1313. 解压缩编码列表『简单』
题目来源于力扣(LeetCode)
目录
一、题目
题目相关标签:数组
说明:
2 <= nums.length <= 100nums.length % 2 == 01 <= nums[i] <= 100
二、解题思路
2.1 线性扫描法
-
分析题意得到:nums 数组中 0 和偶数索引上的元素表示需要“解压缩”的次数,奇数索引上的元素表示需要进行“解压缩”的数字
-
创建 list 列表,用于记录“解压缩”后的数字
-
遍历 nums 数组的奇数位(即初始索引为 1,每次遍历索引加 2)
-
每次遍历都得到当前遍历元素的前一位元素(即“解压缩”的次数)
-
循环需要“解压缩”的次数(从 0 开始),将“解压缩”的数字添加到 list 中
-
最后将 list 结果集转换成 int 数组,返回 int 数组
2.2 Arrays.fill() 填充方式
-
遍历 nums 数组的索引 0 和偶数位元素,元素相加得到“解压缩”后的元素个数
-
根据计算得到的元素个数,创建 int 数组,用于记录结果
不使用 list 列表,程序更高效
-
遍历 nums 数组,对于数组奇数索引位上的元素进行“解压缩”的操作
-
对当前遍历的奇数索引位的元素,获取其前一位元素的值,即次数 count
-
调用
Arrays.fill()方法,一次性向结果数组中填充 count 次开始索引:初始值为 0,后续每次操作时,开始索引为上一次操作结束后记录的结束索引
结束索引:初始索引 + count(fill 方法填充元素时,不会填充元素到结束索引位上)
三、代码实现
3.1 线性扫描法
public static int[] decompressRLElist(int[] nums) {
// 记录结果的列表
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i += 2) {
// 0 和偶数索引上的数值代表次数
count = nums[i - 1];
// 循环 count 次,添加数字到 list 中
for (int j = 0; j < count; j++) {
// 奇数索引上表示需要循环添加的数字
list.add(nums[i]);
}
}
// list 列表转数组
int[] arr = new int[list.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
arr[i] = list.get(i);
}
return arr;
}
3.2 Arrays.fill() 填充方式
public static int[] decompressRLElist(int[] nums) {
int len = 0;
// 遍历 nums 数组的索引 0 和偶数位索引,得到需要“解压缩”的数字个数
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 2) {
len += nums[i];
}
// 记录起始的索引
int fromIndex = 0;
// 记录结束的索引(不包括最后一位)
int toIndex = 0;
// 创建 len 个长度的数组,记录“解压缩”的数字
int[] ans = new int[len];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i += 2) {
// 计算出本次填充的结束索引位(不包含 toIndex 索引位)
toIndex = fromIndex + nums[i - 1];
// 使用 fill 方法来填充数组元素(不包含 toIndex 索引位)
// 参数:填充数组,起始索引,结束索引(不包括),填充的元素
Arrays.fill(ans, fromIndex, toIndex, nums[i]);
// 每次操作完毕,改变下次操作时的起始索引
// 起始索引等于本次的结束索引
fromIndex = toIndex;
}
return ans;
}
四、执行用时
4.1 线性扫描法
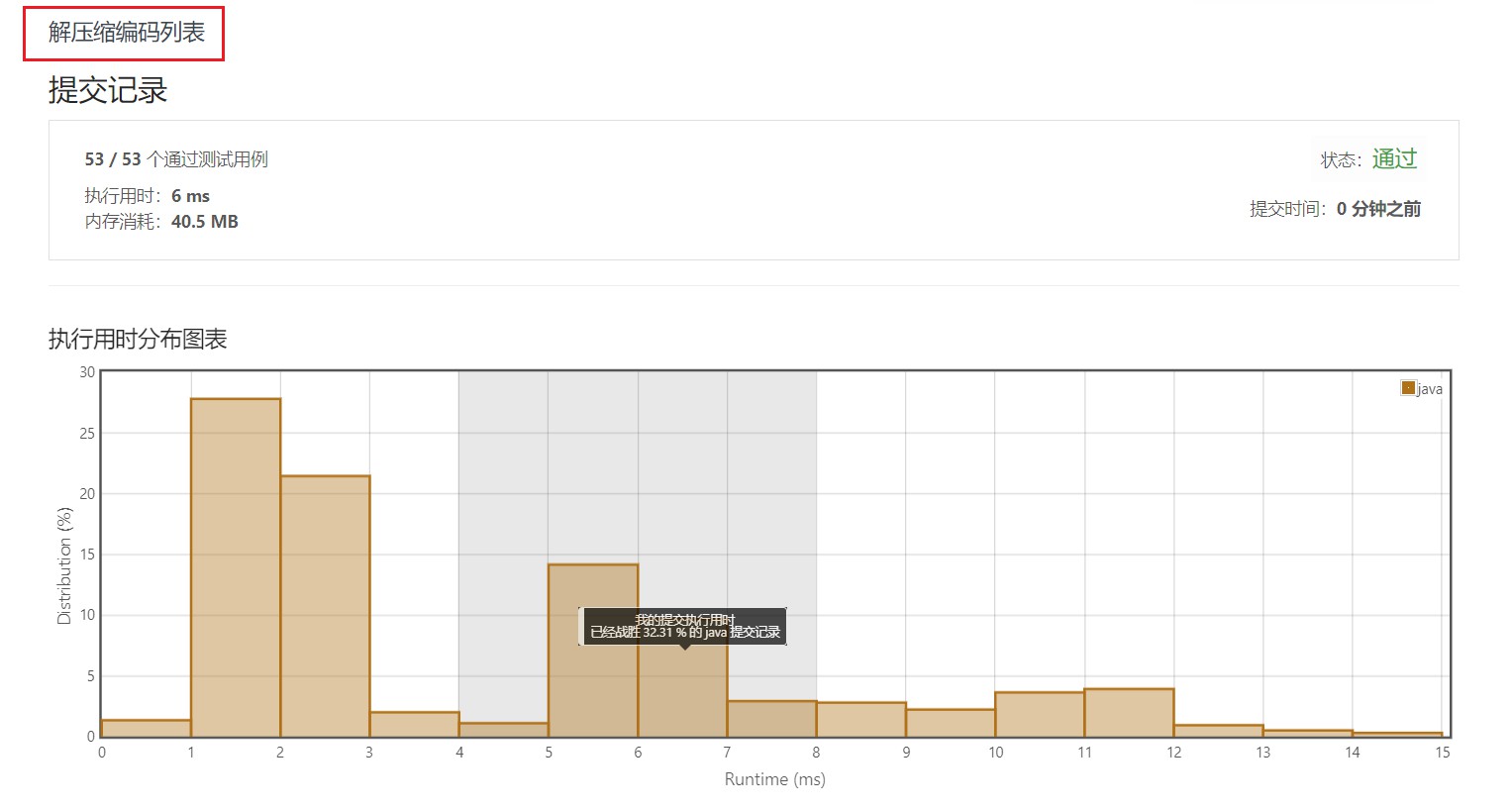
4.2 Arrays.fill() 填充方式
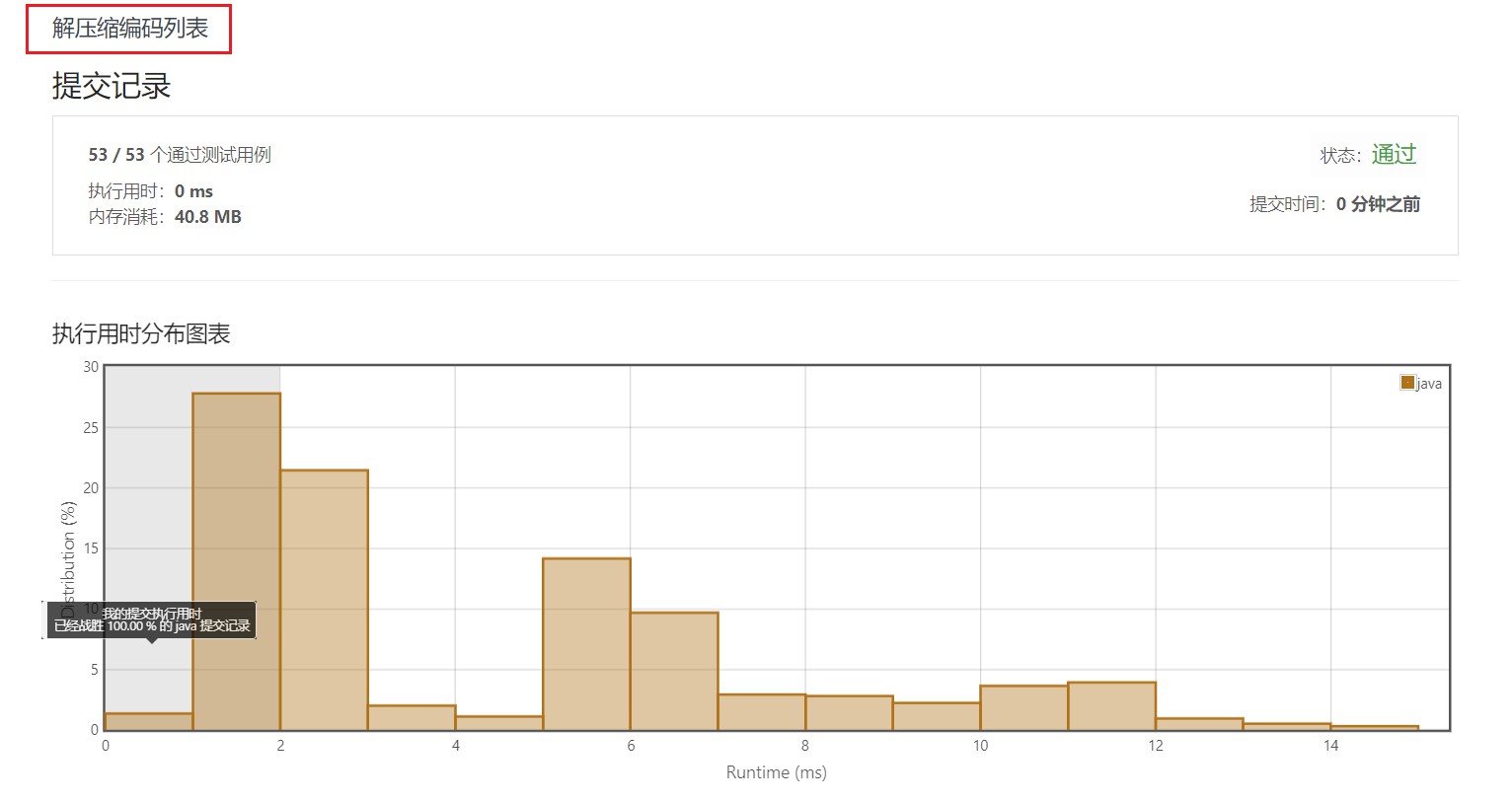
五、部分测试用例
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {1, 2, 3, 4}; // output:{2, 4, 4, 4}
// int[] nums = {1, 1, 2, 3}; // output:{1, 3, 3}
int[] result = decompressRLElist(nums);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}


