转载:https://blog.kuangstudy.com/index.php/archives/520/
一.什么是依赖注入(DI)
-
依赖注入(Dependency Injection,DI)。
-
依赖 : 指Bean对象的创建依赖于容器 . Bean对象的依赖资源 .
-
注入 : 指Bean对象所依赖的资源 , 由容器来设置和装配 .
1.依赖注入的三种方式:
-
构造器注入:前面已经说过
-
Set方式注入
-
拓展方式注入
2.Set方式注入
依赖注入:
-
依赖:bean对象的创建依赖于容器
-
注入:bean对象中的所有属性,由容器注入!
(1)项目搭建:
复杂类型Adress类
1 public class Address {
2
3 private String address;
4
5 public String getAddress() {
6 return address;
7 }
8
9 public void setAddress(String address) {
10 this.address = address;
11 }
12
13 @Override
14 public String toString() {
15 return "Address{" +
16 "address='" + address + '\'' +
17 '}';
18 }
19 }
真实对象Student类
1 public class Student {
2
3 private String name;
4 private Address address;
5 private String[] books;
6 private List<String> hobbys;
7 private Map<String, String> card;
8 private Set<String> games;
9 private String wife;
10 private Properties info;
11
12 public String getName() {
13 return name;
14 }
15
16 public void setName(String name) {
17 this.name = name;
18 }
19
20 public Address getAddress() {
21 return address;
22 }
23
24 public void setAddress(Address address) {
25 this.address = address;
26 }
27
28 public String[] getBooks() {
29 return books;
30 }
31
32 public void setBooks(String[] books) {
33 this.books = books;
34 }
35
36 public List<String> getHobbys() {
37 return hobbys;
38 }
39
40 public void setHobbys(List<String> hobbys) {
41 this.hobbys = hobbys;
42 }
43
44 public Map<String, String> getCard() {
45 return card;
46 }
47
48 public void setCard(Map<String, String> card) {
49 this.card = card;
50 }
51
52 public Set<String> getGames() {
53 return games;
54 }
55
56 public void setGames(Set<String> games) {
57 this.games = games;
58 }
59
60 public String getWife() {
61 return wife;
62 }
63
64 public void setWife(String wife) {
65 this.wife = wife;
66 }
67
68 public Properties getInfo() {
69 return info;
70 }
71
72 public void setInfo(Properties info) {
73 this.info = info;
74 }
75
76 @Override
77 public String toString() {
78 return "Student{" +
79 "name='" + name + '\'' +
80 ", address=" + address.toString() +
81 ", books=" + Arrays.toString(books) +
82 ", hobbys=" + hobbys +
83 ", card=" + card +
84 ", games=" + games +
85 ", wife='" + wife + '\'' +
86 ", info=" + info +
87 '}';
88 }
89
90 }
beans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="address" class="ustc.wzh.pojo.Address"></bean>
<bean id="student" class="ustc.wzh.pojo.Student">
<!--1.普通值注入,value-->
<property name="name" value="小王"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
测试类MyTest.java
1 public class MyTest {
2
3 public static void main(String[] args) {
4 ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
5
6 Student student = (Student) context.getBean("student");
7
8 System.out.println(student.getAddress());
9 }
10 }
(2)注入详解
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
2 <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
3 xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
4 xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
5 https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
6
7 <bean id="address" class="ustc.wzh.pojo.Address">
8 <property name="address" value="合肥"></property>
9 </bean>
10
11 <bean id="student" class="ustc.wzh.pojo.Student">
12 <!--1.普通值注入,value-->
13 <property name="name" value="小王"></property>
14 <!--2.Bean对象注入,ref-->
15 <property name="address" ref="address"></property>
16 <!--3.数组注入,array,value-->
17 <property name="books">
18 <array>
19 <value>语文</value>
20 <value>数学</value>
21 <value>英语</value>
22 <value>科学</value>
23 </array>
24 </property>
25 <!--4.list注入,list,value-->
26 <property name="hobbys">
27 <list>
28 <value>写代码</value>
29 <value>看动漫</value>
30 <value>看电影</value>
31 <value>打篮球</value>
32 </list>
33 </property>
34 <!--5.map注入,map,entry,key,value-->
35 <property name="card">
36 <map>
37 <entry key="身份证" value="12131231321"></entry>
38 <entry key="学生证" value="45644654646"></entry>
39 <entry key="银行卡" value="79797979797"></entry>
40 </map>
41 </property>
42 <!--6.set注入,set,value-->
43 <property name="games">
44 <set>
45 <value>LOL</value>
46 <value>COC</value>
47 <value>BOB</value>
48 </set>
49 </property>
50 <!--7.null注入,null(注意空值“”和null不同)-->
51 <property name="wife">
52 <null></null>
53 </property>
54 <!--8.Properties注入,props,prop,key-->
55 <property name="info">
56 <props>
57 <prop key="学号">123456789</prop>
58 <prop key="性别">男</prop>
59 <prop key="姓名">小王</prop>
60 </props>
61 </property>
62 </bean>
63
64
65 </beans>
3.拓展方式注入
两种方式:
-
p命名空间注入:用于属性注入,有无参构造函数
-
导入约束 : xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
-
c命名空间注入:有参构造函数注入
-
导入约束 : xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
userbeans.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--P(属性: properties)命名空间 , 属性依然要设置set方法-->
<bean id="user" class="ustc.wzh.pojo.User" p:name="小王" p:age="24"></bean>
<!--C(构造: Constructor)命名空间 , 属性依然要设置set方法-->
<bean id="user2" class="ustc.wzh.pojo.User" c:name="小王" c:age="18"/>
</beans>
二.Bean的作用域
1.六种作用域
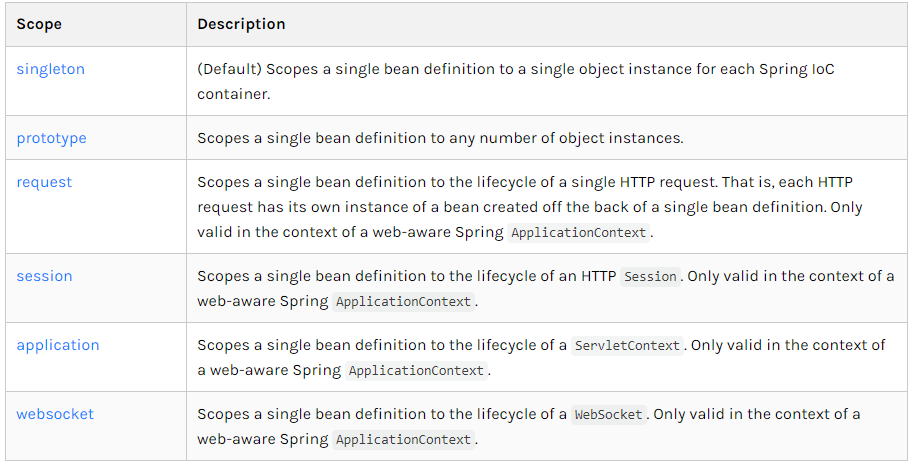
2.Singleton单例模式(默认就是单例)
- 当一个bean的作用域为Singleton,那么Spring IoC容器中只会存在一个共享的bean实例,并且所有对bean的请求,只要id与该bean定义相匹配,则只会返回bean的同一实例。Singleton是单例类型,就是在创建起容器时就同时自动创建了一个bean的对象,不管你是否使用,他都存在了,每次获取到的对象都是同一个对象。注意,Singleton作用域是Spring中的缺省作用域。要在XML中将bean定义成singleton,可以这样配置:
1 <bean id="ServiceImpl" class="cn.csdn.service.ServiceImpl" scope="singleton">
@Test
public void test03(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User user = (User) context.getBean("user");
User user2 = (User) context.getBean("user");
System.out.println(user==user2); //true
}
3.Prototype原型模式
- 当一个bean的作用域为Prototype,表示一个bean定义对应多个对象实例。Prototype作用域的bean会导致在每次对该bean请求(将其注入到另一个bean中,或者以程序的方式调用容器的getBean()方法)时都会创建一个新的bean实例。Prototype是原型类型,它在我们创建容器的时候并没有实例化,而是当我们获取bean的时候才会去创建一个对象,而且我们每次获取到的对象都不是同一个对象。根据经验,对有状态的bean应该使用prototype作用域,而对无状态的bean则应该使用singleton作用域。在XML中将bean定义成prototype,可以这样配置:创建多个对象
<bean id="account" class="com.foo.DefaultAccount" scope="prototype"/>
4.其余的request、session、application这些都只能在web开发中使用到!




