如何在 VS Code 中搭建 Qt 开发环境
前言
VS Code 高大上的界面、强大的智能联想和庞大的插件市场,着实让人对他爱不释手。虽然可以更改 Qt Creator 的主题,但是 Qt Creator 的代码体验实在差劲。下面就来看看如何在 VS Code 中搭建 Qt 开发环境。
安装拓展
工欲善其事,必先利其器。在开干之前,先来安装一些拓展,他们将提供函数提示、语法高亮等功能。
C/C++ 拓展
提供智能联想功能、语法高亮、Debug 等功能,确实很好用。设置 "C_Cpp.autocompleteAddParentheses": true,可以把函数名后面的括号也给补全了。

Qt 拓展
提供在 VS Code 中打开 Qt Designer、预览 ui 文件、编译 ui 文件和 qrc 文件为 python 源代码、 qss 和 pro 文件语法高亮的功能(之前这两个拓展评分还都是 5 分,VS Code 更新到 1.57 之后突然变成 0 分了,有点奇怪)。


使用之前,需要去设置里面配置下 Qt Designer 可执行文件的路径,如果想要编译 ui 和 qrc 文件为 python 源代码的话,还需要配置 pyuic.exe 和 pyqrc.exe 的路径,示例如下:
复制{
"qtForPython.designer.path": "D:/Qt/6.1.0/mingw81_64/bin/designer.exe",
"pyqt-integration.qtdesigner.path": "D:/Qt/6.1.0/mingw81_64/bin/designer.exe",
"pyqt-integration.pyuic.cmd": "D:/Python38/Scripts/pyuic5.exe",
"qtForPython.rcc.path": "D:/Python38/Scripts/pyrcc5.exe",
"qtForPython.lupdate.path": "D:/Python38/Scripts/pylupdate5.exe",
"qtForPython.rcc.liveExecution": false,
"qtForPython.uic.liveExecution": false
}
这些配置都是根据最新的拓展版本来设置的,像 Qt for Python 拓展更新之后的那些配置项的键就和上个版本不一样了,所以推荐使用最新版本。配置好之后右击资源管理器中的 ui 文件,可以在右击菜单中看到和 Qt 相关的菜单项,点击 Edit in Designer 就可以打开 Qt Designer。
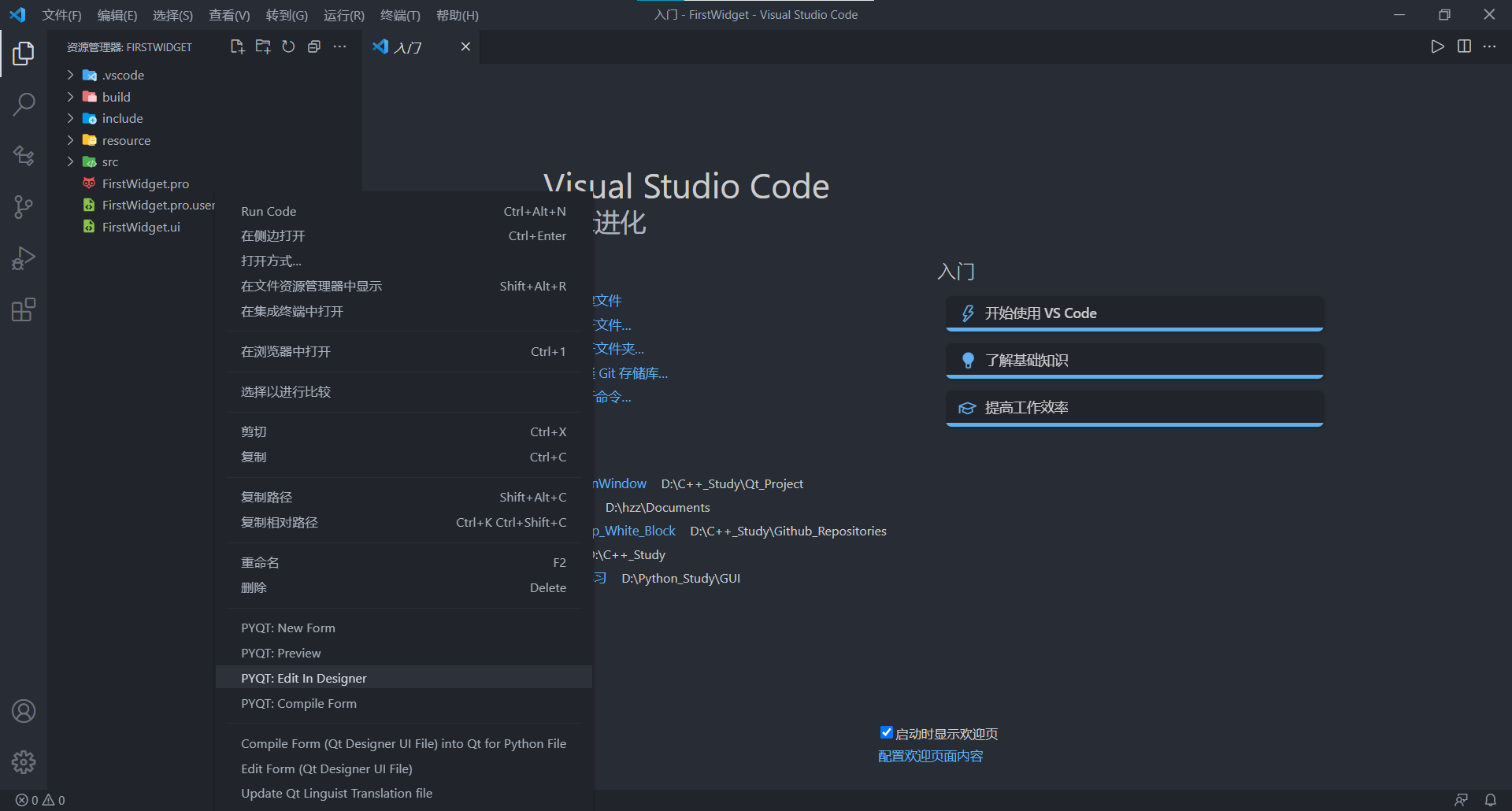
创建项目
假设我们的项目结构如上图资源管理器中所示(点击这里下载源代码和 VSCode 配置文件),下面看下如何在脱离 Qt Creator 的情况下创建一个项目。
创建 pro 文件
在终端输入 qmake -project 就可以在顶层目录下生成一个和顶层目录同名的 pro 文件,在这里为 FirstWidget.pro。写完代码之后在终端输入 qmake,就会在顶层目录下生成 Makefile、debug 文件夹和 release 文件夹,一下子就让整个文件夹变得混乱。所以这里我们让 qmake 生成的文件移到 build 文件夹下,方法是在 pro 文件中加入如下代码,然后在终端输入 qmake -o .\build\Makefile:
复制release: DESTDIR = ./release
debug: DESTDIR = ./debug
OBJECTS_DIR = $$DESTDIR/.obj
MOC_DIR = $$DESTDIR/.moc
RCC_DIR = $$DESTDIR/.qrc
UI_DIR = $$DESTDIR/.ui
但是每次创建项目都写上这么一段太麻烦了,这时候 VS Code 的 Snippets 功能就派上用场了。在 VS Code 中 Ctrl + Shift + P -> 首选项:配置用户代码片段 -> qmake,将打开的 qmake.json 的内容替换为如下代码,关于用户片段的写法参见 《[VS Code]跟我一起在Visual Studio Code 添加自定义snippet(代码段),附详细配置》:
复制{
// Place your snippets for qmake here. Each snippet is defined under a snippet name and has a prefix, body and
// description. The prefix is what is used to trigger the snippet and the body will be expanded and inserted. Possible variables are:
// $1, $2 for tab stops, $0 for the final cursor position, and ${1:label}, ${2:another} for placeholders. Placeholders with the
// same ids are connected.
// Example:
"config build dir": {
"prefix": "build",
"body": [
"release: DESTDIR = ./release",
"debug: DESTDIR = ./debug",
"",
"OBJECTS_DIR = $$$DESTDIR/.obj",
"MOC_DIR = $$$DESTDIR/.moc",
"RCC_DIR = $$$DESTDIR/.qrc",
"UI_DIR = $$$DESTDIR/.ui"
],
"description": "配置输出文件路径"
},
"initialize project": {
"prefix": "init",
"body": [
"QT += core gui",
"",
"greaterThan(QT_MAJOR_VERSION, 4): QT += widgets",
"",
"CONFIG += c++11",
"",
"# You can make your code fail to compile if it uses deprecated APIs.",
"# In order to do so, uncomment the following line.",
"#DEFINES += QT_DISABLE_DEPRECATED_BEFORE=0x060000 # disables all the APIs deprecated before Qt 6.0.0",
"",
"INCLUDEPATH += ${1:include}",
"",
"SOURCES += \\",
" ${2:src/main.cpp} \\",
" ${3:src/$WORKSPACE_NAME.cpp}",
"",
"HEADERS += \\",
" ${1:include}/$WORKSPACE_NAME.h",
"",
"FORMS += \\",
" $WORKSPACE_NAME.ui",
"",
"release: DESTDIR = ./release",
"debug: DESTDIR = ./debug",
"",
"OBJECTS_DIR = \\$\\$DESTDIR/.obj",
"MOC_DIR = \\$\\$DESTDIR/.moc",
"RCC_DIR = \\$\\$DESTDIR/.qrc",
"UI_DIR = \\$\\$DESTDIR/.ui",
"",
"# Default rules for deployment.",
"qnx: target.path = /tmp/\\$\\$TARGET/bin",
"else: unix:!android: target.path = /opt/\\$\\$TARGET/bin",
"!isEmpty(target.path): INSTALLS += target",
"$0"
],
"description": "初始化工程文件"
},
}
使用起来如下所示,真的太香了:
创建 tasks.json
在 VS Code 中按下 Ctrl + Shift + P,在命令面板中输入 task,选择配置任务,具体操作如下:
将 tasks.json 的内容替换成如下代码:
复制{
"tasks": [
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "qmake build makefile (debug)",
"command": "qmake",
"args": [
"-o",
"./build/Makefile",
"CONFIG += debug",
"CONFIG += console",
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}"
},
"problemMatcher": [],
"group": "build",
"detail": "生成 Makefile (debug)"
},
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "qmake build makefile (release)",
"command": "qmake",
"args": [
"-o",
"./build/Makefile"
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}"
},
"problemMatcher": [],
"group": "build",
"detail": "生成 Makefile (release)"
},
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "Qt build debug",
"command": "make",
"args": [
"debug"
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/build"
},
"problemMatcher": [],
"group": "build",
"detail": "Qt 生成可调试文件",
"dependsOn": [
"qmake build makefile (debug)"
]
},
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "Qt build release",
"command": "make",
"args": [
"release"
],
"options": {
"cwd": "${workspaceFolder}/build"
},
"problemMatcher": [],
"group": "build",
"detail": "Qt 生成可执行文件",
"dependsOn": [
"qmake build makefile (release)"
]
},
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "Qt build and run release",
"command": "${workspaceFolder}/build/release/${workspaceRootFolderName}.exe",
"args": [],
"problemMatcher": [],
"group": "build",
"detail": "Qt 生成并运行可执行文件",
"dependsOn": [
"Qt build release"
],
// close 键在 VS Code 1.57 引入
"presentation": {
"close": true
}
},
{
"type": "shell",
"label": "Qt build and run debug",
"command": "${workspaceFolder}/build/debug/${workspaceRootFolderName}.exe",
"args": [],
"problemMatcher": [],
"group": "build",
"detail": "Qt 生成并运行可调试文件",
"dependsOn": [
"Qt build debug"
]
},
],
"version": "2.0.0"
}
tasks.json 是 VS Code 的一大亮点,可以在里面配置多个任务,每个任务其实就是帮你在终端输入指令。虽然每个任务的 command 键只能输入一条指令,但是你可以配合 dependsOn 的值,这样在输入这个 command 之前就会依次输入 dependsOn 中各个任务的 command,相当于一个任务在终端输入了多条指令。如果知道 Qt Creator 的编译过程的话就很容易看懂上面 tasks.json 中的每条指令在干些什么。
比如现在我想要在 build 目录下生成 Makefile,那么只要 Alt + T + R,在任务菜单中选择 qmake build makefile (release) 任务,具体过程如下:
再比如我们现在想要编译生成 exe 并运行之,那么只要选择 Qt build and run release,具体过程如下:
运行任务之后就可以在 ./build/release 目录下看到可执行文件。如果编译 makefile 的时候报错很有可能是因为你没有把 D:\Qt\6.2.1\mingw81_64\bin(这个是我的 Qt6.2.1 MinGW 套件目录) 添加到环境变量里,这个路径最好放的前面一点,如果电脑里面装了 Anaconda 还配置了 Anaconda 的路径的话 qmake 可能会发生冲突然后报错。
配置 C++ 智能联想
要想让 C/C++ 拓展解析 Qt 源文件,提供智能联想功能,就需要告诉他 Qt 的源文件在哪。只要打开了C/C++文件,就能在 VS Code 的状态栏看到 C/C++ 的配置按钮,我这里的配置按钮的文字是 Win32,因为我选了 Win32 配置集。下面看下怎么配置智能联想功能:
如动图中所示,我们只要在包含路径中填入需要解析的 Qt 源文件所在的文件夹即可,一种偷懒的方法是直接填入 D:/Qt/6.1.0/mingw81_64/include/** (这是我的 Qt 路径),但是这样会让 C/C++ 拓展递归解析 include 文件夹下的所有文件,会很慢,所以只需填入要用的那些头文件所在文件夹即可,比如:
复制D:/Qt/6.1.0/mingw81_64/include
D:/Qt/6.1.0/mingw81_64/include/QtGui
D:/Qt/6.1.0/mingw81_64/include/QtCore
D:/Qt/6.1.0/mingw81_64/include/QtWidgets
填好之后会在 .vscode 文件夹下面看到一个 c_cpp_properties.json,里面记录了用户的配置,之后就可以直接修改这个文件中的键的值来配置拓展。配置好之后就可以看到语法高亮和函数提示了,比如下图所示:
后记
至此在 VS Code 中搭建 Qt 开发环境的步骤全部介绍完毕了,但是 VS Code 的强大之处不止如此,可以在官网的文档和每个月的发行文档中了解更多正确的打开方式,而且VS Code 每个月都会更新,带来更多好用的特性,赶紧用起来吧!以上~~















【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· 没有源码,如何修改代码逻辑?
· 全程不用写代码,我用AI程序员写了一个飞机大战
· MongoDB 8.0这个新功能碉堡了,比商业数据库还牛
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 白话解读 Dapr 1.15:你的「微服务管家」又秀新绝活了
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」