1.java基础回顾常用类
一.java.lang包中的类不需要导包
1.特点:
java.lang包是java语言的核心,它提供了java中的基础类。包括基本Object类、Class类、String类、基本类型的包装类、基本的数学类等等最基本的类。
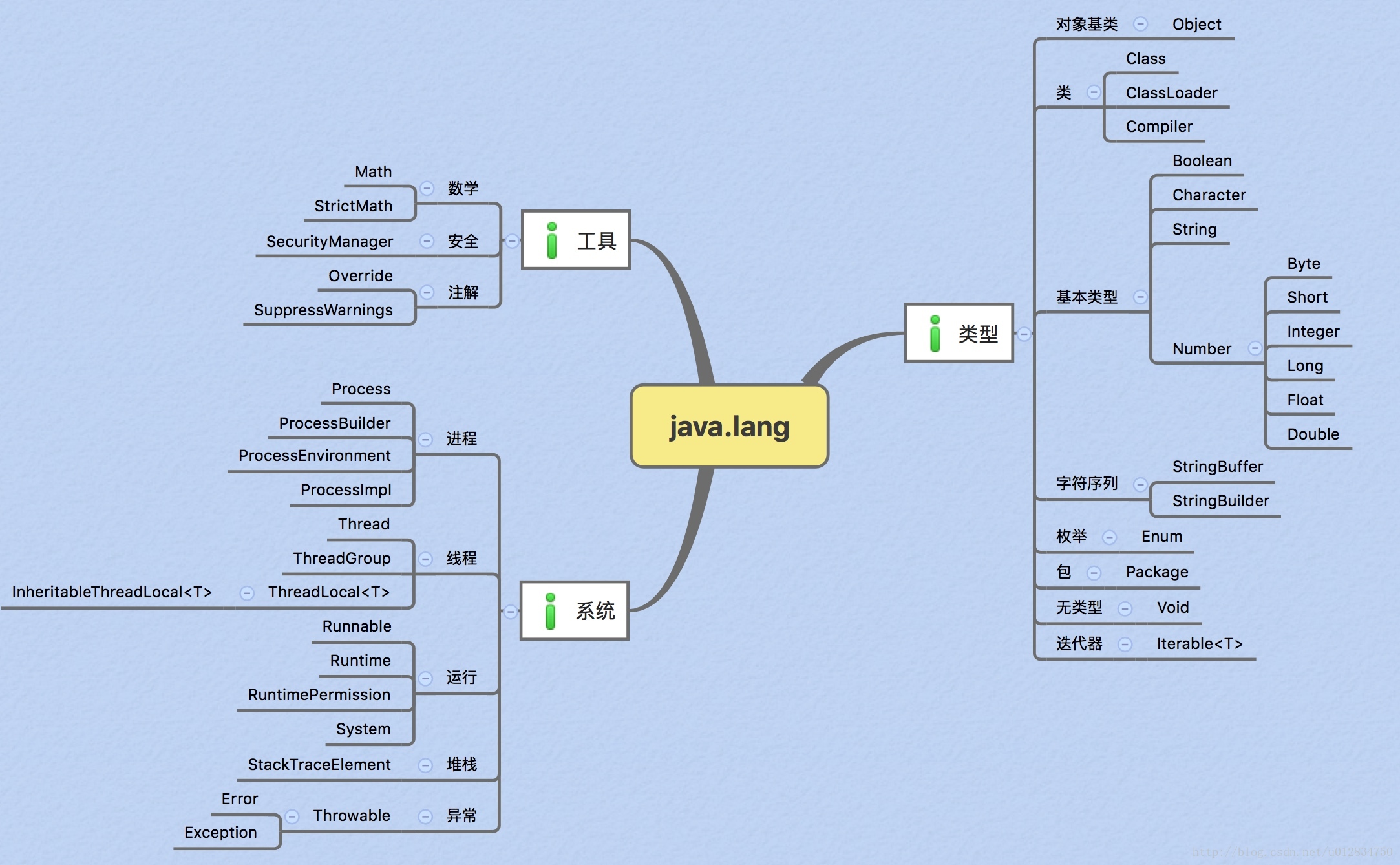
2. 8种基本类型初始化默认值:
注:char类型初始化默认值为null(也就是'\u0000')
|
Java中8种基本数据类型总结 |
|||||
|
序号 |
数据类型 |
大小/位 |
封装类 |
默认值 |
可表示数据范围 |
|
1 |
byte(位) |
8 |
Byte |
0 |
-128~127 |
|
2 |
short(短整数) |
16 |
Short |
0 |
-32768~32767 |
|
3 |
int(整数) |
32 |
Integer |
0 |
-2147483648~2147483647 |
|
4 |
long(长整数) |
64 |
Long |
0 |
-9223372036854775808~9223372036854775807 |
|
5 |
float(单精度) |
32 |
Float |
0.0 |
1.4E-45~3.4028235E38 |
|
6 |
double(双精度) |
64 |
Double |
0.0 |
4.9E-324~1.7976931348623157E308 |
|
7 |
char(字符) |
16 |
Character |
空 |
0~65535 |
|
8 |
boolean |
8 |
Boolean |
flase |
true或false |
补充:《Thinking in java》时, 书中有 9 中基本数据类型的说法,加入了 void其包装器类型为Void类
转载:https://www.jb51.net/article/131118.htm
Void类是一个不可实例化的占位符类,如果方法返回值是Void类型,那么该方法只能返回null类型。
public Void test() { return null; }
使用场景一:
Future<Void> f = pool.submit(new Callable() { @Override public Void call() throws Exception { ...... return null; } });
比如使用 Callable接口,该接口必须返回一个值,但实际执行后没有需要返回的数据。 这时可以使用Void类型作为返回类型。
使用场景二:
通过反射获取所有返回值为void的方法。
public class Test { public void hello() { } public static void main(String args[]) { for (Method method : Test.class.getMethods()) { if (method.getReturnType().equals(Void.TYPE)) { System.out.println(method.getName()); } } } }
ps:下面介绍java.lang.Void 与 void的比较及使用
void关键字表示函数没有返回结果,是java中的一个关键字。
java.lang.Void是一种类型。例如给Void引用赋值null。
总结:
泛型出现后,某些场景下会用到Void类型。例如Future<T>用来保存结果。Future的get方法会返回结果(类型为T)。
但如果操作并没有返回值呢?这种情况下就可以用Future<Void>表示。当调用get后结果计算完毕则返回后将会返回null。
另外Void也用于无值的Map中,例如Map<T,Void>这样map将具Set<T>有一样的功能。
因此当你使用泛型时函数并不需要返回结果或某个对象不需要值时候这是可以使用java.lang.Void类型表示。
3.其它类型默认值都是null
二.java类的使用
0. Object类:
特征:所有类的基类,即使不显示继承也会继承Object类并拥有Object类中的方法。
1 public final native Class<?> getClass() //返回此 Object 运行时的类 2 3 public native int hashCode() //返回对象的哈希码 4 5 public boolean equals(Object obj) //判断其他对象与此对象是否“相等” 6 7 protected native Object clone() throws CloneNotSupportedException //创建并返回此对象的一个副本 8 9 public String toString() //返回对象的字符串表示 10 11 public final native void notify() //唤醒在此对象监视器上等待的单个线程 12 13 public final native void notifyAll() //唤醒在此对象监视器上等待的所有线程 14 15 public final native void wait(long timeout) throws InterruptedException //使当前对象的线程等待 timeout 时长 16 17 public final void wait(long timeout, int nanos) throws InterruptedException //使当前对象的线程等待 timeout 时长,或其他线程中断当前线程 18 19 public final void wait() throws InterruptedException //使当前对象的线程等待
1.Objects类:
1 /** 2 * 1.Objects类:java.util.Objects 3 * JDK1.7开始添加了一个工具类 4 * 用于计算对象的hashcode,返回对象的字符串表示形式,比较两个对象等 5 * 这些方法都是空指针安全的 6 */ 7 String s = null; 8 String s1 = "s1"; 9 10 //报错:java.lang.NullPointerException,由于s为null所以不能调用任何方法 11 //System.out.println(s.equals(s1)); 12 13 System.out.println(Objects.equals(s,s1)); //false
2.Date类:
1 /** 2 * 2.Date类:日期时间类,java.util.Date 3 * 精确到毫秒 4 */ 5 System.out.println(new Date()); //显示当前日期 6 System.out.println(new Date(1000000000L)); //将毫秒值转换为日期 7 System.out.println(new Date().getTime()); //将系统当前时间转换为毫秒显示 8 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); //返回系统当前时间以毫秒显示
3.DateFormat类:
1 /** 2 * 3.DateFormat类:是时间/日期格式化的抽象类,java.text.DateFormat 3 * 作用: 4 * 格式化:日期-->文本,解析:文本-->日期 5 * 成员方法: 6 * String format(Date date):将日期转化为字符串 7 * Date parse(String source):将字符串解析为日期 8 * 9 * 由于DateFormat类为抽象类,我们使用SimpleDateFormat类来使用 10 * SimpleDateFormat构造方法: 11 * SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) 12 * 参数: 13 * String pattern:传递的指定模式 14 * 模式:区分大小写 15 * y 年,M 月,d 日,H 时,m 分,s 秒 16 * 一般默认模式: 17 * yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss 18 * 模式的字母不能修改,但是连接符可以修改 19 * yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒 20 */ 21 //格式化: 22 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒").format(new Date())); 23 //解析: 24 System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH时mm分ss秒").parse("2019年12月26日 18时33分35秒"));
4.Calendar类:
1 /** 2 * 4.Calendar类:日历类,java.util.Calendar,抽象类,提供操作日历的方法 3 * 使用静态方法getInstance()返回Calendar类的子类对象 4 * 常用的成员方法: 5 * public int get(int field):返回给定日历字段的值 6 * public void set(int field,int value):将给定日历字段设置为给定值 7 * public abstract void add(int field, int amount):根据日历的规则,给日历字段添加或减去指定时间量 8 * public Date getTime():返回一个表示此Calendar时间值的Date对象 9 * 成员方法参数: 10 * int feild:日历类字段,可以使用Calendar类的静态成员变量获取 11 * YEAR = 1 年 12 * MONTH = 2 月 13 * DATE = 5 日 14 * DAY_OF_MONTH = 5 月中的某一天 15 * HOUR = 10 时 16 * MINUTE = 12 分 17 * SECOND = 13 秒 18 */ 19 Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance(); 20 21 //返回当前年 22 System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); 23 24 //设置当前年 25 c.set(Calendar.YEAR,9999); 26 System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); 27 28 //增加年 29 c.add(Calendar.YEAR,3); 30 System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); 31 32 //获取日期 33 System.out.println(c.getTime());
5.System类:
1 /** 2 * 5.System类:获取与系统相关的信息或操作系统操作,java.lang.System 3 * 4 */ 5 //返回以毫秒为单位的系统时间 6 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()); 7 8 //将数组指定的数据拷贝到另一个数组中 9 int[] src = {1,2,3,4,5}; 10 int[] dest = {6,7,8,9,0}; 11 System.arraycopy(src,0,dest,0,3); 12 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dest)); //[1, 2, 3, 9, 0]
6.StringBuilder类:
1 /** 2 * 6.StringBuilder类:字符串缓冲区,可变的字符串,初始值为16个字符 3 * String类不可变字符串 4 */ 5 //空的构造函数 6 StringBuilder bu1 = new StringBuilder(); 7 System.out.println(bu1); 8 9 //带参构造函数 10 StringBuilder bu2 = new StringBuilder("abc"); 11 System.out.println(bu2); 12 13 //链式编程 14 bu2.append(1).append(true).append("你好"); 15 System.out.println(bu2); 16 17 //StringBuilder->String 18 String bu2tos = bu2.toString(); 19 System.out.println(bu2tos); 20 21 //String->StringBuilder 22 bu2.append(bu2tos); 23 System.out.println(bu2);
7.包装类:
1 /** 2 * 7.包装类:8个,java.lang中 3 * 由于基本类型好用但是没有对应的方法操作基本类型, 4 * 我们定义一个类,将基本数据类型封装起来并在这个类中定义一些方法用于操作 5 * 基本类型 包装类 6 * byte Byte 7 * short Short 8 * int Integer 9 * long Long 10 * float Float 11 * double Double 12 * char Character 13 * boolean Boolean 14 * 15 * 16 * 从JDK1.5开始,支持自动装箱和自动拆箱 17 * 装箱:基本类型->包装类 18 * 拆箱:包装类->基本类型 19 */ 20 //int -> Integer 21 Integer i = Integer.valueOf(11111); 22 System.out.println(i); 23 24 //String -> Integer 25 i = Integer.valueOf("22222222"); 26 System.out.println(i); 27 28 //Integer -> int 29 int num = i.intValue(); 30 System.out.println(num); 31 32 //由于泛型必须是非基本类型 33 ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>(); 34 35 //自动装箱:list.add(new Integer(1)) 36 list.add(1); 37 //自动拆箱:list.get(0).intValue(); 38 int a = list.get(0); 39 40 //基本类型转字符串 41 String ss = 100 + ""; 42 System.out.println(ss); 43 ss = Integer.toString(123); 44 System.out.println(ss); 45 ss = String.valueOf(444); 46 System.out.println(ss); 47 48 //字符串转基本类型 49 int nn = Integer.parseInt(ss); 50 System.out.println(nn);
8.UUID类:
- 表示通用唯一标识符 (UUID) 的类。 UUID 表示一个 128 位的值。
- 作用:生成唯一的编号
- 常用方法:UUID.randomUUID() 用于生成唯一的编号
1 UUID u; 2 for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) { 3 u = UUID.randomUUID(); 4 System.out.println(u.toString().replaceAll("-","")); 5 }
9.Format类:
- Format类是一个用于格式化语言环境敏感的信息(如日期、消息和数字)的抽象基类。
- 拥有的子类:
- DateFormat:为抽象日期类
- SimpleDateFormat:是一个以与语言环境有关的方式来格式化和解析日期的具体类。
- MessageFormat:提供了以与语言无关方式生成连接消息的方式。
- NumberFormat:是所有数值格式的抽象基类。
- ChoiceFormat:是一个允许将格式应用到某个范围的数。
- DecimalFormat:用于格式化十进制数字。
- DateFormat:为抽象日期类
(1)ChoiceFormat:
注:
- 两个数组长度必须相同,才能进行格式化。
- 当数字小于数组第一个数时,输出第一个数。当数字大于数组最后一个数时输出最后一个数。
- 输出规则 :当且仅当 limit[j] <= X < limit[j+1] 时,X 匹配 j (就是输出左侧数字)
1 double[] limits = {3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 2 String[] formats = {"星期一", "星期二", "星期三", "星期四", "星期五", "星期六", "星期日"}; 3 ChoiceFormat format = new ChoiceFormat(limits, formats); 4 System.out.println(format.format(-100)); //星期一 5 System.out.println(format.format(3.6)); //星期一
(2)DecimalFormat:
- 使用‘0’和‘#’号表示数字,区别在于‘#’号会省略末尾多余的0
1 // 取整数部分 2 String s1 = new DecimalFormat("0").format(12345.1512134567); 3 System.out.println(s1);//12345 4 5 // 取小数点后1位,四舍五入 6 String s2 = new DecimalFormat("0.0").format(12345.1512134567); 7 System.out.println(s2);//12345.2 8 9 // 取小数点后3位,不足部分取0 10 String s3 = new DecimalFormat("0.000").format(12345.1); 11 System.out.println(s3);//12345.100 12 13 // 百分比 14 String s4 = new DecimalFormat("0.0%").format(12345.1512134567); 15 System.out.println(s4);// 1234515.1% 16 17 // 科学计数法 18 String s5 = new DecimalFormat("0.00E0").format(12345.1512134567); 19 System.out.println(s5);//1.23E4 20 21 // 每三位以逗号分开 22 String s6 = new DecimalFormat(",000.000").format(12345.1512134567); 23 System.out.println(s6);//12,345.151 24 25 //小数点后3位,如果是0则不显示 26 String s7 = new DecimalFormat("#.###").format(123.300); 27 System.out.println(s7);//123.3 28 29 //将格式嵌入文本 30 System.out.println(new DecimalFormat("每秒#.###米。").format(123.300));//每秒123.3米。
9.Arrays类:
- Arrays是一个针对数组的工具类,可以进行复制,转换,排序,搜索,比较,填充等功能
(1).复制
- copyOfRange(int[] original, int from, int to):
- 第一个参数表示源数组
- 第二个参数表示开始位置(取得到)
- 第三个参数表示结束位置(取不到)
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int a[] = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 5 6 //1.Arrays复制 7 int[] b = Arrays.copyOfRange(a, 0, 3); 8 for (int i : b) { 9 System.out.print(i + " "); 10 } 11 System.out.println(); 12 13 //2.System复制 14 System.arraycopy(a, 0, b, 0, 3); 15 for (int i : b) { 16 System.out.print(i + " "); 17 } 18 19 } 20 }
(2).转换为字符串
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //1.返回一维数组的字符串形式 5 int[] a = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 6 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 7 8 //2.返回多维数组的字符串形式 9 int[][][] b = {{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6}, {7, 8, 9}}, {{11, 12, 13}, {21, 22, 23}}}; 10 System.out.println(Arrays.deepToString(b)); 11 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b)); 12 13 /** 14 * 输出: 15 * [18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9] 16 * [[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6], [7, 8, 9]], [[11, 12, 13], [21, 22, 23]]] 17 * [[[I@135fbaa4, [[I@45ee12a7] 18 */ 19 } 20 }
(3).数组排序
1 public class ArraysSortTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 //1.Arrays自带升序排序 5 Integer[] nums1 = {5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 9, 0, 7, 8, 6}; 6 Arrays.sort(nums1); 7 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums1)); 8 9 //2.自定义类 10 Integer[] nums2 = {5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 9, 0, 7, 8, 6}; 11 Comparator<Integer> comparator = new MyComparator(); 12 Arrays.sort(nums2, comparator); 13 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums2)); 14 15 //3.匿名内部类 16 Integer[] nums3 = {5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 9, 0, 7, 8, 6}; 17 Arrays.sort(nums3, new Comparator<Integer>() { 18 @Override 19 public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) { 20 return b - a; 21 } 22 }); 23 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums3)); 24 25 //4.lambda表达式 26 Integer[] nums4 = {5, 2, 1, 3, 4, 9, 0, 7, 8, 6}; 27 Arrays.sort(nums4, (a, b) -> b - a); 28 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums4)); 29 } 30 } 31 32 33 class MyComparator implements Comparator<Integer> { 34 @Override 35 public int compare(Integer a, Integer b) { 36 return b - a; 37 } 38 }
补充:
Comparable和Comparator区别比较:
- Comparable是排序接口,若一个类实现了Comparable接口,就意味着“该类支持排序”。而Comparator是比较器,我们若需要控制某个类的次序,可以建立一个“该类的比较器”来进行排序。
- Comparable相当于“内部比较器”,而Comparator相当于“外部比较器”。
- 两种方法各有优劣, 用Comparable 简单, 只要实现Comparable 接口的对象直接就成为一个可以比较的对象,但是需要修改源代码。 用Comparator 的好处是不需要修改源代码, 而是另外实现一个比较器, 当某个自定义的对象需要作比较的时候,把比较器和对象一起传递过去就可以比大小了, 并且在Comparator 里面用户可以自己实现复杂的可以通用的逻辑,使其可以匹配一些比较简单的对象,那样就可以节省很多重复劳动了
(4).搜索
注意:搜索之前必须排序
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int a[] = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 5 6 Arrays.sort(a); 7 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 8 9 //二分搜索之前必须排序 10 System.out.println("数字62出现在数组中的位置"+Arrays.binarySearch(a,62)); 11 12 /**输出: 13 * [9, 18, 62, 65, 68, 82] 14 * 数字62出现在数组中的位置2 15 */ 16 } 17 }
(5).判断两个数组内容是否相同
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int a[] = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 5 int b[] = new int[]{18, 62, 68, 82, 65, 9}; 6 int c[] = new int[]{99, 62, 68, 82, 65, 8}; 7 8 System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a,b)); 9 System.out.println(Arrays.equals(a,c)); 10 System.out.println(Arrays.equals(b,c)); 11 12 /** 13 * 输出: 14 * true 15 * false 16 * false 17 */ 18 } 19 }
(6).填充
1 public class ArraysTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) { 4 int[] a = new int[10]; 5 6 //1.填充全部 7 Arrays.fill(a, 5); 8 9 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 10 11 /** 12 * 输出: 13 * [5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5] 14 */ 15 16 //2.填充下标[2,4]为1 17 Arrays.fill(a, 2, 5, 1); 18 System.out.println(Arrays.toString(a)); 19 20 /** 21 * 输出: 22 * [5, 5, 1, 1, 1, 5, 5, 5, 5, 5] 23 */ 24 } 25 }





