496. 下一个更大元素 I『简单』
题目来源于力扣(LeetCode)
目录
一、题目

说明:
nums1和nums2中所有元素是唯一的。nums1和nums2的数组大小都不超过1000。
二、解题思路
2.1 哈希表 + 暴力法
-
因为不确定数组中元素的取值范围,所以采用 map 来记录 nums2 数组中每个元素的下个更大元素
-
遍历 nums2 数组,对于每一个元素,都再次遍历其后的全部元素,判断是否存在大于该元素的数
-
大于时,用 map 记录下该数的下一个更大元素
-
遍历到最后未找到更大元素时,按题意存储 -1
2.2 哈希表 + 栈
-
遍历 nums2 数组,如 Stack 栈中不为空时,即循环对于栈顶的元素进行判断
-
栈顶元素小于当前遍历元素时,说明当前遍历元素是栈顶元素的下一个更大元素
-
通过 pop 方法弹出栈顶元素,并将栈顶元素作为键,当前遍历元素作为值存储到 map 中
-
直到 Stack 中不存在元素或栈顶的元素不小于当前遍历元素时,结束栈的循环
-
每次都将当前遍历元素 push 到 Stack 中
-
最后栈中剩余的元素即是未找到下一个更大元素的,需要手动 put 值 -1 到 map 中
三、代码实现
3.1 哈希表 + 暴力法
public static int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
int[] ans = new int[nums1.length];
// 定义哈希表记录 nums2 每个元素的下一个更大元素
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++) {
// 未找到时更大元素时,输出 -1
int num = -1;
// 查找当前遍历元素后面的全部元素
for (int j = i + 1; j < nums2.length; j++) {
// 在索引 i 之后,数组范围内遍历查找下一个更大元素
while (j <= nums2.length - 1 && nums2[j] <= nums2[i]) {
j++;
}
// 找到当前元素后面的较大元素时,put 到哈希表中
if (j <= nums2.length - 1) {
num = nums2[j];
break;
}
}
map.put(nums2[i], num);
}
int j = 0;
// 遍历 nums1 数组,根据元素值在哈希表中找到其对应的下一个更大元素
for (int i : nums1) {
ans[j++] = map.get(i);
}
return ans;
}
3.2 哈希表 + 栈
public static int[] nextGreaterElement(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int[] ans = new int[nums1.length];
for (int i = 0; i < nums2.length; i++) {
// 查找当前遍历元素是否大于 stack 中的最后一个元素
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() < nums2[i]) {
// 弹出较小的元素,作为 map 的键,值为当前遍历元素,即键的下一个更大元素
map.put(stack.pop(), nums2[i]);
}
// 每次遍历的元素都 push 到栈中
stack.push(nums2[i]);
}
// 手动对 stack 中剩下的元素(不存在下一个更大值的元素)进行 put -1 的操作
// 比后续用 map.containsKey 来判断 nums1 中某元素是否存在于 map 中效率更高
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
map.put(stack.pop(), -1);
}
int j = 0;
for (int i : nums1) {
ans[j++] = map.get(i);
}
return ans;
}
四、执行用时
4.1 哈希表 + 暴力法
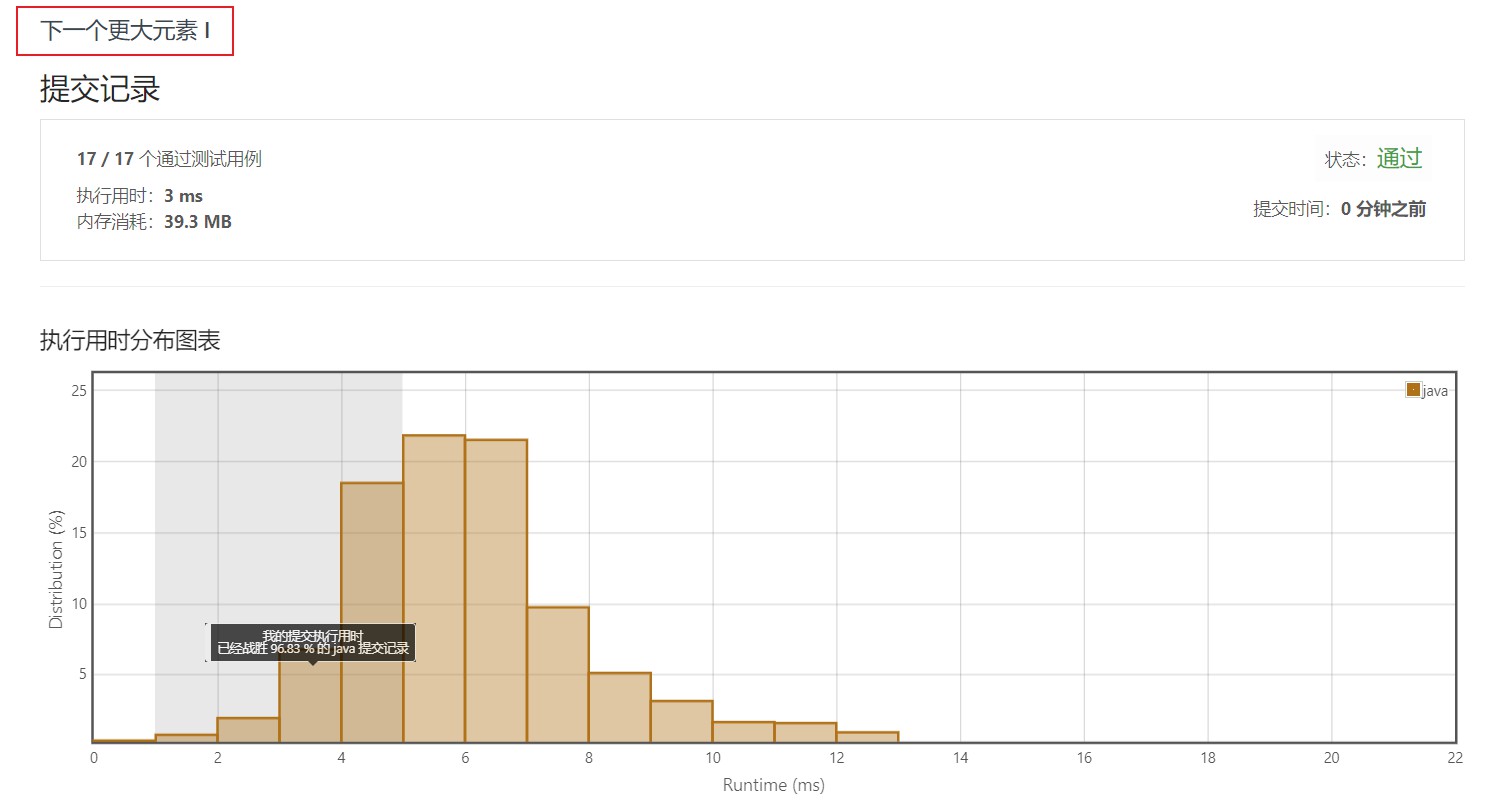
4.2 哈希表 + 栈
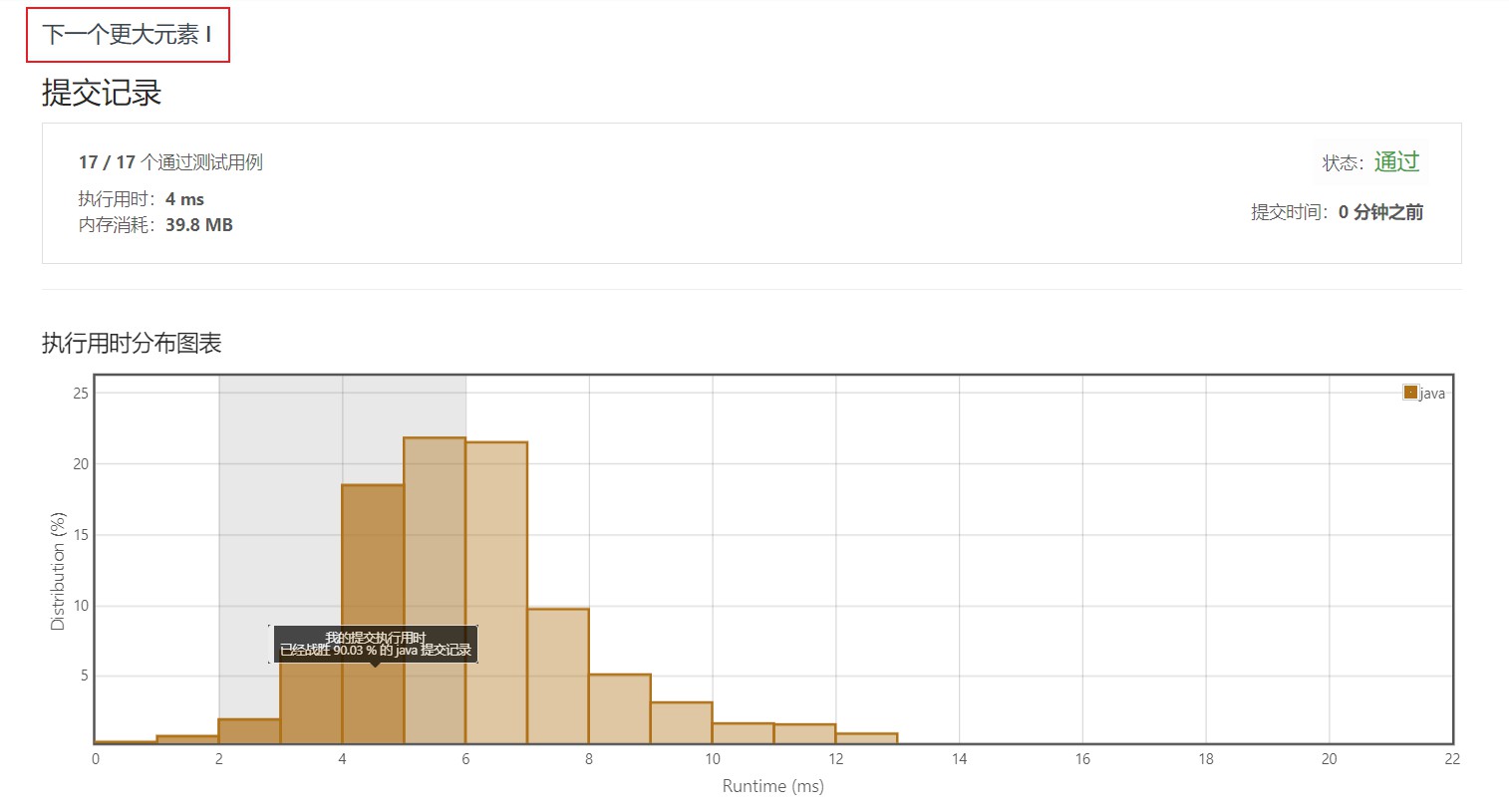
五、部分测试用例
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums1 = {4, 1, 2}, nums2 = {1, 3, 4, 2}; // output:{-1, 3, -1}
// int[] nums1 = {2, 4}, nums2 = {1, 2, 3, 4}; // output:{3, -1}
int[] result = nextGreaterElement(nums1, nums2);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(result));
}


