km"
}
}
]
}
在这里,使用sort来对搜索结果进行排序,按照升序排列:
{
"took" : 32,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 3,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : null,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老王",
"message" : "Happy BirthDay My Friend!",
"uid" : 6,
"age" : 50,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.918256",
"lon" : "116.467910"
}
},
"sort" : [
1.1882901656104885
]
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : null,
"_source" : {
"user" : "东城区-老刘",
"message" : "出发,下一站云南!",
"uid" : 3,
"age" : 30,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市东城区台基厂三条3号",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.904313",
"lon" : "116.412754"
}
},
"sort" : [
3.9447355972239952
]
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : null,
"_source" : {
"user" : "东城区-李四",
"message" : "happy birthday!",
"uid" : 4,
"age" : 30,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市东城区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.893801",
"lon" : "116.408986"
}
},
"sort" : [
4.837769064666224
]
}
]
}
}
可以看到有三个显示结果。在sort里面可以看到距离越来越大。另外,如果_score不是sort的field,那么在使用sort后,所有的结果_score都变为null。所有上述的搜索也可以直接写为:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {
"match": {
"address": "北京"
}
},
"filter": {
"geo_distance": {
"distance": "5km",
"location": {
"lat": 39.920086,
"lon": 116.454182
}
}
}
}
},
"sort": [
{
"_geo_distance": {
"location": "39.920086,116.454182",
"order": "asc",
"unit": "km"
}
}
]
}
11、范围查询
如查询年龄介于30到40的文档:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 30,
"lte": 40
}
}
}
}
同样的也可以进行排序
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 30,
"lte": 40
}
}
},
"sort": [
{
"age": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
12、Exists查询
我们可以通过exists来查询一个字段是否存在。比如我们可以增加一个文档:
PUT twitter/_doc/20
{
"user" : "王二",
"message" : "今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去",
"uid" : 20,
"age" : 40,
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市海淀区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.970718",
"lon" : "116.325747"
}
}
这个文档中,city这个字段不存在。那么以下搜索将不会返回上面这个文档。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "city"
}
}
}
要查询不含city的这个字段的所有文档,可以这样查询:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
"exists": {
"field": "city"
}
}
}
}
}
假如创建另外一个索引twitter10:
PUT twitter10/_doc/1
{
"locale": null
}
执行查询:
GET twitter10/_search
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "locale"
}
}
}
并没有查询到结果。如下所示:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 0,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
}
}
如果想要找到一个missing的字段,可以这样:
GET twitter10/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"exists": {
"field": "locale"
}
}
]
}
}
}
返回结果如下:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter10",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.0,
"_source" : {
"locale" : null
}
}
]
}
}
这这是我们想要的结果。
13、匹配短语
可以用如下方法来查找happy birthday。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"message": "happy birthday"
}
}
}
默认情况下,这个匹配是"或",也就是找打文档里含有"happy"或"birthday"的文档。如果在增加一个文档:
PUT twitter/_doc/8
{
"user": "朝阳区-老王",
"message": "Happy",
"uid": 6,
"age": 50,
"city": "北京",
"province": "北京",
"country": "中国",
"address": "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location": {
"lat": "39.918256",
"lon": "116.467910"
}
}
重新进行搜索,可以看到新增加的id为8的文档也在搜索之列。
如果想得到"与"的关系,则可以用如下方法:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"message": {
"query": "happy birthday",
"operator": "and"
}
}
}
}
这样就搜索不到id为8的文档了。因为必须在message中同时匹配"happy"或"birthday"这两个词。当然还可以用如下方法:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"message": {
"query": "happy birthday",
"minimum_should_match": 2
}
}
}
}
在这里,采用了"minimum_should_match"来表示至少有2个匹配才可以。
在搜索结果中,无论文档是大小写字母,都能匹配到,并且在message中,happy birthday这两个词先后顺序也不是很重要。比如我们把id为5的文档改为:
PUT twitter/_doc/5
{
"user": "朝阳区-老王",
"message": "BirthDay My Friend Happy !",
"uid": 6,
"age": 50,
"city": "北京",
"province": "北京",
"country": "中国",
"address": "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location": {
"lat": "39.918256",
"lon": "116.467910"
}
}
有意识的把birthday和happy顺序调换后,再次使用上面”或“和”与“查询,仍然可以搜索到。显然,match查询时不分先后顺序。
如果要固定顺序时,可以使用match_phrase。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"message": "Happy birthday"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"message": {}
}
}
}
搜索结果中显示 happy 在birthday前面的文档才能被搜索到。
再次把id为5的文档修改为:
PUT twitter/_doc/5
{
"user": "朝阳区-老王",
"message": "Happy Good BirthDay My Friend!",
"uid": 6,
"age": 50,
"city": "北京",
"province": "北京",
"country": "中国",
"address": "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location": {
"lat": "39.918256",
"lon": "116.467910"
}
}
此时用之前的match_phrase是找不到文明的的。此时可以这样:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"message": {
"query": "Happy birthday",
"slop": 1
}
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"message": {}
}
}
}
注意:在这里,我们使用了 slop 为1,表面 Happy 和 birthday 之前是可以允许一个 token 的差别。
14、Name queries
可以使用_name为一个filter或query来获取一个名字。比如:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"match": {
"city": {
"query": "北京",
"_name": "城市"
}
}
},
{
"match": {
"country": {
"query": "中国",
"_name": "国家"
}
}
}
],
"should": [
{
"match": {
"_id": {
"query": "1",
"_name": "ID"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
返回结果:
{
"took" : 2,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 6,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.4672297,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.4672297,
"_source" : {
"user" : "双榆树-张三",
"message" : "今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去",
"uid" : 2,
"age" : 20,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市海淀区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.970718",
"lon" : "116.325747"
}
},
"matched_queries" : [
"国家",
"ID",
"城市"
]
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "2",
"_score" : 0.46722972,
"_source" : {
"user" : "东城区-老刘",
"message" : "出发,下一站云南!",
"uid" : 3,
"age" : 30,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市东城区台基厂三条3号",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.904313",
"lon" : "116.412754"
}
},
"matched_queries" : [
"国家",
"城市"
]
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "3",
"_score" : 0.46722972,
"_source" : {
"user" : "东城区-李四",
"message" : "happy birthday!",
"uid" : 4,
"age" : 30,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市东城区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.893801",
"lon" : "116.408986"
}
},
"matched_queries" : [
"国家",
"城市"
]
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "4",
"_score" : 0.46722972,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老贾",
"message" : "123,gogogo",
"uid" : 5,
"age" : 35,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区建国门",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.718256",
"lon" : "116.367910"
}
},
"matched_queries" : [
"国家",
"城市"
]
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "8",
"_score" : 0.46722972,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老王",
"message" : "Happy",
"uid" : 6,
"age" : 50,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.918256",
"lon" : "116.467910"
}
},
"matched_queries" : [
"国家",
"城市"
]
},
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "5",
"_score" : 0.46722972,
"_source" : {
"user" : "朝阳区-老王",
"message" : "Happy Good BirthDay My Friend!",
"uid" : 6,
"age" : 50,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市朝阳区国贸",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.918256",
"lon" : "116.467910"
}
},
"matched_queries" : [
"国家",
"城市"
]
}
]
}
}
从上面的返回结果可以看出来多了一个叫做 matched_queries 的字段。在它的里面罗列了每个匹配了的查询。第一个返回的查询结果是三个都匹配了的,但是第二个来说就只有两项是匹配的。
15、通配符查询
可以使用wildcard查询一个字符串里含有的字符。
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"city.keyword": {
"value": "*海"
}
}
}
}
上述查询在city字段中含有"海"的文档。所以返回结果中显示了city为"上海"的文档。
16、Disjunction max 查询
返回与一个或多个包在一起的查询(称为查询子句或子句)匹配的文档。
如果返回的文档与多个查询子句匹配,则 dis_max 查询为该文档分配来自任何匹配子句的最高相关性得分,并为任何其他匹配子查询分配平局打破增量。
可以使用 dis_max 在以不同 boost 因子映射的字段中搜索术语。比如:
GET twitter/_search
{
"query": {
"dis_max": {
"queries": [
{
"term": {
"city.keyword": "北京"
}
},
{
"match": {
"address": "北京"
}
}
],
"tie_breaker": 0.7
}
}
}
在上面的 dis_max 查询中,它将返回任何一个在 queries 中所定的查询的文档。每个匹配分分数是按照如下的规则来进行计算的:
- 如果一个文档匹配其中的一个或多个查询,那么最终的得分将以其中最高的那个得分来进行计算。
- 在默认的情况下,tie_breaker 的值为0。它可以是 0 到 1.0 之间的数。
如果文档匹配多个子句,则 dis_max 查询将计算该文档的相关性得分,如下所示:
- 从具有最高分数的匹配子句中获取相关性分数。
- 将来自其他任何匹配子句的得分乘以 tie_breaker 值。
- 将最高分数加到相乘的分数上。
如果 tie_breaker 值大于0.0,则所有匹配子句均计数,但得分最高的子句计数最高。
17、SQL查询
对于与很多已经习惯用 RDMS 数据库的工作人员,他们更喜欢使用 SQL 来进行查询。Elasticsearch 也对 SQL 有支持:
GET /_sql?
{
"query": """
SELECT * FROM twitter
WHERE age = 30
"""
}
得到的结果是:
{
"columns" : [
{
"name" : "address",
"type" : "text"
},
{
"name" : "age",
"type" : "long"
},
{
"name" : "city",
"type" : "text"
},
{
"name" : "country",
"type" : "text"
},
{
"name" : "location",
"type" : "geo_point"
},
{
"name" : "message",
"type" : "text"
},
{
"name" : "province",
"type" : "text"
},
{
"name" : "uid",
"type" : "long"
},
{
"name" : "user",
"type" : "text"
}
],
"rows" : [
[
"中国北京市东城区台基厂三条3号",
30,
"北京",
"中国",
"point (116.41275395639241 39.90431299433112)",
"出发,下一站云南!",
"北京",
3,
"东城区-老刘"
],
[
"中国北京市东城区",
30,
"北京",
"中国",
"point (116.40898595564067 39.8938009981066)",
"happy birthday!",
"北京",
4,
"东城区-李四"
]
]
}
可以通过如下方法得到对于的DSL语句:
GET /_sql/translate
{
"query": """
SELECT * FROM twitter
WHERE age = 30
"""
}
结果:
{
"size" : 1000,
"query" : {
"term" : {
"age" : {
"value" : 30,
"boost" : 1.0
}
}
},
"_source" : {
"includes" : [
"address",
"city",
"country",
"message",
"province",
"user"
],
"excludes" : [ ]
},
"docvalue_fields" : [
{
"field" : "age"
},
{
"field" : "location"
},
{
"field" : "uid"
}
],
"sort" : [
{
"_doc" : {
"order" : "asc"
}
}
]
}
18、Multi Search API
使用单个 API 请求执行几次搜索。这个 API 的好处是节省 API 的请求个数,把多个请求放到一个 API 请求中来实现。
为了说明问题的方便,我们可以多加一个叫做 twitter1 的 index。它的内容如下:
POST _bulk
{"index":{"_index":"twitter1","_id":1}}
{"user":"张庆","message":"今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去","uid":2,"age":20,"city":"重庆","province":"重庆","country":"中国","address":"中国重庆地区","location":{"lat":"39.970718","lon":"116.325747"}}
这样在我们的 Elasticsearch 中就有两个索引了。我们可以做如下的 _msearch。
GET twitter/_msearch
{"index":"twitter"}
{"query":{"match_all":{}},"from":0,"size":1}
{"index":"twitter"}
{"query":{"bool":{"filter":{"term":{"city.keyword":"北京"}}}}, "size":1}
{"index":"twitter1"}
{"query":{"match_all":{}}}
通过 _msearch 终点来实现在一个 API 请求中做多个查询,对多个 index 进行同时操作。显示结果为:
{
"took" : 18,
"responses" : [
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 8,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"user" : "双榆树-张三",
"message" : "今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去",
"uid" : 2,
"age" : 20,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市海淀区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.970718",
"lon" : "116.325747"
}
}
}
]
},
"status" : 200
},
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 6,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.0,
"_source" : {
"user" : "双榆树-张三",
"message" : "今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去",
"uid" : 2,
"age" : 20,
"city" : "北京",
"province" : "北京",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国北京市海淀区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.970718",
"lon" : "116.325747"
}
}
}
]
},
"status" : 200
},
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 1.0,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "twitter1",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"user" : "张庆",
"message" : "今儿天气不错啊,出去转转去",
"uid" : 2,
"age" : 20,
"city" : "重庆",
"province" : "重庆",
"country" : "中国",
"address" : "中国重庆地区",
"location" : {
"lat" : "39.970718",
"lon" : "116.325747"
}
}
}
]
},
"status" : 200
}
]
}
19、多个索引操作
在上面我们引入了另外一个索引 twitter1。在实际的操作中,我们可以通过通配符,或者直接使用多个索引来进行搜索:
GET twitter*/_search
上面的操作是对所有的以 twitter 为开头的索引来进行搜索,显示的结果是在所有的 twitter 及 twitter1 中的文档。
同样也可以写成:
GET /twitter,twitter1/_search
在写上面的查询的时候,在两个索引之间不能加入空格。
20、Profile API
rofile API 是调试工具。 它添加了有关执行的详细信息搜索请求中的每个组件。 它为用户提供有关搜索的每个步骤的洞察力。请求执行并可以帮助确定某些请求为何缓慢。
GET twitter/_search
{
"profile": "true",
"query": {
"match": {
"city": "北京"
}
}
}
在上面,我们加上了 "profile":"true" 后,除了显示搜索的结果之外,还显示 profile 的信息:
"profile" : {
"shards" : [
{
"id" : "[qjdrmbcpS7aSUxbTtR4mTg][twitter][0]",
"searches" : [
{
"query" : [
{
"type" : "BooleanQuery",
"description" : "city:北 city:京",
"time_in_nanos" : 4260236,
"breakdown" : {
"set_min_competitive_score_count" : 0,
"match_count" : 6,
"shallow_advance_count" : 0,
"set_min_competitive_score" : 0,
"next_doc" : 83628,
"match" : 12840,
"next_doc_count" : 7,
"score_count" : 6,
"compute_max_score_count" : 0,
"compute_max_score" : 0,
"advance" : 178844,
"advance_count" : 3,
"score" : 48384,
"build_scorer_count" : 7,
"create_weight" : 1113902,
"shallow_advance" : 0,
"create_weight_count" : 1,
"build_scorer" : 2822608
},
"children" : [
{
"type" : "TermQuery",
"description" : "city:北",
"time_in_nanos" : 293348,
"breakdown" : {
"set_min_competitive_score_count" : 0,
"match_count" : 0,
"shallow_advance_count" : 9,
"set_min_competitive_score" : 0,
"next_doc" : 0,
"match" : 0,
"next_doc_count" : 0,
"score_count" : 6,
"compute_max_score_count" : 9,
"compute_max_score" : 61365,
"advance" : 12242,
"advance_count" : 10,
"score" : 11943,
"build_scorer_count" : 10,
"create_weight" : 52244,
"shallow_advance" : 39245,
"create_weight_count" : 1,
"build_scorer" : 116264
}
},
{
"type" : "TermQuery",
"description" : "city:京",
"time_in_nanos" : 122102,
"breakdown" : {
"set_min_competitive_score_count" : 0,
"match_count" : 0,
"shallow_advance_count" : 9,
"set_min_competitive_score" : 0,
"next_doc" : 0,
"match" : 0,
"next_doc_count" : 0,
"score_count" : 6,
"compute_max_score_count" : 9,
"compute_max_score" : 18830,
"advance" : 17598,
"advance_count" : 10,
"score" : 6348,
"build_scorer_count" : 10,
"create_weight" : 33689,
"shallow_advance" : 9560,
"create_weight_count" : 1,
"build_scorer" : 36032
}
}
]
}
],
"rewrite_time" : 34800,
"collector" : [
{
"name" : "CancellableCollector",
"reason" : "search_cancelled",
"time_in_nanos" : 596185,
"children" : [
{
"name" : "SimpleTopScoreDocCollector",
"reason" : "search_top_hits",
"time_in_nanos" : 77604
}
]
}
]
}
],
"aggregations" : [ ]
}
]
}
从上面可以看出,这个搜索是搜索了“北”及“京”,而不是把北京作为一个整体来进行搜索的。我们可以在以后的文档中可以学习使用中文分词器来进行分词搜索。
除了上面的通过命令来进行 profile 以外,我们也可以通过 Kibana 的 UI 对我们的搜索进行 profile:
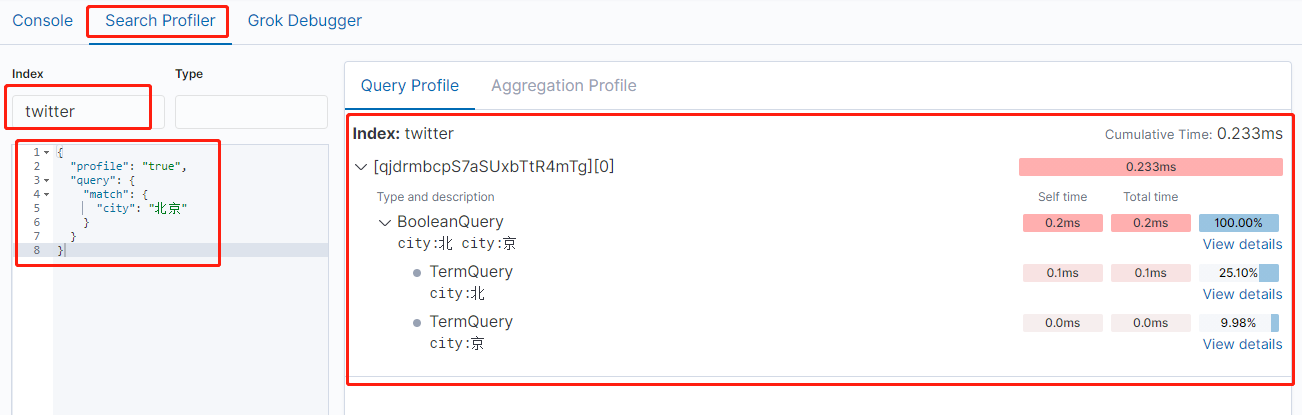
https://blog.csdn.net/UbuntuTouch/article/details/99546568


