922. 按奇偶排序数组 II『简单』
题目来源于力扣(LeetCode)
一、题目
题目相关标签:排序、数组

提示:
2 <= A.length <= 20000A.length % 2 == 00 <= A[i] <= 1000
二、解题思路
2.1 新数组存储方式
-
创建与数组 A 相同长度的新数组用于保存元素
-
定义两个变量,用于记录往新数组中插入元素的索引
-
遍历数组 A,判断当前遍历元素的奇偶性
-
为奇数时,往新数组的奇数索引上插入该元素,同时索引 + 2
-
为偶数时,往新数组的偶数索引上插入该元素,同时索引 + 2
-
返回新数组
2.2 奇偶替换方式
-
无需额外空间,即创建新数组来记录结果的方式
-
定义变量用于记录奇数元素所在的索引 j,默认为 1,即数组中最小的奇数位
-
遍历数组的偶数位,判断当前遍历元素是否为偶数
-
不为偶数时,则通过索引 j 循环找到数组中在奇数位上却是偶数的元素
-
找到后,交换两个元素,实现奇数位索引上存储奇数元素,偶数位索引上存储偶数元素
索引 j 每次加 2 是不会越界的,因为数组长度为偶数,且元素一半为奇数,一半为偶数
三、代码实现
3.1 新数组存储方式
public static int[] sortArrayByParityII2(int[] A) {
int[] nums = A;
// 创建新数组存储结果
int[] res = new int[nums.length];
// 偶数索引位
int i = 0;
// 奇数索引位
int j = 1;
for (int k = 0; k < nums.length; k++) {
// 判断当前遍历元素的奇偶性
if ((nums[k] & 1) == 0) {
// 偶数存储到偶数索引上
res[i] = nums[k];
// 改变索引位
i+=2;
} else {
// 奇数存储到奇数索引上
res[j] = nums[k];
// 改变索引位
j+=2;
}
}
return res;
}
3.2 奇偶替换方式
public static int[] sortArrayByParityII3(int[] A) {
int[] nums = A;
// 维护奇数元素的索引
int j = 1;
// 遍历数组的偶数位元素:0 2 4...
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 2) {
// 偶数索引上的数不为偶数时
if ((nums[i] & 1) != 0) {
// 找到奇数索引上不为奇数的元素
while ((nums[j] & 1) == 1) {
j += 2;
}
// 找到后两个元素替换
int temp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[j];
nums[j] = temp;
}
}
return nums;
}
四、执行用时
3.1 新数组存储方式
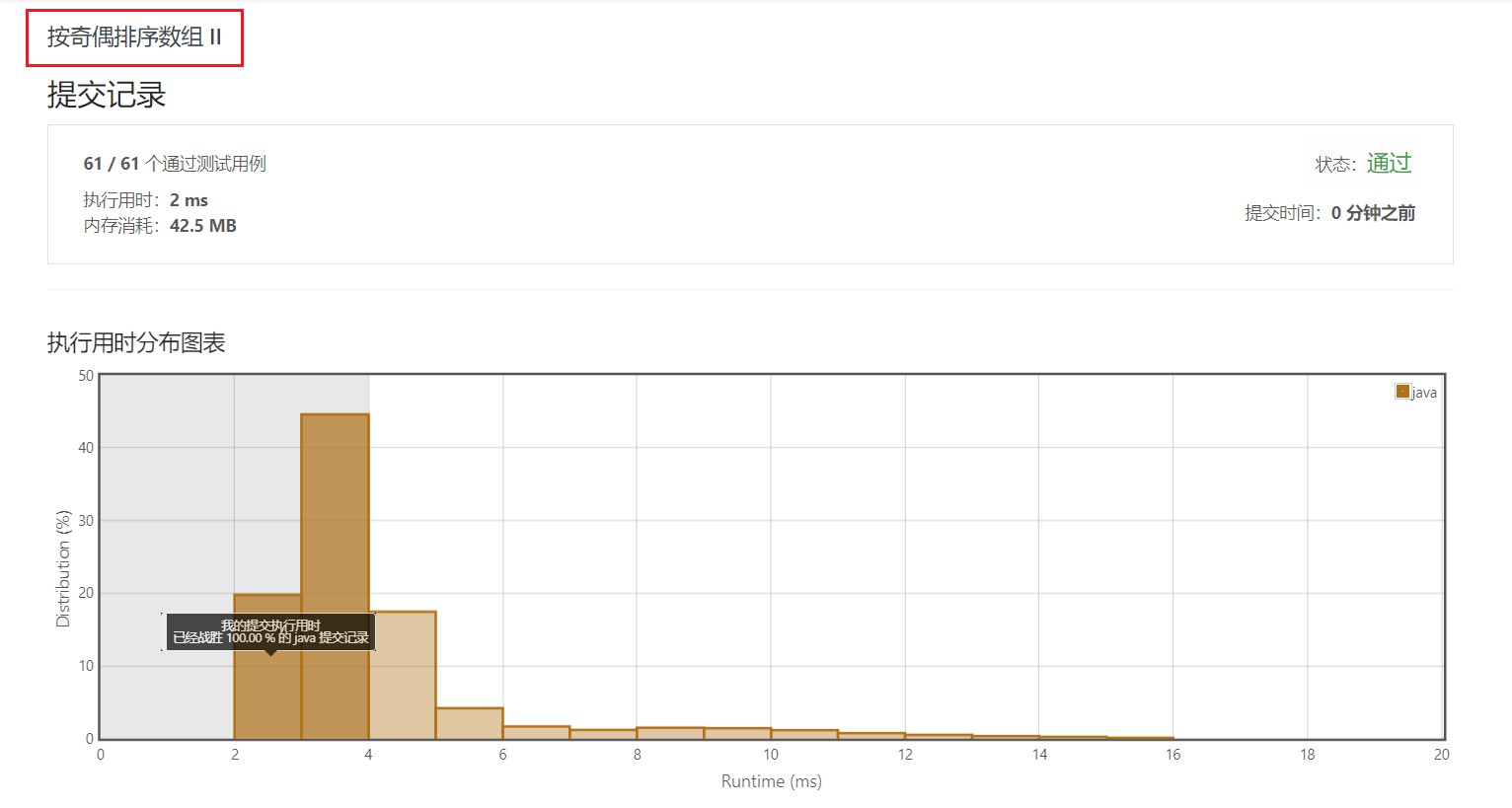
3.2 奇偶替换方式
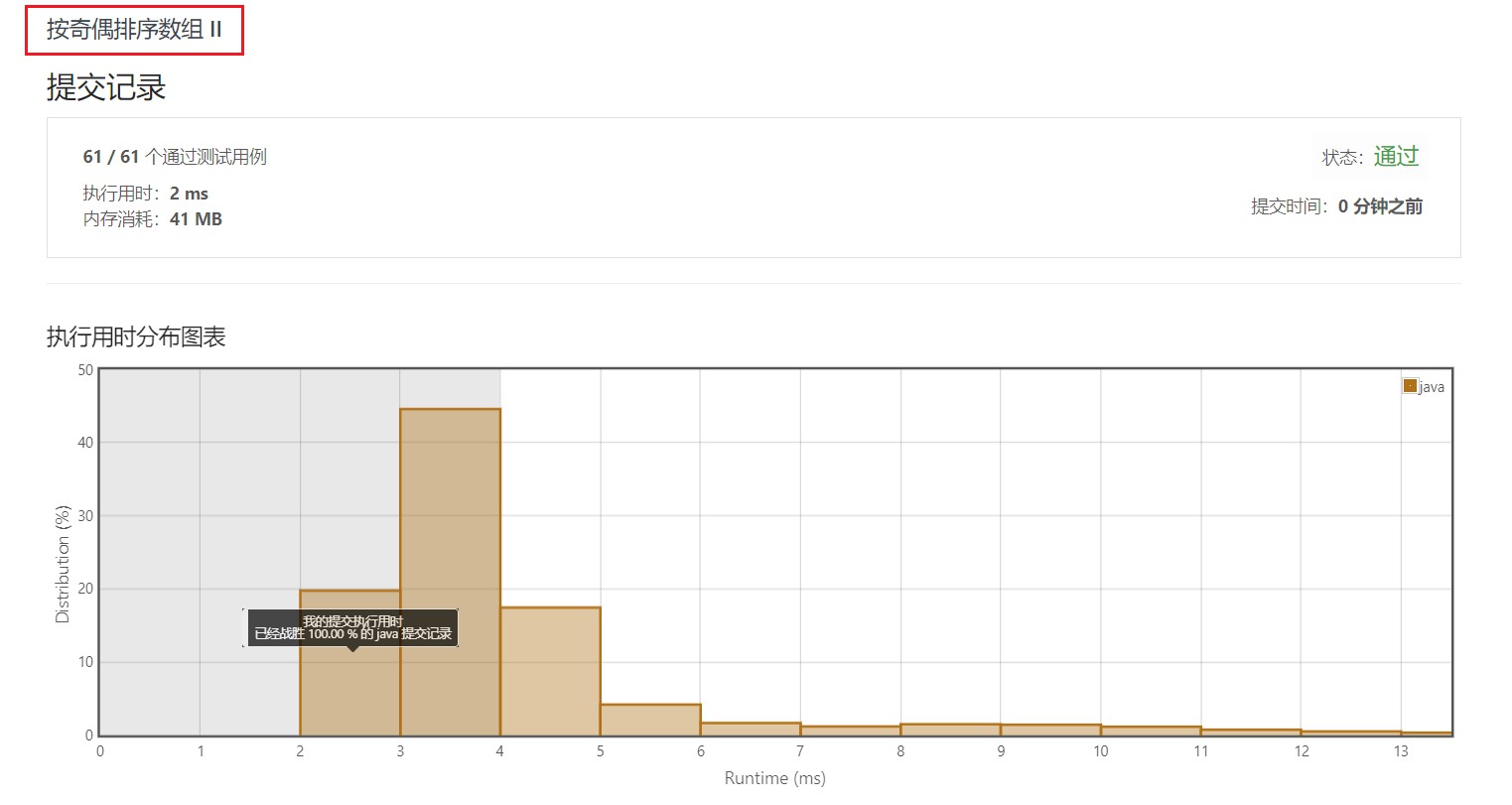
五、部分测试用例
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {4, 2, 5, 7}; // output: {4, 5, 2, 7}
int[] result = sortArrayByParityII3(nums);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}


