图像求导及模糊
在很多应用中,图像强度的变化情况是非常重要的信息。强度的变化可以灰度图像的\(x\)和\(y\)方向导数\(I_x\)和\(I_y\)进行描述。图像的梯度向量为\(\nabla I = [I_x, I_y]^T\)。梯度有两个重要属性,一个是梯度的大小:
\[| \nabla I | = \sqrt{I_x^2+I_y^2}
\]
它描述了图像强度变化的强弱,另一个是梯度的角度:
\[\alpha = arctan2(I_y, I_x)
\]
描述了图像中每个像素点上强度变化最大的方向。我们可以使用离散近似的方式来计算图像的导数。图像导数大多数可以通过卷积简单地实现:
\[I_x = I*D_x \ 和\ I_y = I*D_y
\]
对于\(D_x\)和\(D_y\),通常选择Priwitt滤波器:
\[D_x = \left[
\begin{matrix}
-1 & 0 & 1 \\
-1 & 0 & 1 \\
-1 & 0 & 1
\end{matrix}
\right]
和D_y=\left[
\begin{matrix}
-1 & -1 & -1 \\
0 & 0 & 0 \\
1 & 1 & 1
\end{matrix}
\right]
\]
或者Sobel滤波器:
\[D_x = \left[
\begin{matrix}
-1 & 0 & 1 \\
2 & 0 & 2 \\
-1 & 0 & 1
\end{matrix}
\right]
和D_y=\left[
\begin{matrix}
-1 & -2 & -1 \\
0 & 0 & 0 \\
1 & 2 & 1
\end{matrix}
\right]
\]
上面两种计算图像导数的方法存在一些缺陷:滤波器的尺度需要随着图像分辨率的变化而变化。为了在图像噪声方面更稳健,以及在任意尺度上计算导数,我们可以使用高斯导数滤波器:
\[I_x = I*G_{\sigma x} 和 I_y = I*G_{\sigma y}
\]
其中,\(G_{\sigma x}\) 和 \(G_{\sigma y}\) 表示 \(G_\sigma\) 在\(x\)和\(y\)方向上的导数,\(G_\sigma\) 为标准差为\(\sigma\)的高斯函数。
样例演示
from scipy.ndimage import filters
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
class ScipyFilter:
def __init__(self, path: str):
self.img = np.array(Image.open(path))
self.grayImg = np.array(Image.open(path).convert('L'))
self.Ix = np.zeros(self.grayImg.shape)
self.Iy = np.zeros(self.grayImg.shape)
self.manitude = np.zeros(self.grayImg.shape)
def cal_derivatives_sobel(self):
"""
使用sobel滤波器计算导数
:return:
"""
filters.sobel(self.grayImg, 1, self.Ix)
filters.sobel(self.grayImg, 0, self.Iy)
self.manitude = np.sqrt(self.Ix**2 + self.Iy**2)
def cal_derivatives_prewitt(self):
"""
使用prewitt滤波器计算导数
:return:
"""
filters.prewitt(self.grayImg, 1, self.Ix)
filters.prewitt(self.grayImg, 0, self.Iy)
self.manitude = np.sqrt(self.Ix**2 + self.Iy**2)
def cal_derivatives_gaussian(self, sigma):
"""
计算图像高斯导数
:param img: 图像数据
:param sigma: 标准差
:return:
"""
filters.gaussian_filter(self.grayImg, (sigma, sigma), (0, 1), self.Ix)
filters.gaussian_filter(self.grayImg, (sigma, sigma), (1, 0), self.Iy)
def plot(self):
# 绘图
plt.figure()
plt.gray()
plt.subplot(221).set_title("original img")
plt.imshow(self.grayImg)
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(222).set_title('x-directional derivative')
plt.imshow(self.Ix)
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(223).set_title('y-directional derivative')
plt.imshow(self.Iy)
plt.axis('off')
plt.subplot(224).set_title("gradient magnitude")
plt.imshow(self.manitude)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_path = "./imgs/3.jpg"
sc = ScipyFilter(img_path)
sc.cal_derivatives_sobel()
sc.plot()
sc.cal_derivatives_prewitt()
sc.plot()
sc.cal_derivatives_gaussian(3)
sc.plot()
sc.cal_derivatives_gaussian(5)
sc.plot()
结果演示
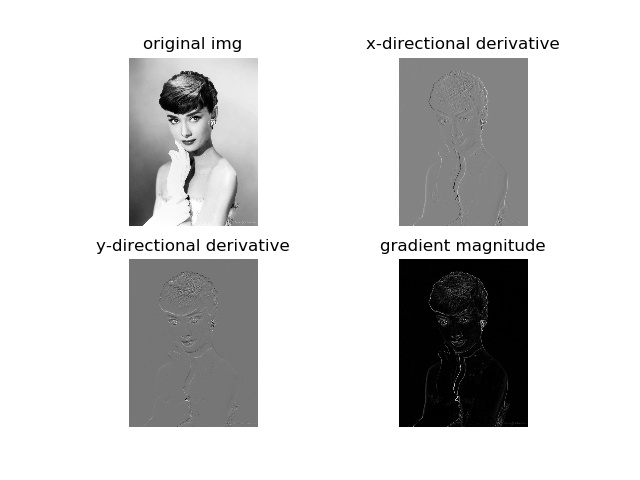
sobel滤波
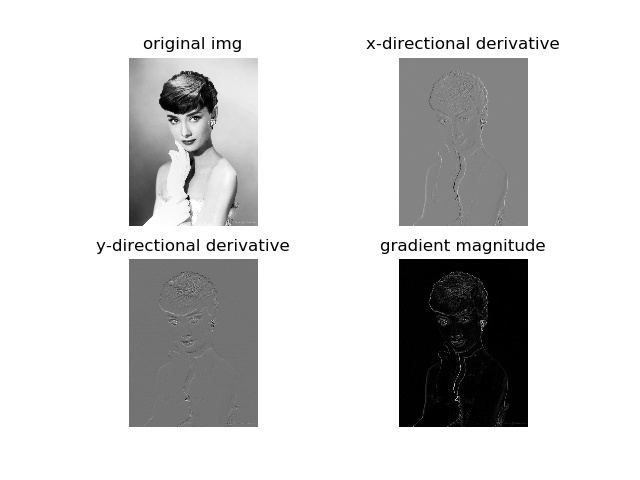
prewitt滤波
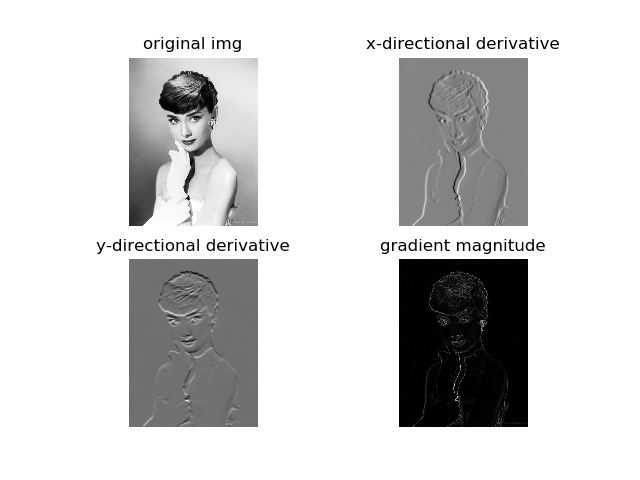
gaussian滤波,标准差设置为3
gaussian滤波,标准差设置为5
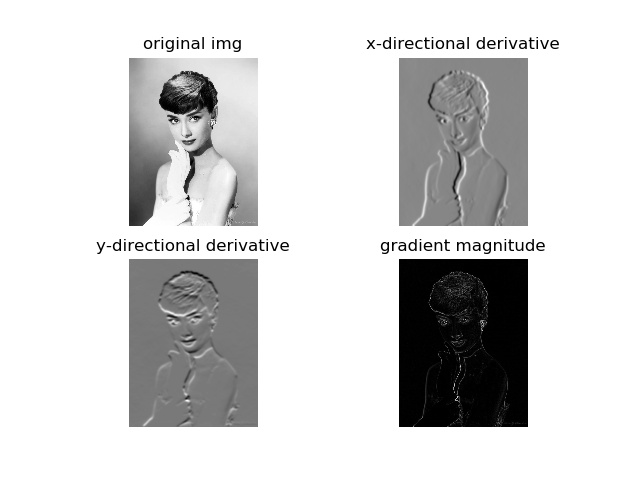
在图像中,正导数显示为亮的像素,负导数显示为暗的像素。灰色区域表示导数的值接近零。
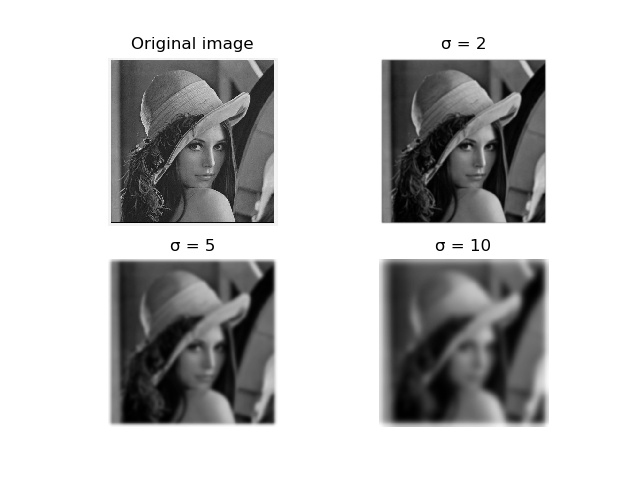
图像高斯模糊
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
from scipy.ndimage import filters
img = Image.open(r"girl.jpg").convert('L')
img = np.array(img)
img2 = filters.gaussian_filter(img, 2)
img3 = filters.gaussian_filter(img, 5)
img4 = filters.gaussian_filter(img, 10)
结果演示

更多参考上一篇




