系统的引导过程与服务控制
一:Linux 操作系统的引导,及systemd单元
1.1 引导过程
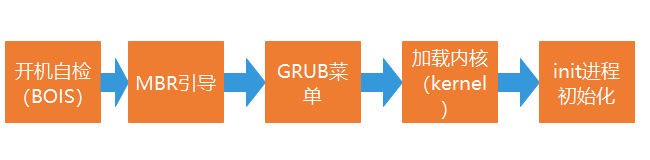
(1 ),开机自检
开机后,将根据主板BIOS 中的设置对硬件进行检测,如cpu,内存,显卡,等设备,检测第一个引导系统的设备,可以是硬盘,光驱,U盘,网络引。
(2),MBR 引导
当从本机硬盘中启动系统时,根据第一个硬盘的第一个扇区里的MBR设置调用GRUB启动菜单。centOS7 使用GRUB2 启动引导器
(3),GRUB菜单
GRUB引导程序读取GRUB的配置文件 /boot/grub2/grub.cfg,获取内核和镜像文件系统的设置和路径位置
(4),加载Linux 内核
将内核和镜像文件系统 加载到内存中 。CentOS 7 默认的内核文件位于"/boot/vmlinuz-3.10.0-514.e17.x86 64"
(5),init 进程初始化
加载硬件驱动程序,内核将init 进程加载到内存中运行。init程序是在/sbin/init 中。CentOS 7 中为Systemd
1.2 系统初始化进程
1.2.1 init 进程
- 由Linux内核加载运行/sbin/init 程序
- init 进程是系统中的第一个进程 ,是所有进程的父进程
- init 进程的 PID 号永远是为1
1.2.2 Systemd (也被称为上帝进程)
- Systemd 是Linux 操作系统的一种init 软件
- Centos 7 中采用全新的Systemd 启动方式 ,取代传统的SysVint
- CentOS 7 中运行的第一个init 进程是 /lib/systemd/systemd
# 传统 SysVinit 依赖于串行执行she11脚本启动服务导致效率低下,系统启动速度较慢
用 pstree 命令 可以查看到 进程树
用 ps -aux 可以查看到PID号
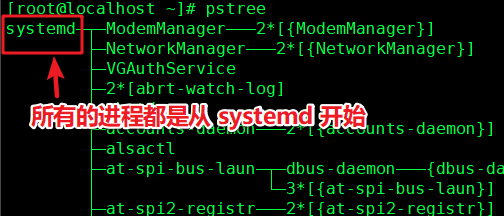

在CentOS 7 中,查看 /sbin/init 可以发现是一个指向 /lib/systemd/systemd 的软链接

1.3 systemd 单元类型
单元类型:
|
单元类型
|
扩展名
|
说明
|
|
Service
|
.service
|
描述一个系统服务
|
|
Socket
|
.socket
|
描述一个进程间通信的套接字
|
|
Device
|
.device
|
描述一个内核识别的设备文件
|
|
Mount
|
.mount
|
描述一个文件的挂载点
|
|
Automount
|
.automount
|
描述一个文件系统的自动挂载点
|
|
Swap
|
.swap
|
描述一个内存交换设备或交换文件
|
|
Path
|
.path
|
描述一个文件系统中文件或目录
|
|
Timer
|
.timer
|
描述一个定时器(用于实现类似cron的调度任务)
|
|
Snapshot
|
.snapshot
|
用于保存一个systemd的状态
|
|
Scope
|
.scope
|
使用systemd的总线接口以编程的方式创建外部进程
|
|
Slice
|
.slice
|
描述居于Cgroup的一组通过层次组织的管理系统进程
|
|
Target
|
.target
|
描述一组systemd的单元
|
二: Linux 系统的运行级别
2.1 运行级别
CentOS 7 的 /etc/rc.d 目录下有7个 rc0-6.d 的目录,对应系统的7个运行级别(0-6)

init 运行级别
此命令可以快速切换系统的运行级别
2.2 查看运行级别
2.2.1 runlevel 命令
runlevel 命令可以查看到之前一次的运行级别和当前的运行级别
[root@localhost ~]# runlevel N 5 #N 为null ,表示运行级别尚未改变。 5 为当前的运行级别 [root@localhost ~]# runlevel 5 3 # 5 表示上一次的运行级别为 5 , 当前的运行级别为 3
2.2.2 who 命令
who -r 命令 可以查看到当前和上一次的运行级别
[root@localhost ~]# who -r 运行级别 3 2021-06-22 19:46 最近=5 #当前的运行级别是5 ,上一次的是3
2.2.3 systemctl 工具
systemctl 可以查看到默认的运行级别
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl get-default #查看当前的默认运行级别 graphical.target #这个默认运行级别是 5 图形化模式
2.3 切换运行级别
2.3.1 临时切换运行级别
(1) 使用init 命令
init 命令后面跟上运行级别,可以快速切换
[root@localhost ~]# runlevel 5 3 [root@localhost ~]# init 5 #切换到 5 运行级别 [root@localhost ~]# runlevel 3 5
(2) systemctl 命令
systemctl isolate systemd的target
运行级别与systemd 的target对应
|
运行级别
|
Systemd的target
|
说明
|
|
0
|
target(poweroff.target)
|
系统停机(关机)模式,系统默认运行级别不能设置为0,否则不能正常启动,一开机就自动关机。
|
|
1
|
rescue.target
|
单用户模式,root权限,用于系统维护,禁止远程登陆,就像Windows下的安全模式登录。
|
|
2
|
multi-user.target
|
多用户模式,没有NFS网络支持。
|
|
3
|
multi-user.target
|
完整的多用户文本模式,有NFS,登陆后进入控制台命令行模式。
|
|
4
|
multi-user.target
|
系统未使用,保留一般不用,在一些特殊情况下可以用它来做一些事情。例如在笔记本电脑的电池用尽时,可以切换到这个模式来做一些设置。
|
|
5
|
graphical.target
|
图形化模式,登陆后进入图形GUI模式或GNOME、KDE图形化界面,如X Window系统。
|
|
6
|
reboot.target
|
重启模式,默认运行级别不能设为6,否则不能正常启动,就会一直开机重启开机重启。
|
[root@localhost ~]# runlevel 3 5 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl isolate multi-user.target #切换到运行级别3 [root@localhost ~]# runlevel 5 3 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl isolate poweroff.target #切换到运行级别0 (关机) Connection closing...Socket close.
2.3.2 设置默认运行级别与永久切换运行级别
(1) systemctl set-default systemd的target
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl set-default multi-user.target #设置默认运行级别 Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/default.target. Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/default.target to /usr/lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target. [root@localhost ~]# systemctl get-default #查看默认运行级别 multi-user.target
2 ln -fs /lib/systemd/system/运行级别target标签 /etc/systemd/system/default.target
查看默认运行级别,实际是查看软连接文件 /etc/systemd/system/default.target 。所以,可以通过修改该软连接的源文件,来修改默认运行级别
[root@localhost ~]# ll /etc/systemd/system/default.target lrwxrwxrwx. 1 root root 41 6月 23 19:04 /etc/systemd/system/default.target -> /usr/lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target [root@localhost ~]# ls /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target [root@localhost ~]# ln -sf /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target /etc/systemd/system/default.target
#将/etc/systemd/system/default.target 强制做成 /lib/systemd/system/multi-user.target 的软连接。 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl get-default multi-user.target #默认运行级别是 3 multi-user.target
三:优化启动过程
3.1 ntsysv 工具
(1)特点:
- 该工具提供一个交互式,可视化窗口
- 可以在字符终端运行
- 便于集中管理多个服务
- 用于控制服务是否开机自启动
(2) 使用
命令行使用 ntsysv 命令进入
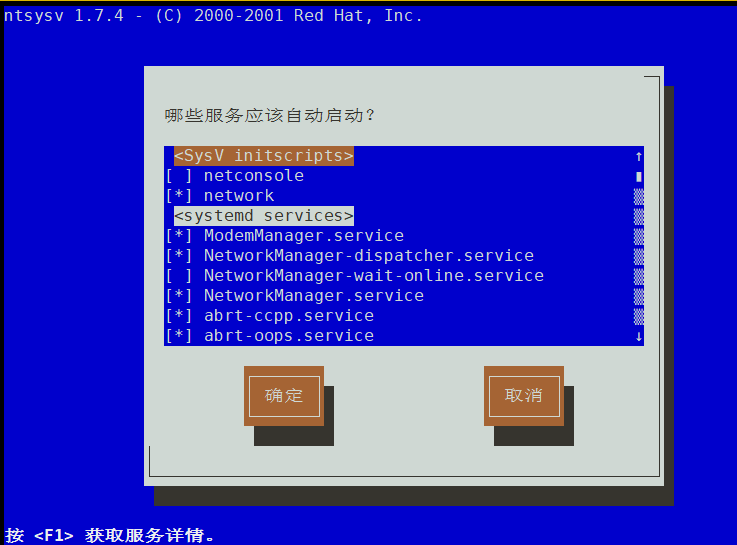
ntsysv 工具操作:
* 号表示启用自启
空格打上 * 或者 取消*
tab 键切换光标 到 【确定】 【取消】 或者切换回选项操作
3. 2 systemctl/chkconfig 命令
systemctl 不提供交互式,可视化窗口
管理单个服务效率更高
用于CentOs 7 版本
systemctl 可以用 enable 和disable 开启和关闭 服务的自动启动
用 is-enabled 查看 服务是否设置了开机自启
[root@localhost ~]# systemctl is-enabled httpd #查看httpd 服务是否设置了开机自启 disabled #httpd 没有设置开机自启 [root@localhost ~]# systemctl enable httpd #设置httpd开机自启 Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service. [root@localhost ~]# systemctl is-enabled httpd enabled [root@localhost ~]# systemctl disable httpd #关闭 httpd 的开机自启 Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service. [root@localhost ~]# systemctl is-enabled httpd disabled
补充:
systemctl [选项] 命令 服务
常用选项
--after #在某个服务之后启动
--before #在某个服务之前启动
#一般用于存在依赖关系的服务。
常用命令:
[root@promote ~]# systemctl stop httpd #停止httpd 服务 [root@promote ~]# systemctl is-active httpd.service #查看httpd 服务是否启用 unknown [root@promote ~]# systemctl start httpd #开启httpd 服务 [root@promote ~]# systemctl is-active httpd #查看httpd 服务是否启用 active #已启用
[root@promote ~]# systemctl restart httpd #重启httpd服务 [root@promote ~]# systemctl status httpd #查看httpd 服务的状态 ● httpd.service - The Apache HTTP Server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service; disabled; vendor preset: disabled) ##disabled 表示此服务没有开机自启 Active: active (running) since 三 2021-06-23 23:05:31 CST; 7s ago ##active (running) 表示此服务已启用 Docs: man:httpd(8) man:apachectl(8) Process: 1960 ExecStop=/bin/kill -WINCH ${MAINPID} (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS) Main PID: 1966 (httpd) #主进程号 Status: "Processing requests..." CGroup: /system.slice/httpd.service ├─1966 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1967 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1968 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1969 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND ├─1970 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND └─1971 /usr/sbin/httpd -DFOREGROUND 6月 23 23:05:31 promote.ldns.rate.local systemd[1]: Starting The Apache HTTP ... 6月 23 23:05:31 promote.ldns.rate.local systemd[1]: Started The Apache HTTP S... #服务日志 Hint: Some lines were ellipsized, use -l to show in full.
[root@promote ~]# systemctl reload httpd.service #重新加载httpd 服务的配置文件
[root@promote ~]# systemctl enable httpd.service #设置httpd 服务开机自启 Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service to /usr/lib/systemd/system/httpd.service. [root@promote ~]# systemctl is-enabled httpd.service #查看httpd 服务是否开机自启 enabled
[root@promote ~]# systemctl disable httpd.service #设置httpd 服务 不开机自启 Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/multi-user.target.wants/httpd.service.
[root@promote ~]# systemctl mask httpd #注销httpd 服务 Created symlink from /etc/systemd/system/httpd.service to /dev/null. [root@promote ~]# systemctl restart httpd #重启httpd 服务 Failed to restart httpd.service: Unit is masked. #注销后,重启失败 [root@promote ~]# systemctl unmask httpd #解除httpd 服务的注销 Removed symlink /etc/systemd/system/httpd.service. [root@promote ~]# systemctl restart httpd #成功重启httpd 服务 [root@promote ~]#




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 25岁的心里话
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列01:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现