[后端人员耍前端系列]KnockoutJs篇:使用KnockoutJs+Bootstrap实现分页
一、引言
由于最近公司的系统需要改版,改版的新系统我打算使用KnockoutJs来制作Web前端。在做的过程中,遇到一个问题——如何使用KnockoutJs来完成分页的功能。在前一篇文章中并没有介绍使用KnockoutJs来实现分页,所以在这篇文章中,将补充用KnockoutJs+Bootstrap来实现数据的分页显示。
二、使用KnockoutJs实现分页
这里采用了两种方式来实现分页,第一种是将所有数据加载出来,然后再将所有数据分页显示;第二种是每次都只加载部分数据,每次请求都重新加载后面的数据。
对于这两种方式,使用Razor方式实现的分页一般都会采用第二种方式来实现分页,但是对于单页面程序来说,第一种实现方式也有其好处,对于不是非常大量的数据完全可以采用第一种实现方式,因为这样的话,后面的数据的加载,用户体验非常的流畅。所以这里将分别介绍这两种实现方式。
2.1 每次加载部分数据的实现
这里的后端代码采用的是前一篇文章的代码,只是多加了一些示例数据而已。具体的后端实现代码为:

/// <summary> /// Web API 服务,为Web前端提供数据服务 /// </summary> public class TaskController : ApiController { private readonly TaskRepository _taskRepository = TaskRepository.Current; public IEnumerable<Task> GetAll() { return _taskRepository.GetAll().OrderBy(a => a.Id); } [Route("api/task/GetByPaged")] public PagedModel GetAll([FromUri]int pageIndex) { const int pageSize = 3; int totalCount; var tasks = _taskRepository.GetAll(pageIndex, pageSize, out totalCount).OrderBy(a => a.Id); var pageData = new PagedModel() { PageIndex = pageIndex, PagedData = tasks.ToList(), TotalCount = totalCount, PageCount = (totalCount+ pageSize -1) / pageSize }; //返回数据 return pageData; } } /// <summary> /// 任务仓储,封装了所有关于数据库的操作 /// </summary> public class TaskRepository { #region Static Filed private static Lazy<TaskRepository> _taskRepository = new Lazy<TaskRepository>(() => new TaskRepository()); public static TaskRepository Current { get { return _taskRepository.Value; } } #endregion #region Fields private readonly List<Task> _tasks = new List<Task>() { new Task { Id =1, Name = "创建一个SPA程序", Description = "SPA(single page web application),SPA的优势就是少量带宽,平滑体验", Owner = "Learning hard", FinishTime = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Now.AddDays(1).ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)) }, new Task { Id =2, Name = "学习KnockoutJs", Description = "KnockoutJs是一个MVVM类库,支持双向绑定", Owner = "Tommy Li", FinishTime = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Now.AddDays(2).ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)) }, new Task { Id =3, Name = "学习AngularJS", Description = "AngularJs是MVVM框架,集MVVM和MVC与一体。", Owner = "李志", FinishTime = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Now.AddDays(3).ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)) }, new Task { Id =4, Name = "学习ASP.NET MVC网站", Description = "Glimpse是一款.NET下的性能测试工具,支持asp.net 、asp.net mvc, EF等等,优势在于,不需要修改原项目任何代码,且能输出代码执行各个环节的执行时间", Owner = "Tonny Li", FinishTime = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Now.AddDays(4).ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)) }, new Task { Id =5, Name = "测试任务1", Description = "测试任务1", Owner = "李志", FinishTime = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Now.AddDays(5).ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)) }, new Task { Id =6, Name = "测试任务2", Description = "测试任务2", Owner = "李志", FinishTime = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Now.AddDays(6).ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)) }, new Task { Id =7, Name = "测试任务3", Description = "测试任务3", Owner = "李志", FinishTime = DateTime.Parse(DateTime.Now.AddDays(7).ToString(CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)) }, }; #endregion #region Public Methods public IEnumerable<Task> GetAll() { return _tasks; } public IEnumerable<Task> GetAll(int pageNumber, int pageSize, out int totalCount) { var skip = (pageNumber - 1) * pageSize; var take = pageSize; totalCount = _tasks.Count; return _tasks.Skip(skip).Take(take); } public Task Get(int id) { return _tasks.Find(p => p.Id == id); } public Task Add(Task item) { if (item == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("item"); } item.Id = _tasks.Count + 1; _tasks.Add(item); return item; } public void Remove(int id) { _tasks.RemoveAll(p => p.Id == id); } public bool Update(Task item) { if (item == null) { throw new ArgumentNullException("item"); } var taskItem = Get(item.Id); if (taskItem == null) { return false; } _tasks.Remove(taskItem); _tasks.Add(item); return true; } #endregion }
Web前端的实现代码:
@{ ViewBag.Title = "Index2"; Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml"; } <div id="list2"> <h2>分页第二种实现方式——任务列表</h2> <div class="table-responsive"> <table class="table table-striped"> <thead> <tr> <th>编号</th> <th>名称</th> <th>描述</th> <th>负责人</th> <th>创建时间</th> <th>完成时间</th> <th>状态</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody data-bind="foreach:pagedList"> <tr> <td data-bind="text: id"></td> <td><a data-bind="text: name"></a></td> <td data-bind="text: description"></td> <td data-bind="text: owner"></td> <td data-bind="text: creationTime"></td> <td data-bind="text: finishTime"></td> <td data-bind="text: state"></td> </tr> </tbody> <tbody data-bind="if: loadingState"> <tr> <td colspan="8" class="text-center"> <img width="60" src="/images/loading.gif" /> </td> </tr> </tbody> <tfoot data-bind="ifnot:loadingState"> <tr> <td colspan="8"> <div class="pull-right"> <div>总共有<span data-bind="text: totalCount"></span>条记录, 每页显示:<span data-bind="text: pageSize"></span>条</div> <div> <ul class="pagination"> <li data-bind="css: { disabled: pageIndex() === 1 }"><a href="#" data-bind="click: previous">«</a></li> </ul> <ul data-bind="foreach: allPages" class="pagination"> <li data-bind="css: { active: $data.pageNumber === ($root.pageIndex()) }"><a href="#" data-bind="text: $data.pageNumber, click: function() { $root.gotoPage($data.pageNumber); }"></a></li> </ul> <ul class="pagination"><li data-bind="css: { disabled: pageIndex() === pageCount }"><a href="#" data-bind="click: next">»</a></li></ul> </div> </div> </td> </tr> </tfoot> </table> </div> </div>
对应的Js实现为:
// 实现分页的第二种方式 var ListViewModel2 = function() { //viewModel本身。用来防止直接使用this的时候作用域混乱 var self = this; self.loadingState = ko.observable(true); self.pageSize = ko.observable(3); //数据 this.pagedList = ko.observableArray(); //要访问的页码 this.pageIndex = ko.observable(1); //总页数 this.pageCount = ko.observable(1); //页码数 this.allPages = ko.observableArray(); //当前页 this.currengePage = ko.observable(1); self.totalCount = ko.observable(1); this.refresh = function() { //限制请求页码在该数据页码范围内 if (self.pageIndex() < 1) self.pageIndex(1); if (self.pageIndex() > self.pageCount()) { self.pageIndex(self.pageCount()); } //post异步加载数据 sendAjaxRequest("GET", function (data) { // 加载新的数据前,先移除原先的数据 self.pagedList.removeAll(); self.allPages.removeAll(); self.totalCount(data.totalCount); self.pageCount(data.pageCount); self.loadingState(false); for (var i = 1; i <= data.pageCount; i++) { //装填页码 self.allPages.push({ pageNumber: i }); } //for...in 语句用于对数组或者对象的属性进行循环操作。 //for ... in 循环中的代码每执行一次,就会对数组的元素或者对象的属性进行一次操作。 for (var i in data.pagedData) { //装填数据 self.pagedList.push(data.pagedData[i]); } }, 'GetByPaged', { 'pageIndex': self.pageIndex() }); }; //请求第一页数据 this.first = function() { self.pageIndex(1); self.refresh(); }; //请求下一页数据 this.next = function() { self.pageIndex(this.pageIndex() + 1); self.refresh(); }; //请求先前一页数据 this.previous = function() { self.pageIndex(this.pageIndex() - 1); self.refresh(); }; //请求最后一页数据 this.last = function() { self.pageIndex(this.pageCount() - 1); self.refresh(); }; //跳转到某页 this.gotoPage = function (data, event) { self.pageIndex(data); self.refresh(); }; }; function sendAjaxRequest(httpMethod, callback, url, reqData) { $.ajax("/api/task" + (url ? "/" + url : ""), { type: httpMethod, success: callback, data: reqData }); } $(document).ready(function () { var viewModel = new ListViewModel2(); viewModel.refresh(); if ($('#list2').length) ko.applyBindings(viewModel, $('#list2').get(0)); });
这里介绍了下使用KnockoutJs实现分页功能的实现思路:
- 页面加载完成之后,发起Ajax请求去异步调用REST 服务来请求部分数据。
- 然后将请求的数据通过KnockoutJs绑定显示。
- 将对应的分页信息绑定到Bootstrap分页中
- 当用户点击翻页时,再发起一个Ajax请求去异步调用Rest服务请求数据,再将请求的数据显示出来。
这上面是描述的代码的调用逻辑关系,你可以参考对应的JS代码来理解上面的描述。到此我们第二种实现方式就实现完成了。
2.2 第一次加载所有数据,然后将所有数据分页显示
接下来就介绍了第一种实现方式,这样的实现方式,用户只会在第一次的时候才会感觉到数据加载中,翻页过程中感觉不到页面的加载,这样对于一些本身数据了不是太多的情况下,对于用户的感觉也是更加流畅的。
其具体的实现思路,也就是将请求的数据不要全部显示在页面上,因为数据太多,一下子显示到页面中,用户可能会眼花缭乱。将数据分页显示将使得用户查看更加清晰。
具体的Web前端Js的实现代码为:
var ListViewModel = function () { var self = this; window.viewModel = self; self.list = ko.observableArray(); self.pageSize = ko.observable(3); self.pageIndex = ko.observable(0); //要访问的页码 self.totalCount = ko.observable(1); //总记录数 self.loadingState = ko.observable(true); self.pagedList = ko.dependentObservable(function () { var size = self.pageSize(); var start = self.pageIndex() * size; return self.list.slice(start, start + size); }); self.maxPageIndex = ko.dependentObservable(function () { return Math.ceil(self.list().length / self.pageSize()) - 1; }); self.previousPage = function () { if (self.pageIndex() > 0) { self.pageIndex(self.pageIndex() - 1); } }; self.nextPage = function () { if (self.pageIndex() < self.maxPageIndex()) { self.pageIndex(self.pageIndex() + 1); } }; self.allPages = ko.dependentObservable(function () { var pages = []; for (var i = 0; i <= self.maxPageIndex() ; i++) { pages.push({ pageNumber: (i + 1) }); } return pages; }); self.moveToPage = function (index) { self.pageIndex(index); }; }; var listViewModel = new ListViewModel(); function bindViewModel() { sendAjaxRequest("GET", function (data) { listViewModel.loadingState(false); listViewModel.list(data); listViewModel.totalCount(data.length); if ($('#list').length) ko.applyBindings(listViewModel, $('#list').get(0)); }, null, null); } $(document).ready(function () { bindViewModel(); });
其前端页面的实现与前面的实现类似。具体页面代码如下:

@{ ViewBag.Title = "Index"; Layout = "~/Views/Shared/_Layout.cshtml"; } <div id="list"> <h2>任务列表</h2> <div class="table-responsive"> <table class="table table-striped"> <thead> <tr> <th>编号</th> <th>名称</th> <th>描述</th> <th>负责人</th> <th>创建时间</th> <th>完成时间</th> <th>状态</th> </tr> </thead> <tbody data-bind="foreach:pagedList"> <tr> <td data-bind="text: id"></td> <td><a data-bind="text: name"></a></td> <td data-bind="text: description"></td> <td data-bind="text: owner"></td> <td data-bind="text: creationTime"></td> <td data-bind="text: finishTime"></td> <td data-bind="text: state"></td> </tr> </tbody> <tbody data-bind="if:loadingState"> <tr> <td colspan="8" class="text-center"> <img width="60" src="/images/loading.gif" /> </td> </tr> </tbody> <tfoot data-bind="ifnot:loadingState"> <tr> <td colspan="8"> <div class="pull-right"> <div>总共有<span data-bind="text: totalCount"></span>条记录, 每页显示:<span data-bind="text: pageSize"></span>条</div> <div> <ul class="pagination"> <li data-bind="css: { disabled: pageIndex() === 0 }"><a href="#" data-bind="click: previousPage">«</a></li> </ul> <ul data-bind="foreach: allPages" class="pagination"> <li data-bind="css: { active: $data.pageNumber === ($root.pageIndex() + 1) }"><a href="#" data-bind="text: $data.pageNumber, click: function() { $root.moveToPage($data.pageNumber-1); }"></a></li> </ul> <ul class="pagination"><li data-bind="css: { disabled: pageIndex() === maxPageIndex() }"><a href="#" data-bind="click: nextPage">»</a></li></ul> </div> </div> </td> </tr> </tfoot> </table> </div> </div>
三、运行效果
接下来,让我们看看,使用KnockoutJs实现的分页效果:
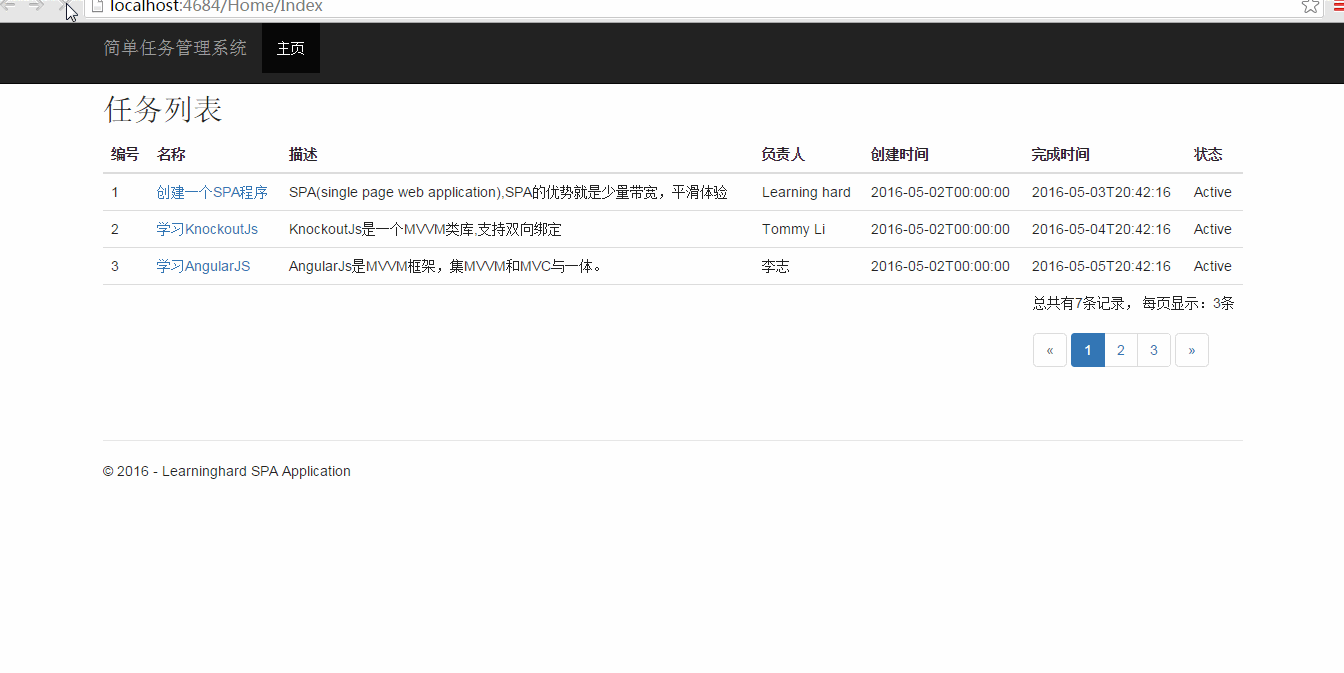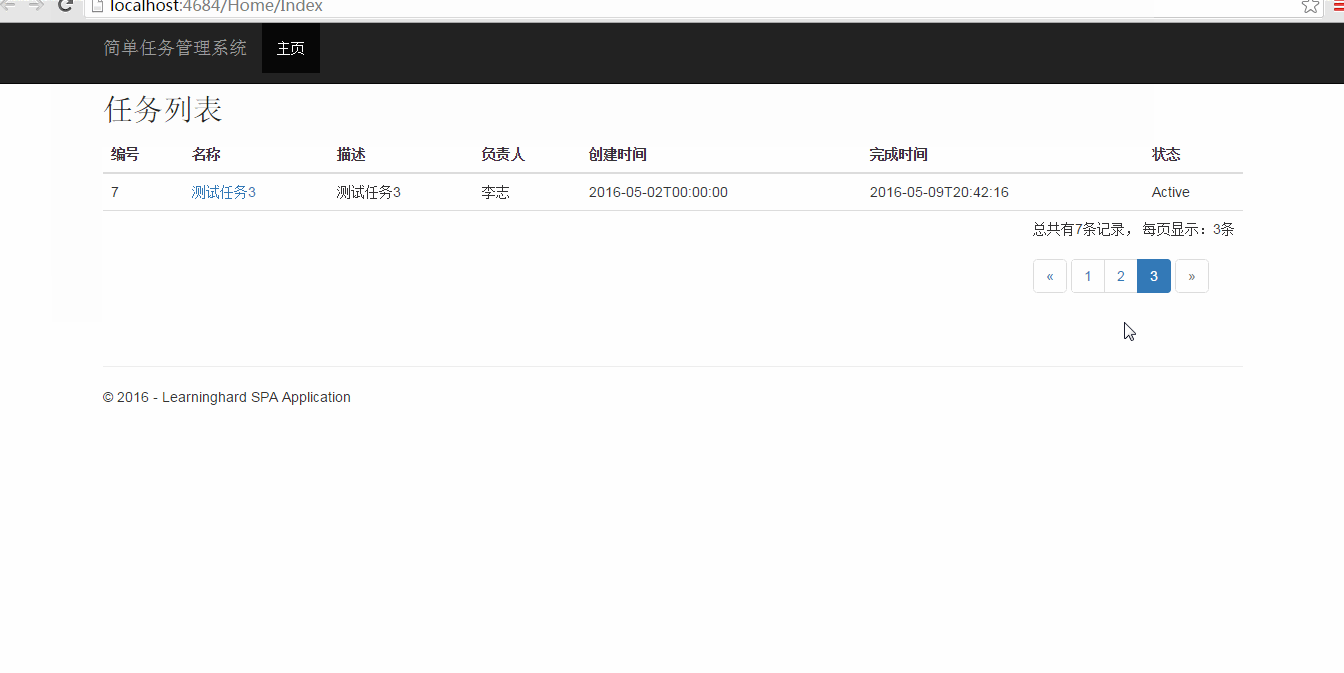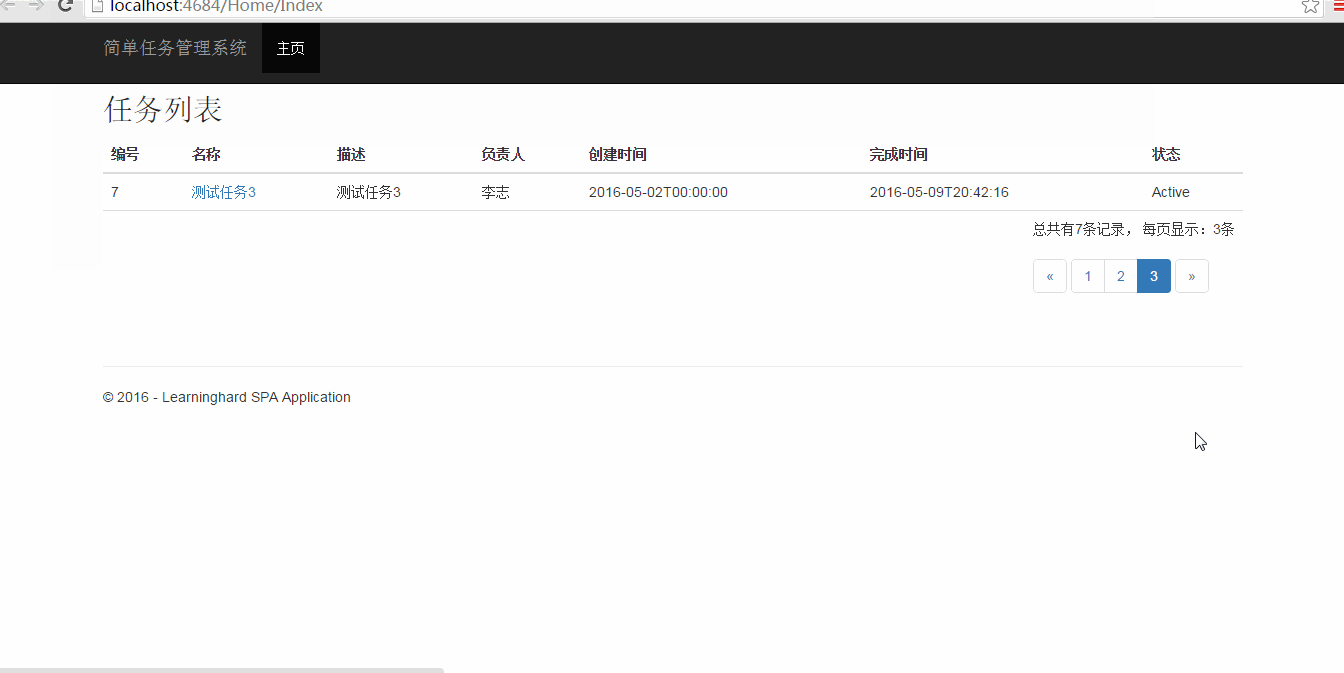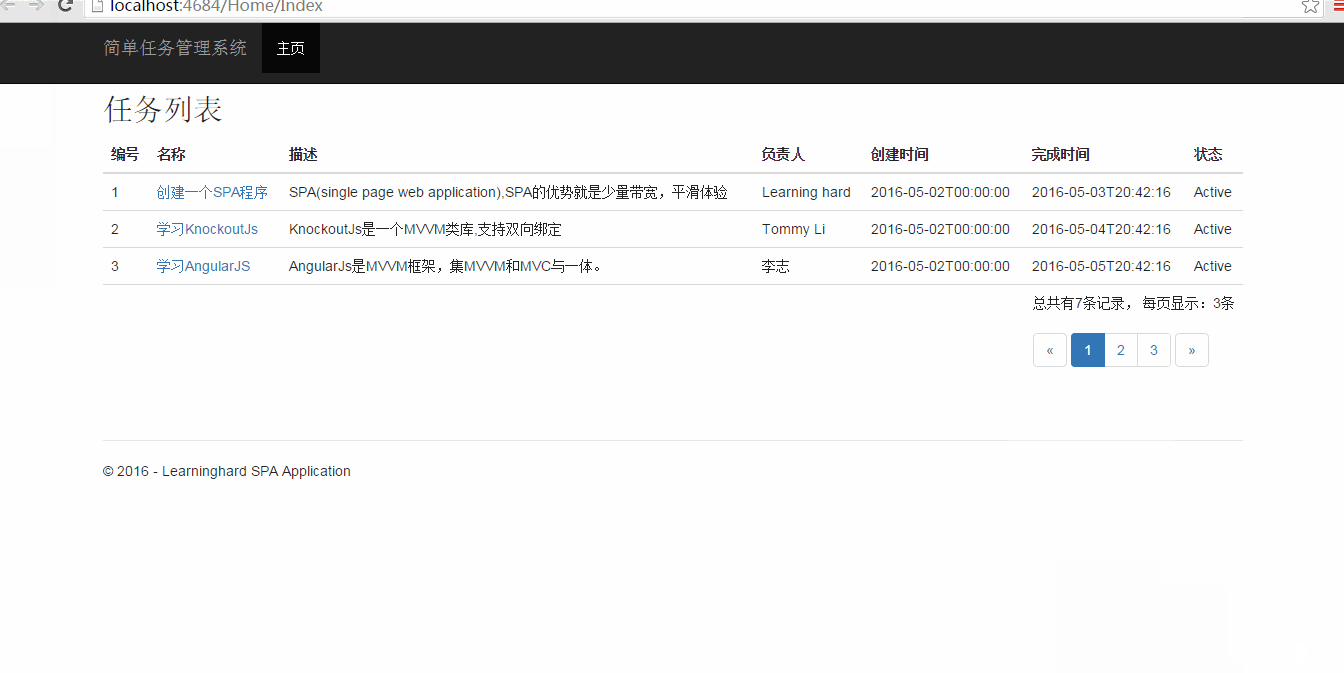
四、总结
到这里,本文要介绍的内容就结束,尽管本文实现的内容相对比较简单,但是对于一些刚接触KnockoutJs的朋友来说,相信本文的实现会是一个很多的指导。接下来,我将会为大家分享下AngularJs的相关内容。
本文所有源码实现:KnockoutJSPaged
如果您认为这篇文章还不错或者有所收获,您可以通过右边的“打赏”功能 打赏我一杯咖啡【物质支持】,也可以点击右下角的【店长推荐】按钮【精神支持】,因为这两种支持都是我继续写作,分享的最大动力





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号