566. 重塑矩阵『简单』
题目来源于力扣(LeetCode)
目录
一、题目
题目相关标签:数组

注意:
- 给定矩阵的宽和高范围在 [1, 100]。
- 给定的 r 和 c 都是正数。
二、解题思路
2.1 list 列表存取方式
-
遍历 nums 数组中的元素,存储到 list 列表中
-
判断 list 列表中的元素个数是否等于 r 乘 c 组成的矩阵能够存储的元素个数
-
元素个数不相等时,即无法转换成新矩阵,返回原矩阵
-
创建 r * c 的矩阵,即二维数组,并进行遍历
-
逐个取出 list 列表中的元素,存储到遍历的二维数组中
2.2 数组元素存储到另一个二维数组
-
判断 nums 矩阵中的元素个数是否正好等于 r 乘 c 组成的矩阵能够存储的元素个数
-
nums 矩阵正好可以转换成新矩阵时,遍历 nums 矩阵,进行转换的操作
-
关键点:如何控制新矩阵的索引
-
定义变量 count 记录已经存储的元素个数
-
应该存入的行 = count / 新数组的列数,应该存入的列 = count % 新数组的列数
三、代码实现
3.1 list 列表存取方式
public static int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
// r 与 c 组成新矩阵的元素个数
int product = r * c;
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums[i].length; j++) {
// 二维数组中的元素加入到 list 列表中,方便后续的取出元素
list.add(nums[i][j]);
}
}
// 判断 list 中元素的个数与新矩阵的元素个数大小(乘积)是否相等
if (list.size() != product) {
// 不相等时说明无法转换,输出原矩阵
return nums;
}
// list 列表的索引,从 0 开始
int i = 0;
int[][] ans = new int[r][c];
for (int j = 0; j < r; j++) {
for (int k = 0; k < c; k++) {
// 将 list 中的元素添加到新创建的矩阵中
ans[j][k] = list.get(i++);
}
}
return ans;
}
3.2 数组元素存储到另一个二维数组
public static int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
int m = nums.length;
int n = nums[0].length;
// nums 中的元素个数不等于 r * c 时,返回原矩阵
if (m * n != r * c) {
return nums;
}
int count = 0;
int[][] ans = new int[r][c];
// 遍历二维数组
for (int[] row : nums) {
for (int num : row) {
// 二维数组中的元素,转到另一个二维数组,当存储的元素个数大于列数时,换行
// 应该存入的行 = count / 新数组的列数
// 应该存入的列 = count % 新数组的列数
ans[count / c][count % c] = num;
// 每次遍历都记录已经存储的元素个数
count ++;
}
}
return ans;
}
四、执行用时
4.1 list 列表存取方式
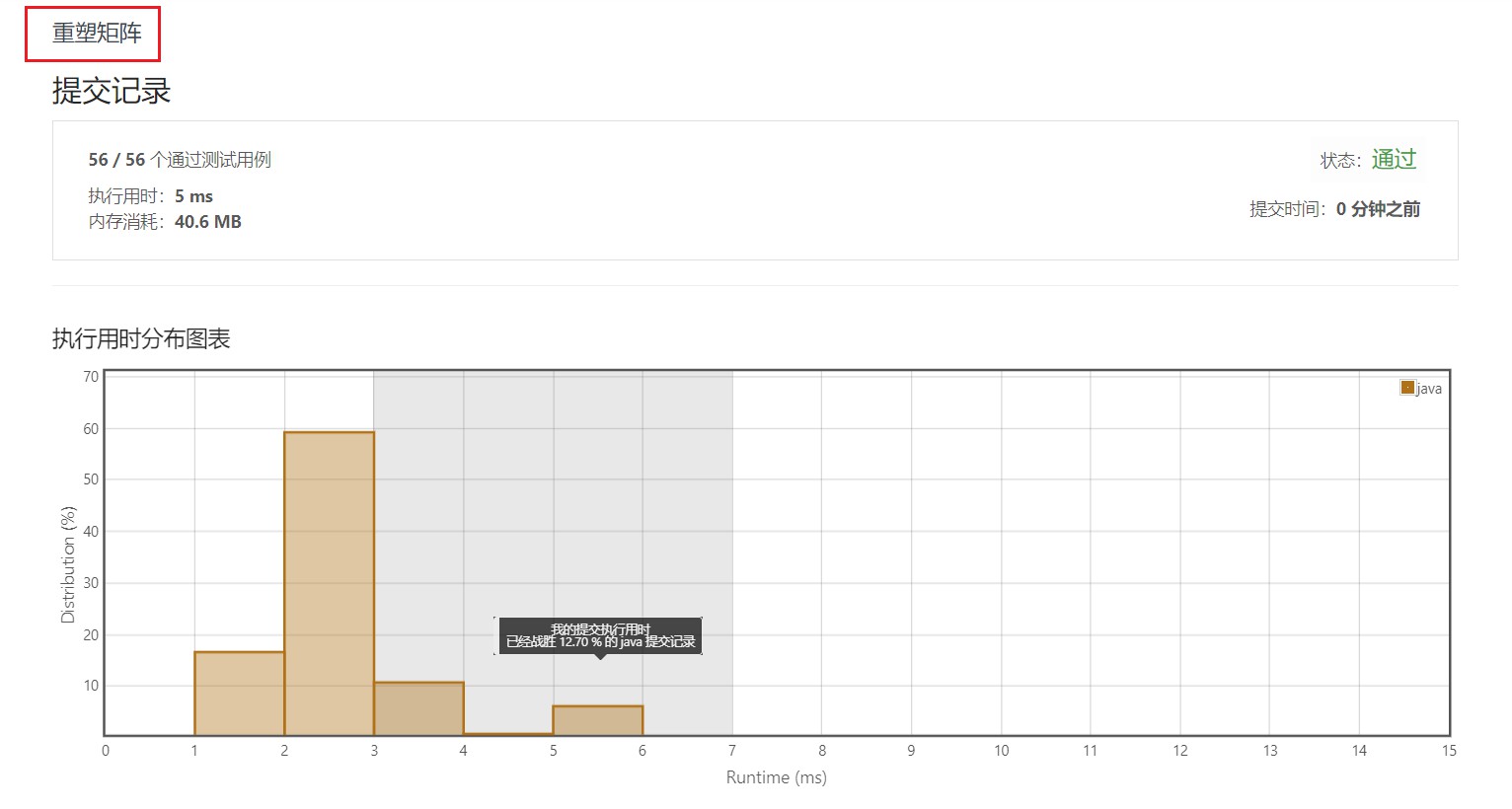
4.2 数组元素存储到另一个二维数组
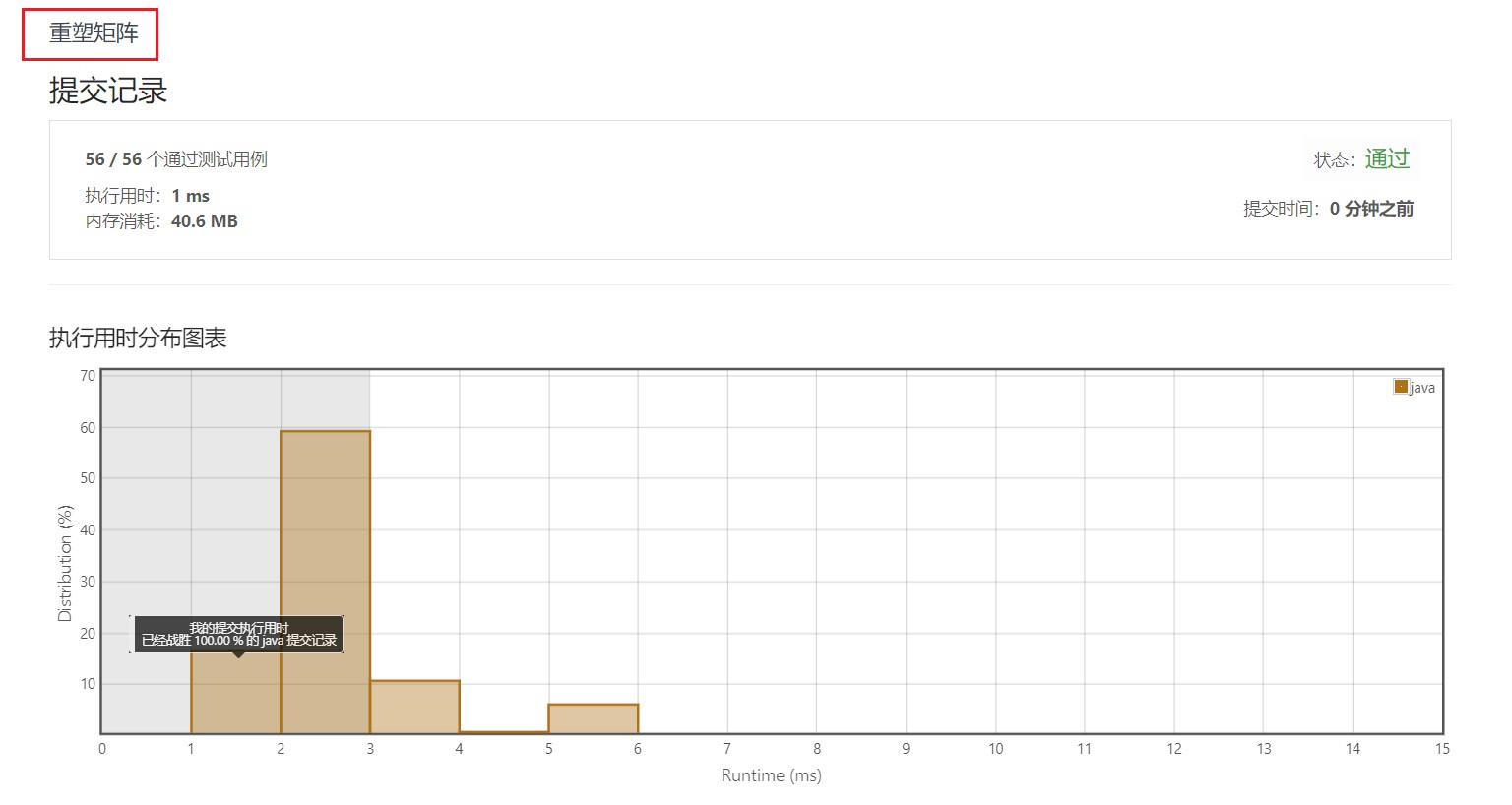
五、部分测试用例
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] nums = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}};
int r = 1, c = 4; // output:{{1, 2, 3, 4}}
// int[][] nums = {{1, 2}, {3, 4}};
// int r = 2, c = 4; // output:{{1, 2}, {3, 4}}
int[][] result = matrixReshape(nums, r, c);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}

