感知机的理解和实现
感知机
感知机是根据输入实例的特征向量 x 对其进行二类分类的线性模型:
f(x)=sign(w⋅x+b)
感知机模型对应于输入空间(特征空间)中的分离超平面 w⋅x+b=0。其中w是超平面的法向量,b是超平面的截距。
可见感知机是一种线性分类模型,属于判别模型。
感知机学习的假设
感知机学习的重要前提假设是训练数据集是线性可分的。
感知机学习策略
感知机学的策略是极小化损失函数。
损失函数的一个自然选择是误分类点的总数。但是,这样的损失函数不是参数 w, b的连续可导的函数,不易于优化。所以通常是选择误分类点到超平面 S 的总距离: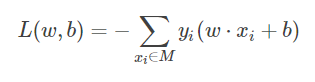
学习的策略就是求得使 L(w,b) 为最小值的 w 和 b。其中 M 是误分类点的集合。
感知机学习的算法
感知机学习算法是基于随机梯度下降法的对损失函数的最优化算法,有原始形式和对偶形式,算法简单易于实现。
原始形式
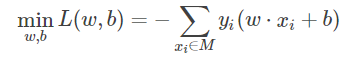
首先,任意选取一个超平面 w0,b0,然后用梯度下降法不断地极小化目标函数。极小化的过程中不是一次使 M 中所有误分类点得梯度下降,而是一次随机选取一个误分类点,使其梯度下降。
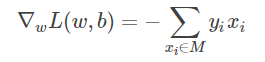
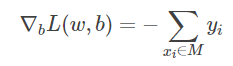
随机选取一个误分类点(xi,yi),对 w,b 进行更新:
w←w+ηyixi
b←b+ηyi
其中 η(0<η≤1)是学习率。
对偶形式
对偶形式的基本想法是,将 w 和 b 表示为是咧 xi和标记 yi的线性组合的形式,通过求解其系数而得到 w 和 b。
w←w+ηyixi
b←b+ηyi
逐步修改 w,b,设修改 n 次,则 w,b 关于 (xi,yi) 的增量分别是 αiyixi和 αiyi, 这里 αi=niη。最后学习到的 w,b 可以分别表示为: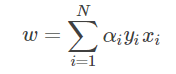
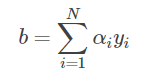
这里, αi≥0, i=1,2,...,N ,当 η=1时,表示第i个是实例点由于误分类而进行更新的次数,实例点更新次数越多,说明它距离分离超平面越近,也就越难区分,该点对学习结果的影响最大。
感知机模型对偶形式: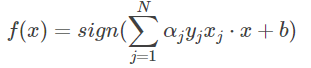
其中
α=(α1,α2,...,αN)T
学习时初始化 α←0,b←0α←0,b←0, 在训练集中找分类错误的点,即: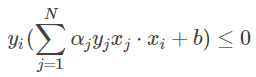
然后更新:
αi←αi+η 这里为什么这样更新,请看推导文章感知机对偶形式 梯度下降法的推导过程
b←b+ηyi
知道训练集中所有点正确分类
对偶形式中训练实例仅以内积的形式出现,为了方便,可以预先将训练集中实例间的内积计算出来以矩阵的形式存储,即 Gram 矩阵。
总结
-
当训练数据集线性可分的时候,感知机学习算法是收敛的,感知机算法在训练数据集上的误分类次数 k 满足不等式:
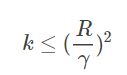
具体证明可见 李航《统计学习方法》或 林轩田《机器学习基石》。
当训练当训练数据集线性可分的时候,感知机学习算法存在无穷多个解,其解由于不同的初值或不同的迭代顺序而可能不同,即存在多个分离超平面能把数据集分开。
感知机学习算法简单易求解,但一般的感知机算法不能解决异或等线性不可分的问题。
感知机(采用原始形式)
创建感知机模型的原始形式的类,并在训练集上训练,测试集上简单测试。
class PerceptronRaw():
def __init__(self):
self.W = None;
self.bias = None;
def fit(self, x_train, y_train, learning_rate=0.05, n_iters=100, plot_train=True):
print("开始训练...")
num_samples, num_features = x_train.shape
self.W = np.random.randn(num_features)
self.bias = 0
while True:
erros_examples = []
erros_examples_y = []
# 查找错误分类的样本点
for idx in range(num_samples):
example = x_train[idx]
y_idx = y_train[idx]
# 计算距离
distance = y_idx * (np.dot(example, self.W) + self.bias)
if distance <= 0:
erros_examples.append(example)
erros_examples_y.append(y_idx)
if len(erros_examples) == 0:
break;
else:
# 随机选择一个错误分类点,修正参数
random_idx = np.random.randint(0, len(erros_examples))
choosed_example = erros_examples[random_idx]
choosed_example_y = erros_examples_y[random_idx]
self.W = self.W + learning_rate * choosed_example_y * choosed_example
self.bias = self.bias + learning_rate * choosed_example_y
print("训练结束")
# 绘制训练结果部分
if plot_train is True:
x_hyperplane = np.linspace(2, 10, 8)
slope = -self.W[0]/self.W[1]
intercept = -self.bias/self.W[1]
y_hpyerplane = slope * x_hyperplane + intercept
plt.xlabel("feature_1")
plt.ylabel("feature_2")
plt.xlim((2, 10))
plt.ylim((-12, 0))
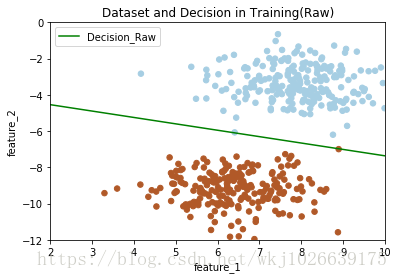
plt.title("Dataset and Decision in Training(Raw)")
plt.scatter(x_train[:, 0], x_train[:, 1], c=y_train, s=30, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.plot(x_hyperplane, y_hpyerplane, color='g', label='Decision_Raw')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
def predict(self, x):
if self.W is None or self.bias is None:
raise NameError("模型未训练")
y_predict = np.sign(np.dot(x, self.W) + self.bias)
return y_predict
感知机(采用对偶形式)
创建感知机模型的对偶形式的类,并在训练集上训练,测试集上简单测试。
class PerceptronDuality():
def __init__(self):
self.alpha = None
self.bias = None
self.W = None
def fit(self, x_train, y_train, learning_rate=1, n_iters=100, plot_train=True):
print("开始训练...")
num_samples, num_features = x_train.shape
self.alpha = np.zeros((num_samples,))
self.bias = 0
# 计算 Gram 矩阵
gram = np.dot(x_train, x_train.T)
while True:
error_count = 0
for idx in range(num_samples):
inner_product = gram[idx]
y_idx = y_train[idx]
distance = y_idx * (np.sum(self.alpha * y_train * inner_product) + self.bias)
# 如果有分类错误点,修正 alpha 和 bias,跳出本层循环,重新遍历数据计算,开始新的循环
if distance <= 0:
error_count += 1
self.alpha[idx] = self.alpha[idx] + learning_rate
self.bias = self.bias + learning_rate * y_idx
break
# 数据没有错分类点,跳出 while 循环
if error_count == 0:
break
self.W = np.sum(self.alpha * y_train * x_train.T, axis=1)
print("训练结束")
# 绘制训练结果部分
if plot_train is True:
x_hyperplane = np.linspace(2, 10, 8)
slope = -self.W[0]/self.W[1]
intercept = -self.bias/self.W[1]
y_hpyerplane = slope * x_hyperplane + intercept
plt.xlabel("feature_1")
plt.ylabel("feature_2")
plt.xlim((2, 10))
plt.ylim((-12, 0))
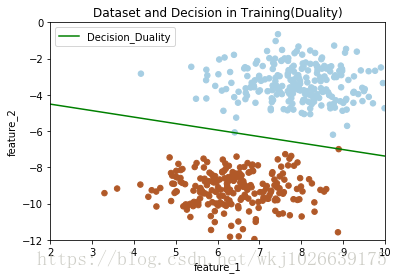
plt.title("Dataset and Decision in Training(Duality)")
plt.scatter(x_train[:, 0], x_train[:, 1], c=y_train, s=30, cmap=plt.cm.Paired)
plt.plot(x_hyperplane, y_hpyerplane, color='g', label='Decision_Duality')
plt.legend(loc='upper left')
plt.show()
def predict(self, x):
if self.alpha is None or self.bias is None:
raise NameError("模型未训练")
y_predicted = np.sign(np.dot(x, self.W) + self.bias)
return y_predicted
详细代码链接:
https://github.com/kenjewu/Machine_Learning_ALS/blob/master/perceptron.ipynb
如果该代码对您的工作学习有帮助,请点个star。欢迎大家指正,提出更好的写法意见,转载请贴上引用。
引用
《统计学习方法》 李航
《机器学习基石》 林轩田
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/wkj1026639175/article/details/79827923
https://blog.csdn.net/mishifangxiangdefeng/article/details/104641962/?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-baidujs_baidulandingword-0&spm=1001.2101.3001.4242




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
· AI Agent开发,如何调用三方的API Function,是通过提示词来发起调用的吗