4、Spring-AOP
1、AOP
1.1什么是AOP
在软件业,AOP为Aspect Oriented Programming的缩写,意为:面向切面编程,通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术。AOP是OOP的延续,是软件开发中的一个热点,也是Spring框架中的一个重要内容,是函数式编程的一种衍生范型。利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时提高了开发的效率。
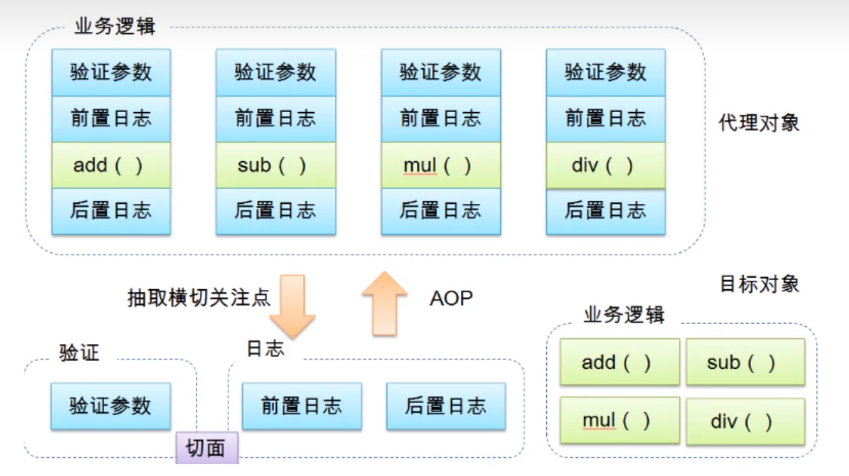
1.2、Aop在Spring中的作用
提供声明式事务:允许用户自定义切面
-
横切关注点:跨越应用程序多个模块的方法或功能。即是,与我们业务逻辑无关的,但是我们需要关注的部分,就是横切关注点。如日志,安全,缓存,事务等...
-
切面(Aspect):横切关注点被模块化 的特殊对象。即,它是一个类。
-
通知(Advice):切面必须要完成的工作。即,它是类中的一个方法。
-
目标(target):被通知对象。
-
代理(Proxy):向目标对象应用通知之后创建的对象。
-
切入点(PointCut):切面通知 执行的“地点”的定义。
-
连接点(jointPoint):与切入点匹配的执行点。
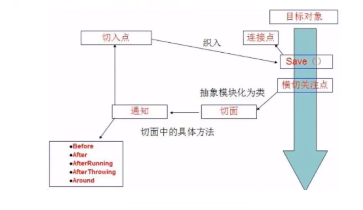
在SpringAop中,通过Advice定义横切逻辑,Spring中支持5中类型的Advice:
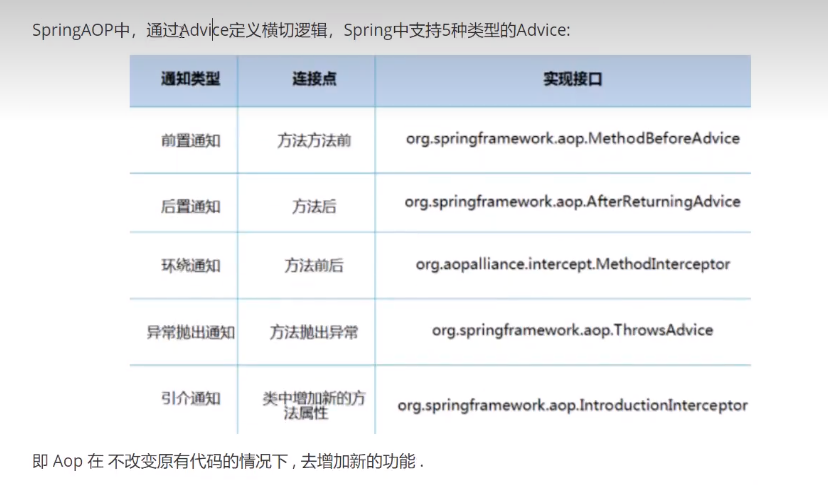
即Aop在不改变原有代码的情况下,去增加新的功能。
1.3、使用Spring实现Aop
【重点】使用aop切入,需要导入一个依赖包
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.aspectj/aspectjweaver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
注意:依赖包下不要有那个runtime的scope,有就在导入包前把它去掉;若没去掉导入了包,用ctrl+shift+alt+s 把依赖包设置成Compile
方式一:使用Spring的API接口
- 接口
package com.jan.service;
public interface UserService {
public void add();
public void delete();
public void update();
public void select();
}
- 实现类
package com.jan.service;
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService{
public void add() {
System.out.println("增加了一个用户");
}
public void delete() {
System.out.println("删除了一个用户");
}
public void update() {
System.out.println("更行了一个用户");
}
public void select() {
System.out.println("查询了一个用户");
}
}
- 日记类
package com.jan.log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
//method:要执行的目标对象的方法
//args: 参数
//target: 目标对象
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName()+"的"+method.getName()+"被执行了");
}
}
package com.jan.log;
import org.springframework.aop.AfterReturningAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
//returnValue ;返回值
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行了"+method.getName()+"方法,返回结果为:"+returnValue);
}
}
- 测试类
import com.jan.service.UserService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class MyText {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext");
//动态代理 代理的是接口!
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
}
- bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.jan.log.AfterLog"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.jan.log.Log"/>
<!-- 方式一:使用Spring的APi接口-->
<!-- 配置aop:需要导入aop的约束-->
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入点: expression:表达式 execution(要执行的位置!) -->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!-- 执行环绕增加!-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
</beans>
没有切面,只需要定义一个类,去实现它的接口,可以实现多个 类文件的切入,功能比较强大
方法二:自定义来实现AOP
- 日志类
package com.jan.custom;
public class CustomPointCut {
public void before(){
System.out.println("===========方法执行前================");
}
public void after(){
System.out.println("===========方法执行后================");
}
}
- bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.jan.log.AfterLog"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.jan.log.Log"/>
<!-- 方式一:使用Spring的APi接口-->
<!-- 配置aop:需要导入aop的约束-->
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入点: expression:表达式 execution(要执行的位置!) -->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!-- 执行环绕增加!-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut"/>
</aop:config>
<!-- 方式二:自定义类-->
<bean id="custom" class="com.jan.custom.CustomPointCut"/>
<aop:config>
<!-- 自定义切面: ref 要引用的类-->
<aop:aspect ref="custom">
<!-- 切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="point" expression="execution(* com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))"/>
<!-- 通知-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="point"/>
<aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="point"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
自定义类更加明确了,自定义切面,切入点,再到通知(什么时候执行)
方法三:使用注解实现
- 日志类
package com.jan.custom;
//方式三:使用注解方式实现AOP
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
@Aspect
public class AnnotationPointCut {
@Before("execution(* com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before(){
System.out.println("=====方法执行前========");
}
@After("execution(* com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after(){
System.out.println("=====方法执行后========");
}
@Around("execution(* com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕前");
Object proceed = jp.proceed();//执行方法
System.out.println("环绕后");
}
}
- bean
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--注册bean-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.jan.service.UserServiceImpl"/>
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.jan.log.AfterLog"/>
<bean id="log" class="com.jan.log.Log"/>
<!--开启注释支持-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<!-- JDK:proxy-target-class="false" cglib:proxy-target-class="true" -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="false"/>
<!-- 方式三:注释类-->
<bean id="annotationPointCut" class="com.jan.custom.AnnotationPointCut"/>
</beans>



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端