[LeetCode] 297. Serialize and Deserialize Binary Tree(二叉树的序列化和反序列化)
-
Difficulty: Hard
-
Related Topics: Tree, Design
-
Link: https://leetcode.com/problems/serialize-and-deserialize-binary-tree/
Description
Serialization is the process of converting a data structure or object into a sequence of bits so that it can be stored in a file or memory buffer, or transmitted across a network connection link to be reconstructed later in the same or another computer environment.
序列化是将一数据结构或对象转化为比特序列,使其能够存储于文件或内存缓冲区中,或通过网络连接传输,以便在相同或不同的电脑上还原的过程。
Design an algorithm to serialize and deserialize a binary tree. There is no restriction on how your serialization/deserialization algorithm should work. You just need to ensure that a binary tree can be serialized to a string and this string can be deserialized to the original tree structure.
设计一个算法用于二叉树的序列化和反序列化。不限制算法的实现方式,只要保证你的序列化算法能将二叉树转化为字符串,该字符串能够作为反序列化算法的输入并还原出原先的树结构即可。
Clarification: The input/output format is the same as how LeetCode serializes a binary tree. You do not necessarily need to follow this format, so please be creative and come up with different approaches yourself.
澄清:样例的输入/输出是 LeetCode 序列化二叉树的方式。你并不需要遵循这种方式,所以发挥你的想象力,创造另一种格式。
Examples
Example 1
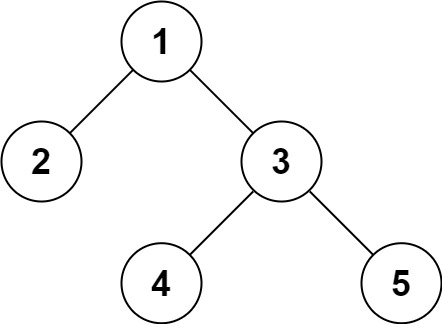
Input: root = [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Output: [1,2,3,null,null,4,5]
Example 2
Input: root = []
Output: []
Example 3
Input: root = [1]
Output: [1]
Example 4
Input: root = [1,2]
Output: [1,2]
Constraints
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 1e4]. -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
Solution
我没有那么多创意,为了后面刷树相关的题目方便写 testcase,我这里使用的格式与官方格式基本接近,只有两处不同:
-
没有首尾的方括号。
-
null用#表示,而非null。
例如,Example 1 的树用我的格式解析后的结果是:1,2,3,#,#,4,5,#,#,#,#。末尾多余的 # 不影响反序列化。
序列化和反序列化都采用中序遍历的形式,代码如下:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* class TreeNode(var `val`: Int) {
* var left: TreeNode? = null
* var right: TreeNode? = null
* }
*/
class Codec() {
fun serialize(root: TreeNode?): String {
if (root == null) {
return ""
}
val result = arrayListOf<String>()
val queue: Queue<TreeNode?> = LinkedList()
queue.offer(root)
while (queue.isNotEmpty()) {
val node = queue.poll()
if (node == null) {
result.add("#")
continue
} else {
result.add("${node.`val`}")
}
queue.offer(node.left)
queue.offer(node.right)
}
return result.joinToString(separator = ",")
}
fun deserialize(data: String): TreeNode? {
if (data.isBlank()) {
return null
}
val valueQueue: Queue<String> = A(data.split(','))
if (valueQueue.peek() == "#") {
return null
}
val root = TreeNode(valueQueue.poll().toInt())
val nodeQueue: Queue<TreeNode> = ArrayDeque()
nodeQueue.offer(root)
while (valueQueue.isNotEmpty()) {
val curNode = nodeQueue.poll()
val leftValue = valueQueue.poll()
if (leftValue != "#") {
val left = TreeNode(leftValue.toInt())
curNode.left = left
nodeQueue.offer(left)
}
val rightValue = valueQueue.poll()
if (rightValue != "#") {
val right = TreeNode(rightValue.toInt())
curNode.right = right
nodeQueue.offer(right)
}
}
return root
}
}
/**
* Your Codec object will be instantiated and called as such:
* var ser = Codec()
* var deser = Codec()
* var data = ser.serialize(longUrl)
* var ans = deser.deserialize(data)
*/

